Investigations
1st investigations to order
ophthalmological evaluation; computerised visual-field examination
Test
Performed in all patients with craniopharyngioma with suprasellar extension and chiasmal compression.
Result
may reveal unilateral or bitemporal hemianopsia
MRI brain (contrast-enhanced)
Test
Most sensitive and specific imaging modality. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: coronal post-contrast MRIFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].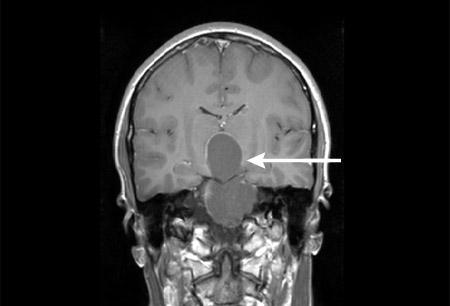 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: axial post-contrast MRIFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: axial post-contrast MRIFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: sagittal post-contrast MRIFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: sagittal post-contrast MRIFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: sagittal post-contrast MRIFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: sagittal post-contrast MRIFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].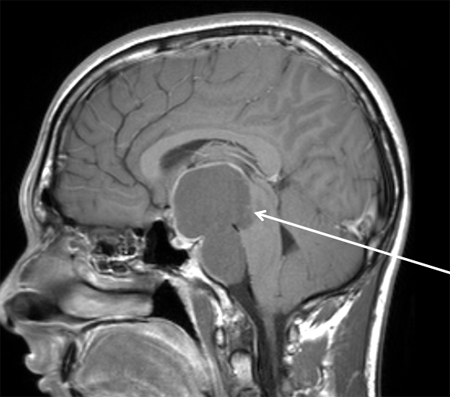
Allows the clinician to define the size, location, and relationship of the tumour to surrounding structures; to determine the surgical approach; to assess the extent of resection; and to plan radiotherapy.
Result
variable; T1-weighted imaging may show hyperintensity secondary to high protein content in cystic component; contrast-enhanced sequences show enhancement of the solid component and cyst wall in mixed solid-cystic lesions; T2-weighted imaging and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) show heterogeneous signal in the solid components and cyst hyperintensity; calcification is hypointense on T2-weighted imaging
CT brain (contrast-enhanced)
Test
Can be helpful in reaching differential diagnosis given the classic calcifications that can be found in craniopharyngiomas. Also used in evaluating relevant sinus anatomy and relationships.
Result
frequent tumour calcification (90% children; 70% adults); mixed cystic and solid mass with enhancement of the solid component and cyst wall
serum prolactin
Test
Increased secretion is due to tumour compression of the pituitary stalk. Measurement of a fasting sample is desirable.
Result
variable; commonly elevated
serum insulin-like growth factor 1
Test
Values of insulin-like growth factor 1 and its binding protein (IGFBP3) more than two standard deviation scores below the mean, corrected for age and sex, are indicative of growth hormone deficiency; however, normal concentrations do not rule out growth hormone deficiency (e.g., in post-irradiation patients).
Result
variable; commonly low
growth hormone (GH) stimulation test
Test
GH deficiency is best evaluated with dynamic testing including either an insulin tolerance test (ITT), glucagon stimulation test, or a growth hormone-releasing hormone/arginine stimulation test, or macimorelin test. ITT is considered the most specific and sensitive test for evaluation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-growth hormone axis. However, it needs to be performed by experienced clinicians and is usually not needed for everyday clinical practice.
Result
variable; commonly may show failure to induce GH
serum luteinising hormone
Test
Used to diagnose gonadotrophin hormone deficiency.
Note that in women a normal menstrual cycle is a more sensitive indicator of an intact pituitary and normal gonadal function than any biochemical test.
Result
variable; commonly low
serum follicle-stimulating hormone
Test
Used to diagnose gonadotrophin hormone deficiency.
Note that in women, a normal menstrual cycle is a more sensitive indicator of an intact pituitary and normal gonadal function than any biochemical test.
Result
variable; commonly low
morning serum testosterone
Test
Used to diagnose gonadotrophin hormone deficiency in men.
Check fasting levels between 6 a.m. and 8 a.m. ideally; sample taken up to 11 a.m. is acceptable.
Result
variable; commonly low
serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxine (FT4)
Test
There may be low bioactivity of TSH (normal TSH levels but reduced activity in stimulating thyroid hormone release). Therefore, TSH alone should not be used to diagnose thyroid hormone deficiency.
Result
TSH level may be inappropriately low, normal, or elevated in the setting of low serum FT4
morning serum cortisol and adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Test
Used to diagnose adrenal insufficiency.
Blood should be drawn between 8 a.m. and 9 a.m., when cortisol levels peak.
It is important to realise that arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D; previously known as central diabetes insipidus) cannot occur in the presence of chronic low mineralocorticoids; administration of corticosteroids can unmask low vasopressin and result in the onset of severe AVP-D.
Result
variable; commonly low cortisol in association with non-elevated levels of ACTH
serum electrolytes
Test
Used to diagnose arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D; previously known as central diabetes insipidus). Elevated serum sodium in association with hypotonic urine (urine osmolality <300 mmol/kg [<300 mOsm/kg]) strongly suggests AVP-D.
Low sodium may be seen with adrenocorticotrophic hormone or thyroid-stimulating hormone deficiency.
Result
variable; electrolyte abnormalities indicate hormonal disorder
urine and serum osmolality
Test
Used to diagnose arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D; previously known as central diabetes insipidus).
Result
variable; commonly low urine osmolality with high plasma osmolality
plain x-rays for bone age
Test
Used to diagnose growth hormone deficiency.
Result
often show a delayed bone age in children
Investigations to consider
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test
Test
A stimulation test may be considered in a patient with an indeterminate serum cortisol value to determine adrenal insufficiency.
Result
serum cortisol <500 nanomols/L (<18 micrograms/dL)
tissue histology
Test
Allows for definitive diagnosis following surgical biopsy/resection with pathological analysis of tumour tissue. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: adamantinous histology (low power) with complex arrangements of epithelium, cysts, and gliotic brainFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].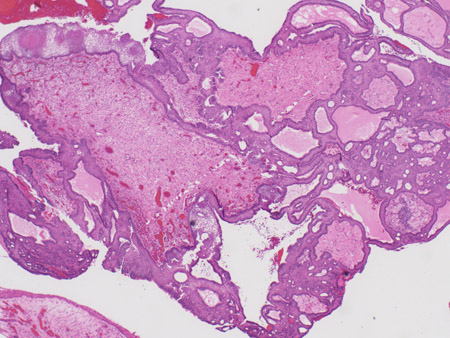 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: adamantinous histology (medium power) with epithelial ribbons showing reticular areas and nodules of keratinFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: adamantinous histology (medium power) with epithelial ribbons showing reticular areas and nodules of keratinFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].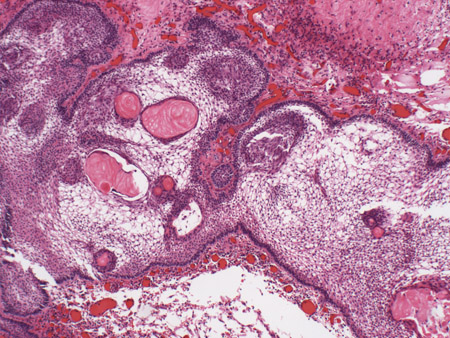 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: adamantinous histology (high power) with basal-aligned columnar cells, stellate reticulum, and epithelial keratinisationFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Craniopharyngioma: adamantinous histology (high power) with basal-aligned columnar cells, stellate reticulum, and epithelial keratinisationFrom the collection of Marc C. Chamberlain [Citation ends].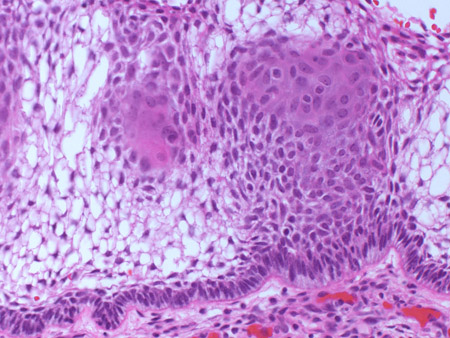
Result
adamantinous/squamous epithelial tumour; calcification
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer