Investigations
1st investigations to order
upper GI endoscopy with biopsy
Test
A diagnosis of Barrett's oesophagus cannot be made without this test.
The endoscopic appearance of Barrett's oesophagus is violaceous epithelium proximal to the gastro-oesophageal junction.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's oesophagus; note salmon-coloured mucosa extending superior to the gastro-oesophageal junction as a continuous columnFrom the personal collection of Dr Vic Velanovich; used with permission [Citation ends].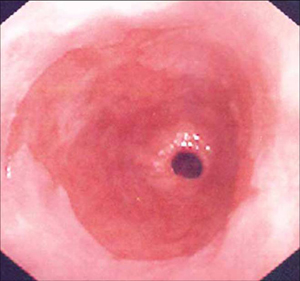 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's oesophagus; note salmon-coloured mucosa extending superior to the gastro-oesophageal junction with marked irregular borderFrom the personal collection of Dr Vic Velanovich; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's oesophagus; note salmon-coloured mucosa extending superior to the gastro-oesophageal junction with marked irregular borderFrom the personal collection of Dr Vic Velanovich; used with permission [Citation ends].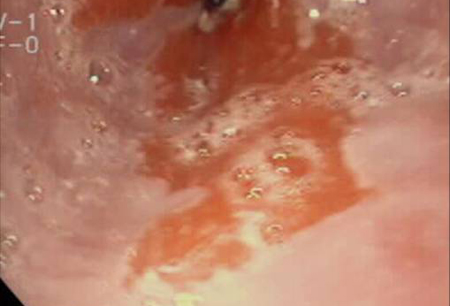
The Z line (boundary between oesophageal and gastric epithelium) is migrated cephalad.
Biopsy is mandatory because Barrett's oesophagus is a pathological diagnosis.
Areas of ulceration, narrowing (stricture), and nodularity should be targeted for biopsy because they are more likely to contain areas of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma.[1]
Barrett's oesophagus is defined histologically as areas of columnar-lined epithelium in the oesophagus cephalad to the gastro-oesophageal junction. Although intestinal metaplasia is a frequent component of Barrett's oesophagus, it is not considered a diagnostic criterion.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's metaplasia without dysplasia, demonstrating columnar epithelium with goblet cells from superior to the gastro-oesophageal junctionCourtesy of Adrian Ormsby, MD, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's metaplasia with low-grade dysplasia; note the more irregular cells and nucleiCourtesy of Adrian Ormsby, MD, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's metaplasia with low-grade dysplasia; note the more irregular cells and nucleiCourtesy of Adrian Ormsby, MD, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI [Citation ends].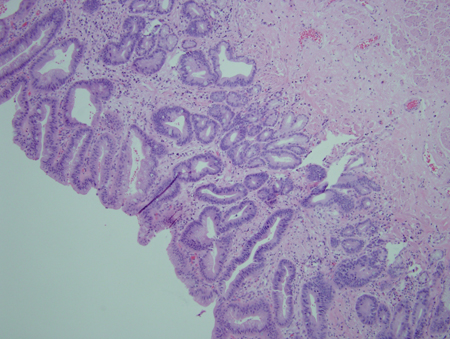 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's metaplasia with high-grade dysplasia; note more advanced irregularity of the cellsCourtesy of Adrian Ormsby, MD, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's metaplasia with high-grade dysplasia; note more advanced irregularity of the cellsCourtesy of Adrian Ormsby, MD, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI [Citation ends].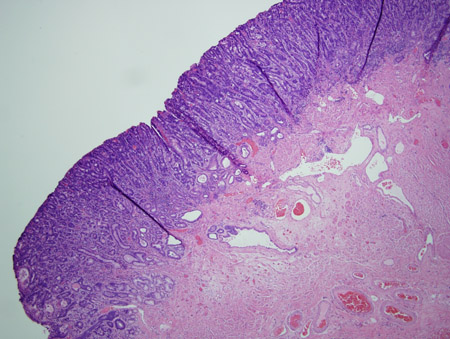 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's metaplasia with high-grade dysplasia associated with a focus of intramucosal carcinoma; note the frankly malignant cells beyond the confines of the basement membrane to involve the lamina propriaCourtesy of Adrian Ormsby, MD, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barrett's metaplasia with high-grade dysplasia associated with a focus of intramucosal carcinoma; note the frankly malignant cells beyond the confines of the basement membrane to involve the lamina propriaCourtesy of Adrian Ormsby, MD, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI [Citation ends].
