Investigations
1st investigations to order
clinical diagnosis
Test
Usually no tests are necessary.
Result
features of tendinopathy
Investigations to consider
ultrasound
Test
Quick and inexpensive way to evaluate tendon structure. However, the quality of the ultrasound images is highly operator dependent.[34][35]
Normal tendons appear echogenic. The degenerative tendon may appear thickened and blurred, and may exhibit hypoechoic foci within the tendon.
Result
thickened, blurred tendon, and possible hypoechoic foci within tendon
MRI
Test
Best imaging modality for evaluating tendon injury.[34]
Allows for evaluation of surrounding soft tissues.
Normal tendons appear dark whereas degenerative tendons may appear thickened and will exhibit intermediate signal intensity (appears grey/white).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI demonstrating mild to moderate tendinopathy of the proximal centimetre of the patellar tendon, characterised by thickening and abnormal signal within the tendonFrom the personal collection of James Wang, PhD [Citation ends].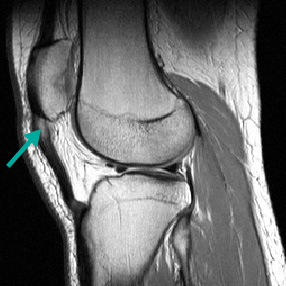
Result
thickened tendon with intermediate signal intensity (grey/white)
x-ray
Test
Plain x-rays do not allow visualisation of soft tissues and therefore are rarely used in the diagnosis of tendinopathy.
They are useful as an adjunct to evaluate for bony spurs or mal-alignment.[38]
Result
calcium deposits may be seen in calcific tendinopathy
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer