Images and videos
Images
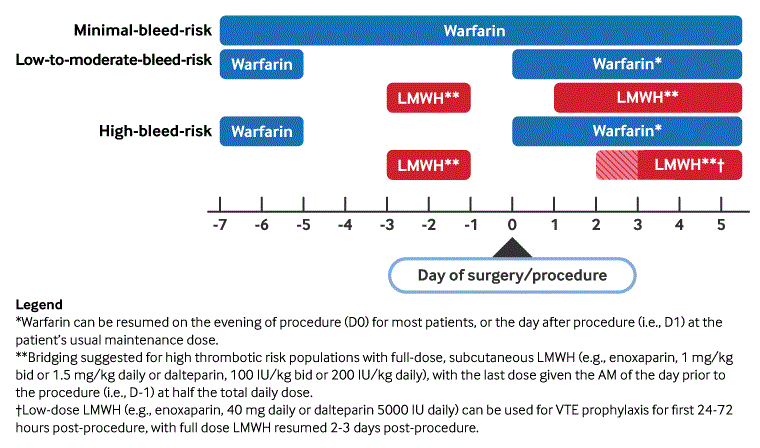
Anticoagulation management principles
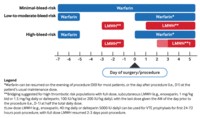
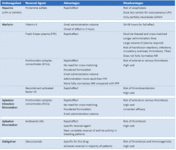
Perioperative management of vitamin K antagonists (warfarin)
Adapted by BMJ Knowledge Centre from Douketis JD et al. Chest. 2022 Nov;162(5):e207-43; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
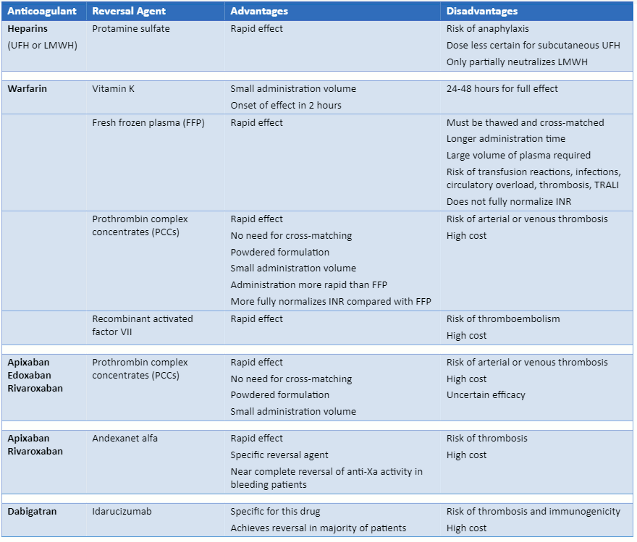
Anticoagulation management principles
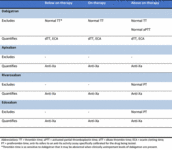
Summary of advantages and disadvantages of reversal agents (UFH = unfractionated heparin; LMWH = low molecular weight heparin; TRALI = transfusion-related acute lung injury *Guidelines support the use of 4-factor PCC in patients with life-threatening bleeding)
Created by the BMJ Knowledge Centre
See this image in context in the following section/s:
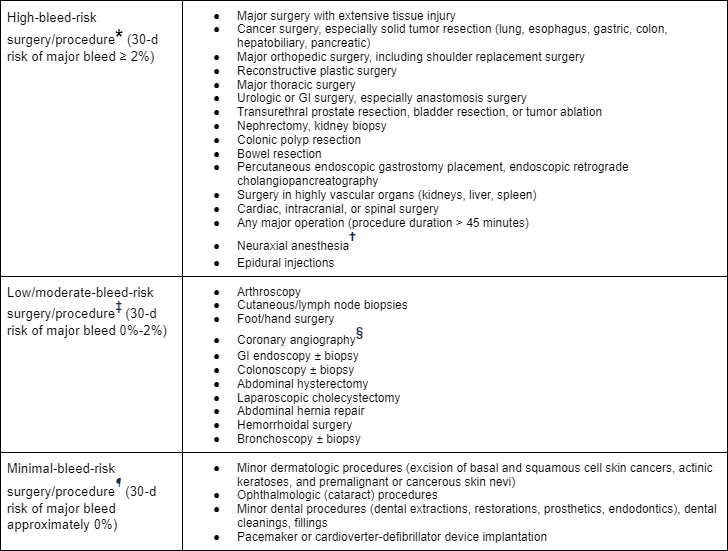
Anticoagulation management principles
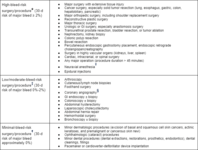
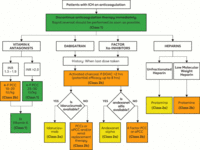
Risk stratification for procedural bleed risk (* No residual anticoagulant effect at the time of procedure [i.e., four to five drug half-life interruptions pre-procedure]; † Includes spinal and epidural anesthesia or any other neuraxial [e.g., pain management] intervention; consider not only absolute risk for major bleeding but potentially devastating consequences of epidural bleeding and associated lower limb paralysis; ‡ Some residual anticoagulant effect allowed [i.e., two to three drug half-life interruptions pre-procedure]; § Radial approach may be considered minimal bleed risk compared with femoral approach; ¶ Procedure can be safely done under full-dose anticoagulation [may consider holding DOAC dose day of procedure to avoid peak anticoagulant effects])
Douketis JD et al. Chest. 2022 Nov;162(5):e207-43; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
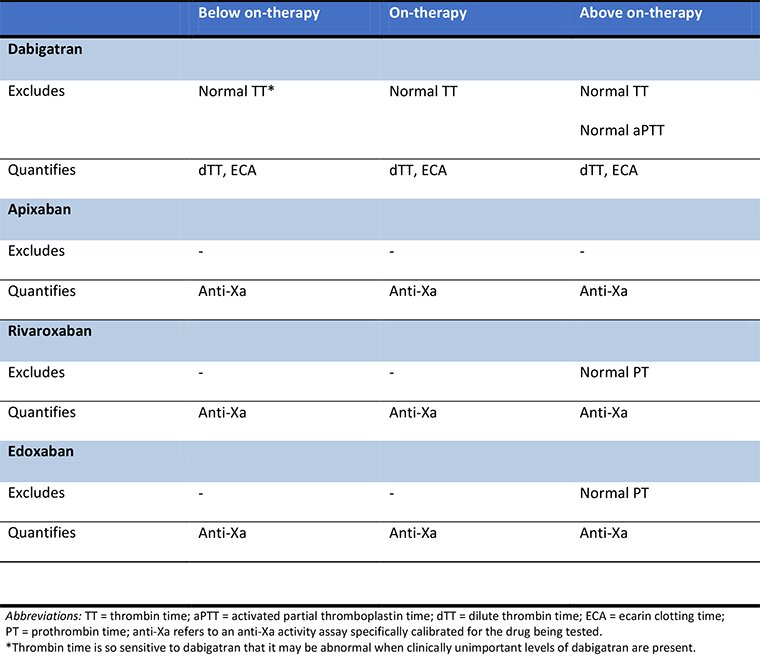
Anticoagulation management principles
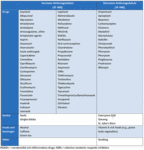
Qualitative laboratory measurement of direct oral anticoagulants with standard tests
Produced by SM Stevens, MD and SC Woller, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Anticoagulation management principles
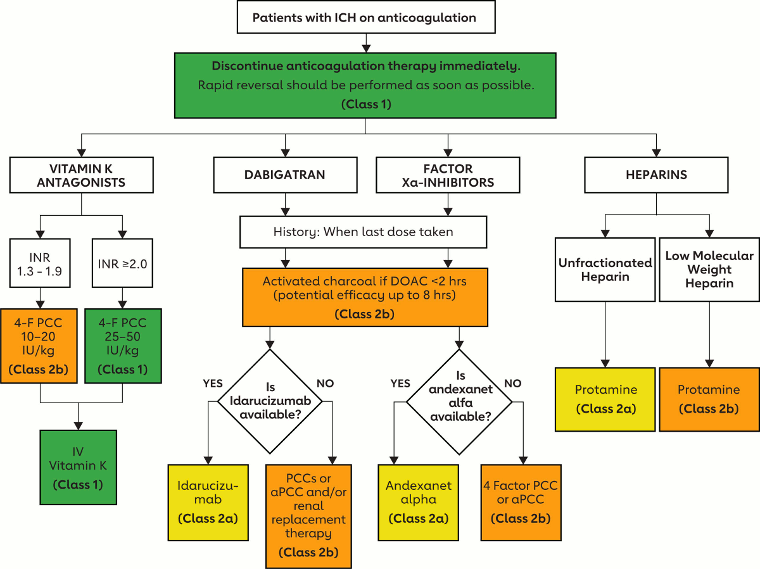
Management of anticoagulant-related hemorrhage. aPCC indicates activated prothrombin complex concentrate; DOAC, direct oral anticoagulant; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; INR, international normalized ratio; and PCC, prothrombin complex concentrate.