High-definition white light endoscopy with systematic biopsy is the standard of care. This can be enhanced with narrow-band imaging. Narrow-band imaging with magnification is accurate with high diagnostic precision for high-grade dysplasia (HGD) in Barrett's oesophagus on the basis of irregular mucosal pit patterns and/or irregular microvasculature. It has high sensitivity, but poor specificity, for characterising specialised intestinal metaplasia.[37] Methylene-blue chromoendoscopy has generally not been shown to be substantially more accurate.[38]
Result
abnormal epithelium characteristic of Barrett's oesophagus
barium oesophagogram
Test
May be considered as the initial test in patients with dysphagia in order to evaluate for a mass lesion or stricture before endoscopy.
Cannot diagnose Barrett's oesophagus.
Can document other signs of GORD or a hiatal hernia, which are risk factors for Barrett's oesophagus.
Result
identifies hiatal hernia and reflux
Emerging tests
chromoendoscopy
Test
Chromoendoscopy involves applying a chemical dye to the mucosal surface of the gastrointestinal tract to highlight specific areas or to distinguish different types of epithelium. Agents used include, but are not limited to, methylene blue, indigo carmine, or Lugol’s solution.
Electronic chromoendoscopy uses specific light filters within the endoscope or the processor to enhance the contrast of the mucosal surface; therefore, chemical dyes are not required.
Both chromoendoscopy and electronic chromoendoscopy have been shown to significantly increase the diagnostic yield for identifying oesophageal dysplasia/cancer in patients with Barrett's oesophagus compared with conventional white-light endoscopy.[39]
Result
visualises different types of epithelium
autofluorescence imaging
Test
Uses endogenous fluorophores which, when excited by light, emit a longer wavelength than the exciting light.
Result
identifies different types of epithelium
confocal laser endomicroscopy
Test
Allows the endoscopist to perform a real-time histological assessment of the gastrointestinal epithelium.
A meta-analysis assessing the accuracy of confocal laser endomicroscopy showed that it had a sensitivity of 89% and a specificity of 75% in detecting neoplasia in Barrett's oesophagus, when analysed per patient.[40] In a per-location analysis, sensitivity was 70% and specificity was 91%.
Result
identifies pathological histology in the oesophageal epithelium
optical coherence tomography
Test
Uses short coherence length broad-band light to provide real-time cross-sectional imaging of the oesophageal mucosa.
Result
identifies abnormalities in oesophageal cross-sectional epithelium
spectroscopy
Test
Imaging modalities involve analysis of interactions between light and tissue to assess nanoscale architecture of the oesophageal epithelium. These modalities include light scattering, reflectance, and Raman-based technology.[41]
Result
assesses changes in epithelial architecture
transnasal endoscopy
Test
Permits office-based, unsedated evaluation of the oesophagus.
Requires a special, thin-calibre digital endoscope, which is not readily available in most practices.
Result
abnormal epithelium characteristic of Barrett's oesophagus
capsule endoscopy
Test
A specially designed video capsule with cameras on both ends that is swallowed by the patient in supine position.
Provides images of the oesophagus, but does not permit tissue sampling.
Diagnostic characteristics are still sub-optimal.
Result
provides images of oesophageal pathology
gelatin-coated sponge
Test
A gelatin-coated sponge attached to a string can be swallowed by the patient, and then pulled out.
Obtains cytology samples from the distal oesophagus, removing the need for sedation or endoscopy.
Studies are ongoing to assess its sensitivity.[7]
Result
obtains specimens for cytology; cannot provide images of affected oesophageal segment
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer