Investigations
1st investigations to order
clinical diagnosis
Test
Routine screening tests may exclude other common conditions.
Result
diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy is often made on clinical grounds
fasting blood glucose
Test
Many patients who present with painful neuropathy may have undiagnosed diabetes.
The American Diabetes Association recommends any of four screening tests to diagnose diabetes: fasting blood glucose, random plasma glucose, HbA1c, or 2-hour post-load glucose after 75 g oral glucose. Random plasma glucose is typically reserved for those with classic symptoms of hyperglycaemia or a hyperglycaemic crisis.[34] In the absence of unequivocal hyperglycaemia, diagnosis requires two abnormal test results.[34]
Result
diagnosis of diabetes mellitus (if not already known to be present)
HbA1c
Test
Many patients who present with painful neuropathy may have undiagnosed diabetes.
The American Diabetes Association recommends any of four screening tests to diagnose diabetes: fasting blood glucose, random plasma glucose, HbA1c, or 2-hour post-load glucose after 75 g oral glucose.[34] In the absence of unequivocal hyperglycaemia, diagnosis requires two abnormal test results.[34]
Poorly controlled hyperglycaemia is associated with increased risk of neuropathy.[34]
Result
correlates with degree of glycaemic control
serum thyroid-stimulating hormone
Test
To exclude thyroid dysfunction.
Result
normal
serum vitamin B12
Test
To exclude deficiency.
Result
normal
renal function tests
Test
Renal function tests are recommended to exclude renal disease as a treatable cause of neuropathy.
Additionally, all patients with diabetes receive regular monitoring of renal function.
Evaluation includes electrolytes, urea, creatinine, urinary microalbumin, and measurement of estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Result
normal or may show renal insufficiency
serum lipid profile
Test
To exclude abnormalities in low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein, triglycerides, and total cholesterol.
Result
may show lipid abnormalities
LFTs
Test
To exclude hepatic disease.
Result
normal
FBC and erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Test
To exclude anaemia and inflammatory disorders.
Result
normal
serum/urine immunoelectrophoresis
Test
To exclude multiple myeloma.
Result
normal
Investigations to consider
2-hour plasma glucose
Test
Many patients who present with painful neuropathy may have undiagnosed diabetes. In this circumstance, plasma glucose may be measured 2 hours after a 75 g oral glucose load.
Patients should be advised to consume a varied diet with at least 150 g of carbohydrate on the 3 days prior to testing, as fasting and carbohydrate restriction can falsely increase plasma glucose levels.[34]
The American Diabetes Association recommends any of four screening tests to diagnose diabetes: fasting blood glucose, random plasma glucose, HbA1c, or 2-hour post-load glucose after 75 g oral glucose.[34] In the absence of unequivocal hyperglycaemia, diagnosis requires two abnormal test results.[34]
Result
diagnosis of diabetes mellitus (if not already known to be present)
nerve conduction studies (nerve conduction velocity [NCV])
Test
Indicated in situations where the clinical features are atypical (such as asymmetrical symptoms and signs or weakness).
Whole nerve electrophysiological procedures (e.g., NCV, F-waves, sensory, and/or motor amplitudes) are performed.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Nerve conduction testing of the lower legCreated by the BMJ Group [Citation ends].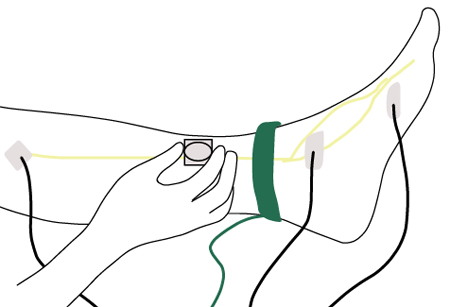
In very mild or asymptomatic cases, the only change may be distal slowing of conduction or none.
As the neuropathy progressively worsens, findings of axonal degeneration predominate, including decreased amplitude of sensory nerve action potentials (SNAPs); decreased amplitude of compound muscle action potentials; relative preservation of proximal conduction velocities; and evidence of fibrillation potentials.
NCV typically declines progressively in DN.[82] However, it may remain completely normal in patients with predominantly small-fibre neuropathy. Several prospective clinical trials have reported a slower decline in NCV outcomes under the current standard of care for patients with diabetes.[18][103]
Longitudinal studies suggest an average loss of SNAP amplitude at a rate of approximately 5% per year over a 10-year period.[82] In patients with type 1 diabetes participating in the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study, the average loss rate was around 3% per year over a 13-14-year period.[18]
Motor nerve studies may demonstrate some slowing, even when patients have no symptoms or signs of neuropathy, with a greater slowing in symptomatic patients. Motor amplitudes may be decreased in more advanced DN.
A key role for electrophysiological assessment is to rule out other causes of neuropathy (e.g., unilateral conditions, such as entrapments) and to identify neuropathies superimposed on DN.
Result
reduced sensory nerve conduction velocity and decreased amplitude are the earliest and most sensitive findings
electromyography (EMG)
Test
Indicated in situations where the clinical features are atypical (such as asymmetrical symptoms and signs, or weakness).
Result
may be normal in mild or neurologically asymptomatic patients, but demonstrates denervation in more severe DN
quantitative sensory testing (QST)
Test
Quantifies vibration perception thresholds (VPT) and thermal perception thresholds using a variety of instruments and algorithms. QST is particularly useful for detecting small-fibre neuropathy when other examinations are normal.[81]
Two main approaches are used: the method of limits, in which the patient indicates when an ascending stimulus is first detected or a descending stimulus is no longer perceived, and the method of levels (a forced-choice approach), in which fixed-intensity stimuli are presented and the patient reports perception.[80] QST is likely more reproducible than bedside subjective assessments of stimulus intensity.[81]
VPT shows high sensitivity and specificity relative to nerve conduction velocity (NCV) testing and neurological examination, and elevated VPTs in the 50-300 Hz range are associated with diabetic neuropathy (DN).[82] Abnormal thermal thresholds are reported in about 75% of patients with moderate-to-severe diabetic peripheral neuropathy, with elevated heat-pain thresholds in 39%.[82] Although thermal and vibration thresholds generally correlate, they may diverge in individual patients, suggesting predominant involvement of either small-fibre or large-fibre systems.
Result
may be normal, or deficits in vibration and/or thermal perception threshold may be detected
skin biopsy
Test
A validated technique for determining intra-epidermal nerve fibre density. May be considered for the diagnosis of DN, particularly small-fibre neuropathy, when electrophysiology does not match clinical presentation.[79]
Result
may be normal or show abnormalities of intra-epidermal nerve fibre density
cardiovascular autonomical reflex testing
Test
A group of standardised bedside tests that assess cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN), primarily parasympathetic (vagal) and sympathetic tone.[22][83]
Tests to evaluate parasympathetic function include: heart rate (HR) response to deep breathing, the Valsalva manoeuvre, and HR response to postural changes.[22][65][66][83] The HR response to deep breathing is the most commonly used test for assessing parasympathetic function, with a specificity of around 80%.[66] The Valsalva manoeuvre, although informative, requires greater patient cooperation and may not be feasible for all individuals.[65] HR response during the Valsalva manoeuvre is influenced by accompanying blood pressure (BP) changes.[65]
Sympathetic function can be evaluated through BP responses to standing and the Valsalva manoeuvre, as well as sustained isometric muscle contraction.[65][66] Despite limited sensitivity, orthostatic BP measurement remains a standard component of CAN assessment.[65]
Cardiovascular autonomic reflex tests are non-invasive, safe, reproducible, and correlate well with peripheral nervous system dysfunction.[22] Because no single test is sufficiently sensitive or specific on its own, more than one HR-based and BP-based test is recommended for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of CAN.[22][65][66]
Result
may be impaired heart rate and/or BP response to deep breathing, Valsalva manoeuvre, and/or standing
corneal confocal microscopy
Test
A non-invasive ophthalmic technique to image the corneal sub-basal nerve plexus. It has been shown to detect small sensory corneal nerve fibre loss in DN.[104][105][106] Studies have found high reproducibility, sensitivity, and specificity.[104][106] Corneal confocal microscopy can detect both early sub-clinical and established DN.[107]
Result
corneal nerve fibre damage correlates with intra-epidermal nerve fibre loss and severity of neuropathy
heart rate variability (HRV)
Test
Short 5-minute resting HRV recordings complement cardiovascular autonomic reflex tests (CARTs) by capturing beat-to-beat sinus arrhythmia under standardised conditions.[22][65][66][67][83][84] HRV can be analysed with time- or frequency-domain methods and broadly reflects autonomic (especially vagal) modulation. Reduced HRV supports a diagnosis of cardiac autonomic neuropathy (CAN) and independently predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality.[22][65][66] HRV is best used alongside CARTs, with results interpreted in light of respiration and age-related norms.
Result
may be reduced
gastric emptying studies
Test
Performed with double isotope scintigraphy.
Indicated in people who have symptoms and/or signs suggesting diabetic gastroparesis where clinical uncertainty exists.
Result
delayed solid phase emptying
gastroduodenoscopy
Test
Recommended along with other gastrointestinal investigations (e.g., gastric emptying studies or gastric electrography) to exclude pyloric or other mechanical obstructions in people with suspected diabetic gastroparesis where clinical uncertainty exists.
Result
may be normal or may demonstrate solid food residues
barium meal
Test
Barium meal studies may be useful for identifying mucosal lesions or mechanical obstruction.
Result
excludes mucosal lesions or obstruction
gastrointestinal manometry
Test
Manometry should be considered as a research technique to investigate gastric and intestinal motility.
Result
may indicate delay in gastric and intestinal motility
hydrogen breath tests
Test
Diarrhoea is evident in 20% of patients with diabetes, particularly those with known autonomic dysfunction.[64]
Diarrhoea in patients with diabetes is often due to bacterial overgrowth, which can be diagnosed with hydrogen breath tests.
Using non-radioactive 13C-acetate or -octanoic acid as a label; these are safe, inexpensive tests that correlate well with scintigraphy results.
Result
may be normal or may suggest bacterial overgrowth
gastric ultrasonography
Test
A non-invasive diagnostic method.
Two-dimensional ultrasound has been validated for measuring gastric emptying of liquids and semi-solids. However, 3-dimensional ultrasound offers a more comprehensive assessment of total gastric volume and motility.
Result
may demonstrate delayed gastric emptying
gastric MRI
Test
Has been used to measure gastric emptying and motility with excellent reproducibility, but its use is limited to research purposes.
Result
may demonstrate delayed gastric emptying
anorectal manometry
Test
Indicated for evaluating sphincter tone and the rectal-anal-inhibitory reflex.
Distinguishes colonic hypomotility from rectosigmoid dysfunction in patients with obstructive defecation symptoms.
Result
may be normal or may suggest hypomotility
faecal fat
Test
For patients with large-volume diarrhoea, faecal fat should be checked and further studied with a 72-hour collection to rule out malabsorptive disorders.
If there is significant steatorrhoea, pancreatic function tests should be performed.
Result
may be normal or elevated (steatorrhoea)
serological tests for coeliac disease
Test
In patients with diabetes being evaluated for neuropathy, especially those with chronic diarrhoea, unexplained iron-deficiency anaemia, weight loss/abdominal distension, or type 1 diabetes, consider testing for coeliac disease to exclude a potentially reversible contributor to symptoms. Use tissue transglutaminase IgA (tTG-IgA) with total IgA (and endomysial antibody or IgG-based tests if IgA deficient). This helps distinguish coeliac-related malabsorption or neuropathy from diabetic autonomic neuropathy-related diarrhoea and guides referral for confirmatory biopsy and dietary management.
Result
negative
D-xylose test
Test
Alternative or additional test to faecal fat measurement. Can be used to rule out malabsorptive disorders in people with large-volume diarrhoea.
Result
normal
urine culture
Test
Part of the assessment of people with symptoms of bladder dysfunction.[89]
Result
normal
cystometry, voiding cystometrogram
Test
Used in addition to post-void urinary tract ultrasound to evaluate diabetic bladder dysfunction.[89]
Residual volume and upper urinary tract dilation are assessed.
Result
may be normal or may suggest bladder dysfunction
post-void urinary tract ultrasound
Test
Used in addition to cystometry and voiding cystogram to evaluate diabetic bladder dysfunction.[89]
Residual volume and upper urinary tract dilation are assessed.
Result
may be normal or may suggest bladder dysfunction
video-urodynamics
Test
The preferred investigation for invasive urodynamics in patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction.[89]
Result
may be normal or may suggest bladder dysfunction
testosterone (morning)
Test
Indicated in men with erectile dysfunction to rule out hypogonadism.[34][88]
Serum testosterone should be a morning sample.
Further specialised testing may also be necessary. See Erectile dysfunction.
Result
normal
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer