Investigations
Your Organisational Guidance
ebpracticenet urges you to prioritise the following organisational guidance:
Aanhoudende hoest bij kinderen in de eerste lijnPublished by: Werkgroep Ontwikkeling Richtlijnen Eerste Lijn (Worel)Last published: 2017La toux prolongée chez l’enfant en première ligne de soinsPublished by: Groupe de Travail Développement de recommmandations de première ligneLast published: 20171st investigations to order
empirical treatment trial
Test
Trial of empirical therapy with a first-generation antihistamine plus a decongestant is both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Required for diagnosis according to American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) criteria.[1]
Result
response to therapy (usually within 2 weeks)
chest x-ray
Test
Recommended in all patients to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
May show pulmonary pathology.
Result
normal
FBC
Test
Recommended in all patients to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
Presence of eosinophilia should prompt investigation for other causes of chronic cough (most commonly allergic causes).
Result
normal
spirometry
Test
Recommended in all patients to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
Airway obstruction may indicate an airway disease.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Spirometry reading showing reduced inspiratory loops consistent with extrathoracic obstruction.From the collection of Kian Fan Chung, MD, FRCP; used with permission [Citation ends].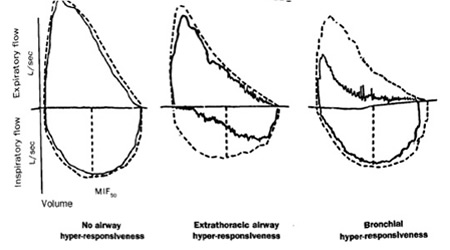
Evidence of airflow obstruction does not necessarily indicate that this is the cause of cough.
Result
normal
fractional exhaled nitric oxide
Test
Recommended in all patients to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
Raised level may indicate the presence of asthma or type 2 airway inflammation.[42]
Result
normal
Investigations to consider
direct nasolaryngoscopy
Test
Used to identify structural or movement (e.g., paradoxical closure on inspiration) abnormalities, evidence of reflux change, and visible postnasal drip.
When performed with provocation (e.g., exposure to perfume) can provide evidence of inducible laryngeal obstruction, which is sometimes termed vocal cord dysfunction.[23]
Characteristic appearance can indicate diagnosis; however, other laryngeal lesions can also cause chronic cough.
Also permits identification of nasal disease (e.g., oedema, polyps).
Result
visible mucus and a cobblestone appearance to the posterior oropharyngeal wall and local upper airway structures
serum IgE level
Test
Recommended in some patients (depending on the history) to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
Elevated level indicates atopy.
Positive result for atopy does not necessarily indicate an allergic aetiology for cough.
Result
normal
specific aeroallergen radioallergosorbent test (RAST)
Test
Recommended in some patients (depending on the history) to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
Positive result indicates atopy.
Positive result for atopy does not necessarily indicate an allergic aetiology for cough.
Result
negative
peak expiratory flow (PEF)
Test
Recommended in some patients (depending on the history) to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
Variability may indicate an airway disease.
Result
normal
CT sinus
Test
Recommended in some patients (depending on the history) to rule out other causes of chronic cough.
May show sinus mucosal thickening, opacification, or air-fluid levels if sinus disease present.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT sinus demonstrating opacification.Image courtesy of Mr Hesham Saleh; used with permission [Citation ends].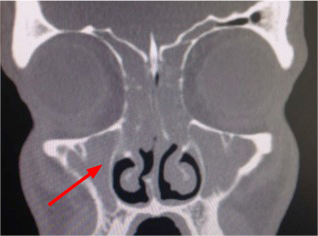
Result
normal
CT chest with or without intravenous contrast
Test
May be appropriate, especially if the results of initial chest x-ray are inconclusive.[40]
Result
normal
Emerging tests
bronchial challenge test
Test
Increasingly being used to measure extrathoracic hyper-responsiveness (i.e., laryngeal dysfunction).
One series showed that a positive result was common in patients with chronic cough.[43]
Further work is needed to establish the clinical value of this test in chronic cough.
Result
positive
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer