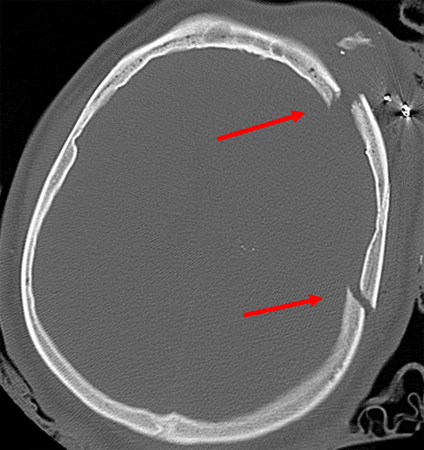
Skull fractures occur in 2% to 20% of all head trauma.[2]Servadei F, Ciucci G, Pagano F, et al. Skull fracture as a risk factor of intracranial complications in minor head injuries: a prospective CT study in a series of 98 adult patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Apr;51(4):526-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3379426?tool=bestpractice.com
[3]Schutzman SA, Greenes DS. Pediatric minor head trauma. Ann Emerg Med. 2001 Jan;37(1):65-74.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11145776?tool=bestpractice.com
According to data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019, the age-standardized rates of skull fractures were 98.9 incident cases (77.1 to 128.5) per 100,000 population and 39.9 prevalent cases (35.7 to 45.8) per 100,000 population.[4]GBD 2019 Fracture Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of bone fractures in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021 Sep;2(9):e580-92.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00172-0
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34723233?tool=bestpractice.com
Skull fractures occur most frequently between the ages of 20 and 50 years.[5]Besenski N. Traumatic injuries: imaging of head injuries. Eur Radiol. 2002 Jun;12(6):1237-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12042929?tool=bestpractice.com
However, children with a head injury have an increased prevalence of skull fracture in comparison with adults. Males are overwhelmingly more commonly affected than females.[4]GBD 2019 Fracture Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of bone fractures in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021 Sep;2(9):e580-92.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00172-0
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34723233?tool=bestpractice.com
[6]Ersahin Y, Mutluer S, Mirzai H, et al. Pediatric depressed skull fractures: analysis of 530 cases. Childs Nerv Syst. 1996 Jun;12(6):323-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8816297?tool=bestpractice.com
[7]Mithani SK, St-Hilaire H, Brooke BS, et al. Predictable patterns of intracranial and cervical spine injury in craniomaxillofacial trauma: analysis of 4786 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Apr;123(4):1293-301.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19337097?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Smits M, Dippel DW, de Haan GG, et al. Minor head injury: guidelines for the use of CT - a multicenter validation study. Radiology. 2007 Dec;245(3):831-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17911536?tool=bestpractice.com
The most common mechanism, found in up to 35% of cases, is a fall.[5]Besenski N. Traumatic injuries: imaging of head injuries. Eur Radiol. 2002 Jun;12(6):1237-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12042929?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Galarneau MR, Woodruff SI, Dye JL, et al. Traumatic brain injury during Operation Iraqi Freedom: findings from the United States Navy-Marine Corps Combat Trauma Registry. J Neurosurg. 2008 May;108(5):950-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18447712?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Shane SA, Fuchs SM. Skull fractures in infants and predictors of associated intracranial injury. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1997 Jun;13(3):198-203.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9220506?tool=bestpractice.com
The most common fractures are simple linear fractures, found in up to 50% to 80% of all skull fractures.[2]Servadei F, Ciucci G, Pagano F, et al. Skull fracture as a risk factor of intracranial complications in minor head injuries: a prospective CT study in a series of 98 adult patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Apr;51(4):526-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3379426?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Galarneau MR, Woodruff SI, Dye JL, et al. Traumatic brain injury during Operation Iraqi Freedom: findings from the United States Navy-Marine Corps Combat Trauma Registry. J Neurosurg. 2008 May;108(5):950-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18447712?tool=bestpractice.com
[11]Macpherson BC, MacPherson P, Jennett B. CT evidence of intracranial contusion and haematoma in relation to the presence, site and type of skull fracture. Clin Radiol. 1990 Nov;42(5):321-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2245568?tool=bestpractice.com
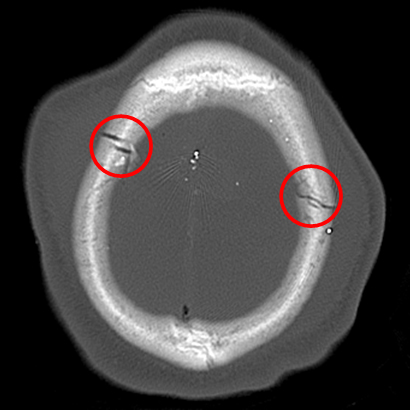 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gunshot wound with comminuted elevated fracture and pneumocephalusFrom the teaching collection of Demetrios Demetriades; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gunshot wound with comminuted elevated fracture and pneumocephalusFrom the teaching collection of Demetrios Demetriades; used with permission [Citation ends].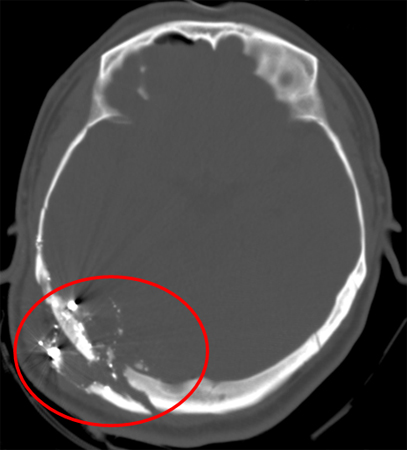 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gunshot wound with perpendicular blowout fractureFrom the teaching collection of Demetrios Demetriades; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gunshot wound with perpendicular blowout fractureFrom the teaching collection of Demetrios Demetriades; used with permission [Citation ends].