Greenberg SM et al. Stroke. 2022;53:e282-361; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Anticoagulation management principles
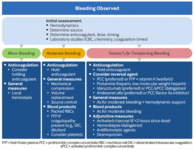
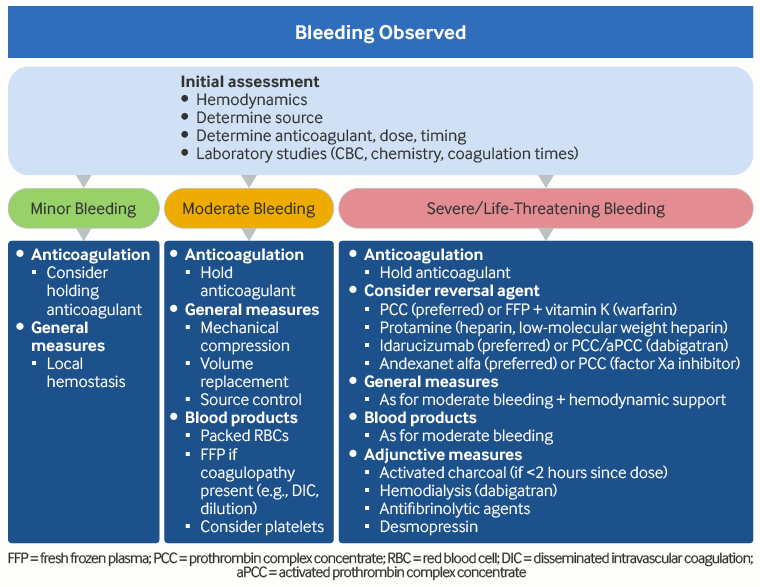
Approach to the management of acute hemorrhage in an anticoagulated patient
Produced by SM Stevens, MD and SC Woller, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Anticoagulation management principles
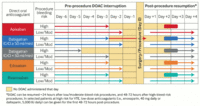
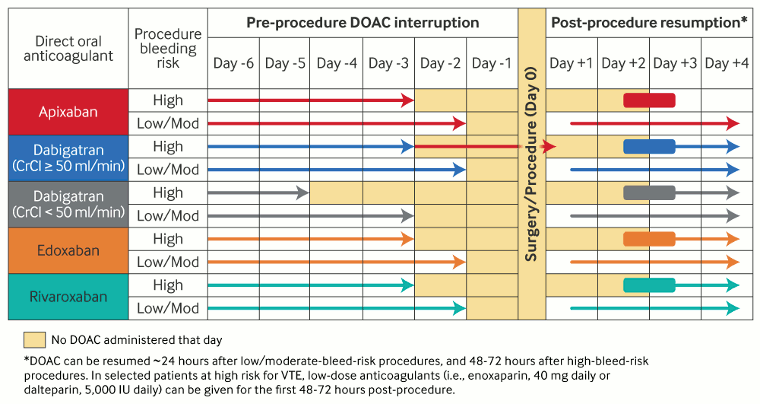
Perioperative management of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs)
Adapted by BMJ Knowledge Centre from Douketis JD et al. Chest. 2022 Nov;162(5):e207-43; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Anticoagulation management principles
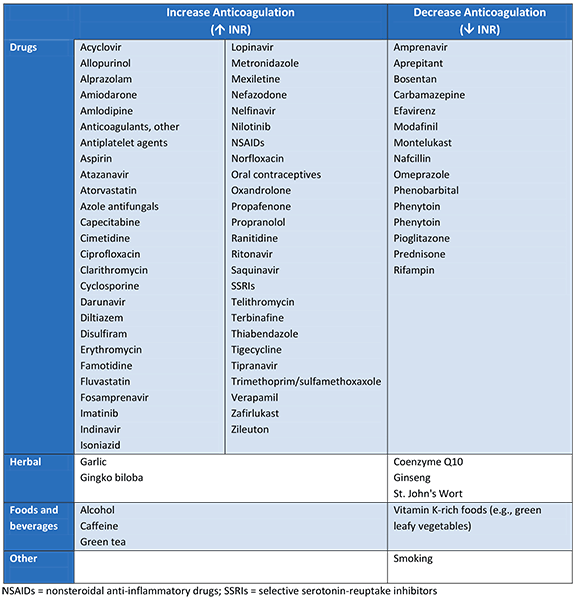
Possible interactions with warfarin. This list is not exhaustive and a local drug formulary should be consulted before prescribing any drug in patients on warfarin
Created by the BMJ Evidence Centre (based on Coumadin® package insert)
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer