Omphalocele and gastroschisis
- Overview
- Theory
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Follow up
- Resources
Treatment algorithm
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups: see disclaimer
gastroschisis
fluid resuscitation and temperature maintenance
Immediate postnatal management of gastroschisis involves fluid resuscitation and temperature maintenance.
The infant should then be urgently transferred to a neonatal intensive unit with specialised paediatric surgical capacity.[32]Government of Western Australia Child and Adolescent Health Service. Gastroschisis. Aug 2008 [internet publication]. https://www.cahs.health.wa.gov.au/-/media/HSPs/CAHS/Documents/Health-Professionals/Neonatology-guidelines/Gastroschisis.pdf
bowel protection
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
A sterile covering or a clear bowel bag should be placed immediately over the herniated abdominal contents to prevent evaporation, heat loss, and infection.
The infant should then be urgently transferred to a neonatal intensive unit with specialised paediatric surgical capacity.[32]Government of Western Australia Child and Adolescent Health Service. Gastroschisis. Aug 2008 [internet publication].
https://www.cahs.health.wa.gov.au/-/media/HSPs/CAHS/Documents/Health-Professionals/Neonatology-guidelines/Gastroschisis.pdf
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Immediately after delivery, an infant with gastroschisis is placed in a protective bowel bagFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].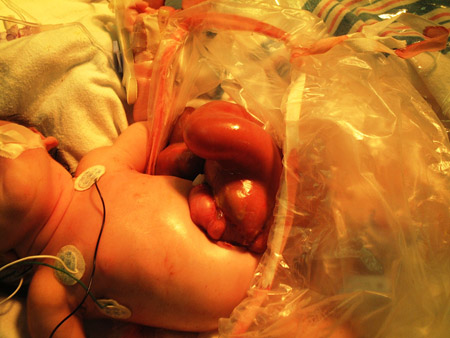
primary surgical repair
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Small defects may be treated with primary surgical repair.[35]Skarsgard ED. Immediate versus staged repair of omphaloceles. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2019 Apr;28(2):89-94. https://www.doi.org/10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2019.04.010 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31072464?tool=bestpractice.com
postsurgical nasogastric tube and parenteral nutrition
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Surgery is followed by a trial of a nasogastric tube for decompression of the bowel and total parenteral nutrition while the inflammatory peel resolves.
staged reduction and surgical repair
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Larger defects or those with extensive herniation of abdominal contents require a staged approach with placement of the abdominal contents into a suspended silo and gradual reduction into the abdominal cavity.[35]Skarsgard ED. Immediate versus staged repair of omphaloceles. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2019 Apr;28(2):89-94.
https://www.doi.org/10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2019.04.010
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31072464?tool=bestpractice.com
Ventilatory support is often required during this process. Once the abdominal contents have been fully reduced into the abdominal cavity, surgery is performed to close the fascia and skin.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A staged repair of gastroschisis involves the placement of a silo to reduce contents into the abdomenFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].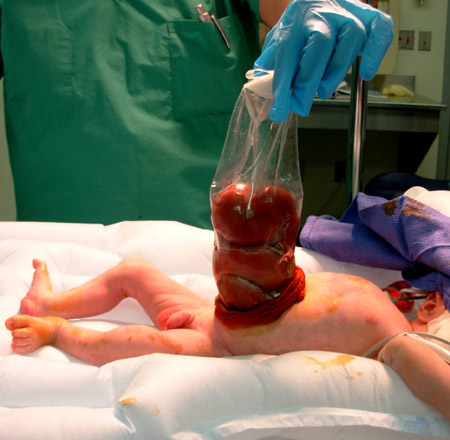 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Once intestinal contents are fully reduced into the abdomen, closure of the abdominal wall followsFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Once intestinal contents are fully reduced into the abdomen, closure of the abdominal wall followsFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].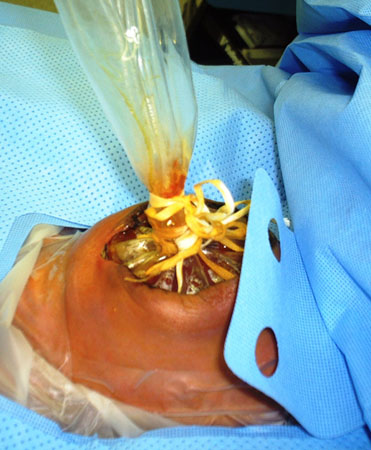
postsurgical nasogastric tube and parenteral nutrition
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Surgery is followed by a trial of a nasogastric tube for decompression of the bowel and total parenteral nutrition while the inflammatory peel resolves.[33]Moran M, Mortell A. Gastroschisis: management prior to transfer to surgical centre. Sep 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.hse.ie/eng/about/who/cspd/ncps/paediatrics-neonatology/resources/national-clinical-guideline-gastroschisis.pdf
secondary surgery
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
If an atretic (ischaemic) segment is present, a small bowel obstruction may develop after enteral feeds, necessitating further surgery.
omphalocele
fluid resuscitation and temperature maintenance
After delivery, infants with omphalocele should receive appropriate fluid resuscitation with temperature maintenance.[34]Bielicki IN, Somme S, Frongia G, et al. Abdominal wall defects-current treatments. Children (Basel). 2021 Feb 23;8(2):170. https://www.doi.org/10.3390/children8020170 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33672248?tool=bestpractice.com
The infant should then be urgently transferred to a neonatal intensive unit with specialised paediatric surgical capacity.
nasogastric tube
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
A nasogastric tube should be inserted to decompress the bowel.
surgical repair
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Surgical repair of omphalocele is elective (non-urgent), unless the membranous sac is ruptured.
Defects without rupture of the membranous sac may be allowed to epithelialise, especially if associated anomalies render immediate surgical intervention inappropriately risky. The resultant ventral hernia can be repaired at a later date.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: This ruptured omphalocele is similar in appearance to gastroschisisFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].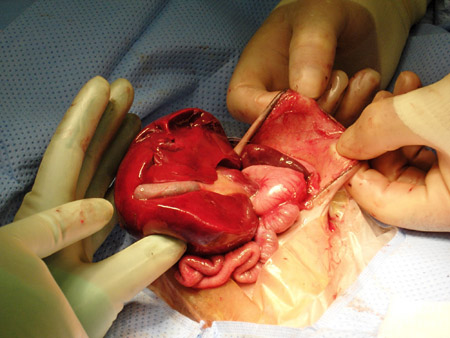 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A ventral hernia results from synthetic wall closure of the omphaloceleFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A ventral hernia results from synthetic wall closure of the omphaloceleFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].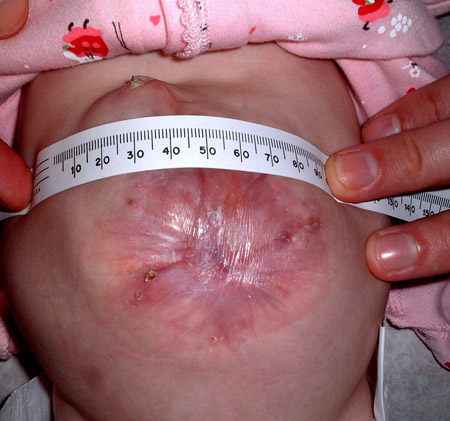 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: The ventral hernia is repaired in a 6-year-old girl born with omphaloceleFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: The ventral hernia is repaired in a 6-year-old girl born with omphaloceleFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].
bowel protection
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
If the membranous sac is not intact, a sterile covering or a clear bowel bag must be placed over the herniated abdominal contents to prevent evaporation, heat loss, and infection.[34]Bielicki IN, Somme S, Frongia G, et al. Abdominal wall defects-current treatments. Children (Basel). 2021 Feb 23;8(2):170.
https://www.doi.org/10.3390/children8020170
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33672248?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: The abdominal wall defect in omphalocele is covered with a synthetic membraneFrom collection of J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS, FAAP [Citation ends].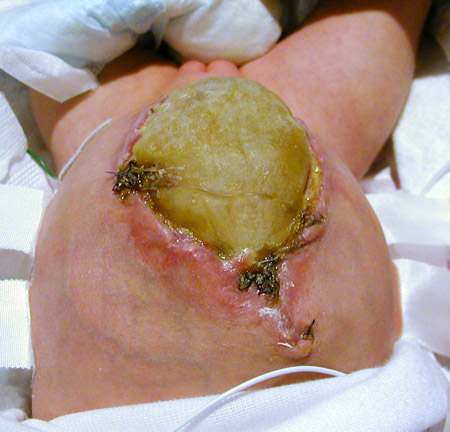
primary surgical repair
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Small defects may be treated with primary surgical repair.[35]Skarsgard ED. Immediate versus staged repair of omphaloceles. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2019 Apr;28(2):89-94. https://www.doi.org/10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2019.04.010 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31072464?tool=bestpractice.com
postsurgical nasogastric tube and parenteral nutrition
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Surgery is followed by a trial of a nasogastric tube for decompression of the bowel and total parenteral nutrition while the inflammatory peel resolves.
staged reduction and surgical repair
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Larger defects or those with extensive herniation of abdominal contents require a staged approach with placement of the abdominal contents into a suspended silo and gradual reduction into the abdominal cavity.[35]Skarsgard ED. Immediate versus staged repair of omphaloceles. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2019 Apr;28(2):89-94. https://www.doi.org/10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2019.04.010 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31072464?tool=bestpractice.com Ventilatory support is often required during this process. Once the abdominal contents have been fully reduced into the abdominal cavity, the fascia and skin are surgically closed.
post-surgical nasogastric tube and parenteral nutrition
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Surgery is followed by a trial of a nasogastric tube for decompression of the bowel and total parenteral nutrition while the inflammatory peel resolves.

Choose a patient group to see our recommendations
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups. See disclaimer
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer