Investigations
1st investigations to order
pulse oximetry
Test
A rapid and accurate method for assessing hypoxaemia, its use should be considered in any infant with moderate to severe symptoms.[2] Routine pulse oximetry use has not been shown to improve outcomes.
Result
hypoxaemia
Investigations to consider
chest x-ray
Test
Reveals atelectasis, hyperinflation, peribronchial cuffing, and infiltrate.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: AtelectasisFrom the personal collections of Melvin L. Wright, DO and Giovanni Piedimonte, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].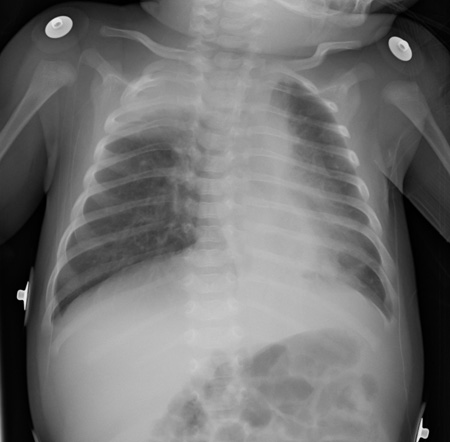 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Air trapping and peribronchial cuffingFrom the personal collections of Melvin L. Wright, DO and Giovanni Piedimonte, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Air trapping and peribronchial cuffingFrom the personal collections of Melvin L. Wright, DO and Giovanni Piedimonte, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].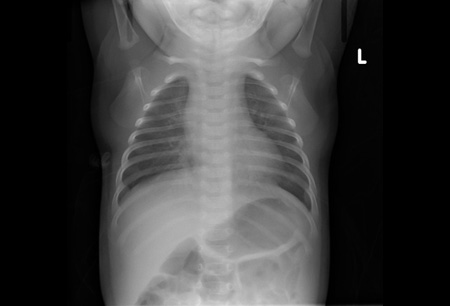
Should be reserved for those patients with severe disease, and those who do not improve at the expected rate.[2][114]
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends only performing a chest x‑ray if intensive care is being proposed for a baby or child. A chest x‑ray in babies or children with bronchiolitis may mimic pneumonia and should not be used to determine the need for antibiotics.[53]
Result
atelectasis, hyperinflation, peribronchial cuffing, infiltrate
hydration status
Test
Clinically assess the hydration status of babies and children with bronchiolitis to determine the hydration requirements of the patient.[53]
Result
Hypovolaemic, euvolaemic or hypervolaemic
rapid antigen detection from respiratory specimen (e.g., nasopharyngeal aspirate)
Test
Commercially available and relatively easy to use. Sensitivity >90%, in young children, but is lower in older children and adults.[115]
Result
detection of viral antigen
reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of respiratory specimen (e.g., nasopharyngeal aspirate)
Test
A rapid and sensitive method for detecting respiratory syncytial virus.
The preferred method of viral testing at most large medical centres.
Clinical sensitivity superior to other diagnostic modalities.
Result
detection of viral ribonucleic acid
viral culture of respiratory specimen (e.g., nasopharyngeal aspirate)
Test
Not generally useful in the clinical setting given long turnaround time and low sensitivity compared to polymerase chain reaction.
Result
growth of virus
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer