Treatment can be conservative or surgical, and the choice depends on symptoms, age of the patient, and whether infection is present.[1]Pundir J, Auld BJ. A review of the management of diseases of the Bartholin's gland. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;28(2):161-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18393010?tool=bestpractice.com
[21]Cobellis PL, Stradella L, De Lucia E, et al. Alcohol sclerotherapy: a new method for Bartholin gland cyst treatment. Minerva Ginecol. 2006 Jun;58(3):245-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16783297?tool=bestpractice.com
Small, asymptomatic cysts may not require any treatment beyond conservative management.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9.[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
Larger cysts are more likely to be symptomatic and therefore more often require surgical intervention. The aims of surgical management are to preserve glandular function and to prevent recurrence of disease.[22]Cho JY, Ahn MO, Cha KS. Window operation: an alternative treatment method for Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;76(5 Pt 1):886-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2216242?tool=bestpractice.com
None of the treatment options are contra-indicated in pregnant women, but the increase in pelvic blood flow during pregnancy may lead to excessive bleeding with surgical treatment.[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
Unless the cyst obstructs the vagina (soft tissue dystocia), surgery should be delayed until after delivery in pregnant women.
Asymptomatic
A small, quiescent, asymptomatic Bartholin's cyst should be left alone and managed with sitz baths or warm compresses to aid drainage.[23]Scott PM. Draining a cyst or abscess in a Bartholin's gland with a Word catheter. JAAPA. 2003 Dec;16(12):51-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14758689?tool=bestpractice.com
No further treatment is usually required in women <40 years of age.[2]Wilkinson EJ, Stone IK. Atlas of vulvar disease. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1995:11-13.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9.[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
Over 40 years, the possibility of malignancy must be considered and biopsy may be indicated, but simple asymptomatic cysts can be managed in the same way once malignancy has been excluded.
Symptomatic
Various surgical modalities have been proposed for symptomatic cysts and are aimed at creating a new ductal ostium to allow continuous drainage, or destruction of the cyst wall lining.[1]Pundir J, Auld BJ. A review of the management of diseases of the Bartholin's gland. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;28(2):161-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18393010?tool=bestpractice.com
The overall success rate of surgery (marked by the absence of swelling and discomfort, and the appearance of a freely draining duct) is 87% to as high as 96% at 1 year regardless of the method used.[18]Omole F, Kelsey RC, Phillips K, et al. Bartholin duct cyst and gland abscess: office management. Am Fam Physician. 2019 Jun 15;99(12):760-6.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0615/p760.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31194482?tool=bestpractice.com
One 2020 systematic review found no clear consensus on the single best surgical intervention.[24]Illingworth B, Stocking K, Showell M, et al. Evaluation of treatments for Bartholin's cyst or abscess: a systematic review. BJOG. 2020 May;127(6):671-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31876985?tool=bestpractice.com
Any procedure that preserves function and prevents the formation of an abscess is preferable to excision of the gland.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9. Morbidity associated with surgical excision of Bartholin's cysts is more frequent than is generally recognised, and includes cellulitis, recurrence, intra-operative and post-operative haemorrhage, haematoma, and painful scar tissue.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9.
In the absence of cellulitis, antibiotic therapy is unnecessary.[1]Pundir J, Auld BJ. A review of the management of diseases of the Bartholin's gland. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;28(2):161-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18393010?tool=bestpractice.com
[18]Omole F, Kelsey RC, Phillips K, et al. Bartholin duct cyst and gland abscess: office management. Am Fam Physician. 2019 Jun 15;99(12):760-6.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0615/p760.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31194482?tool=bestpractice.com
More than 70% of cultures from Bartholin's cysts and about 33% of cultures from Bartholin's abscesses are sterile.[13]Lee YH, Rankin JS, Alpert S, et al. Microbiological investigation of Bartholin's gland abscesses and cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Sep 15;129(2):150-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/900177?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bhide A, Nama V, Patel S, et al. Microbiology of cysts/abscesses of Bartholin's gland: review of empirical antibiotic therapy against microbial culture. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2010;30(7):701-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20925614?tool=bestpractice.com
If cellulitis is present, broad-spectrum antibiotics are recommended, as infection is often polymicrobial.[13]Lee YH, Rankin JS, Alpert S, et al. Microbiological investigation of Bartholin's gland abscesses and cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Sep 15;129(2):150-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/900177?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bhide A, Nama V, Patel S, et al. Microbiology of cysts/abscesses of Bartholin's gland: review of empirical antibiotic therapy against microbial culture. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2010;30(7):701-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20925614?tool=bestpractice.com
[15]Kessous R, Aricha-Tamir B, Sheizaf B, et al. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of Bartholin gland abscesses. Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Oct;122(4):794-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24084536?tool=bestpractice.com
Diabetic patients with cellulitis need careful observation, as they are susceptible to necrotising infection. Admission to hospital should be considered.
Marsupialisation[25]Davis GD. Management of Bartholin duct cysts with the carbon dioxide laser. Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Feb;65(2):279-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3918283?tool=bestpractice.com
The objectives of marsupialisation are to construct a new mucocutaneous junction between the wall of the cyst and the skin of the labia, and to place it in approximately the normal position.[10]Azzan BB. Bartholin's cyst and abscess: a review of treatment of 53 cases. Br J Clin Pract. 1978 Apr;32(4):101-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/666961?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Jacobson P. Marsupialization of vulvovaginal (Bartholin) cysts: report of 140 patients with 152 cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1960 Jan;79:73-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14406421?tool=bestpractice.com
This allows for patency of the gland to be maintained so that secretory function is not lost. The same operation with slight variations can be done regardless of whether the cyst is infected, ruptured, or recurrent.[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Jacobson P. Marsupialization of vulvovaginal (Bartholin) cysts: report of 140 patients with 152 cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1960 Jan;79:73-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14406421?tool=bestpractice.com
However, if infection is accompanied by marked inflammation and necrosis, sutures will pull through and marsupialisation will not be possible. Marsupialisation can be performed under pudendal nerve block or local anaesthetic and is the preferred treatment for many clinicians.[10]Azzan BB. Bartholin's cyst and abscess: a review of treatment of 53 cases. Br J Clin Pract. 1978 Apr;32(4):101-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/666961?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Marsupialisation of a Bartholin’s cyst. The site is cleaned and anaesthetised, and then a 1.5 to 2 cm incision is made just distal to the hymen ring within the introitus into the region of the normal duct opening. The cyst/abscess cavity is irrigated and loculations are broken down if necessary. The incised cyst/abscess wall is then approximated to the edge of the vestibular skin.From the personal collection of Colleen Kennedy Stockdale; used with permission. [Citation ends].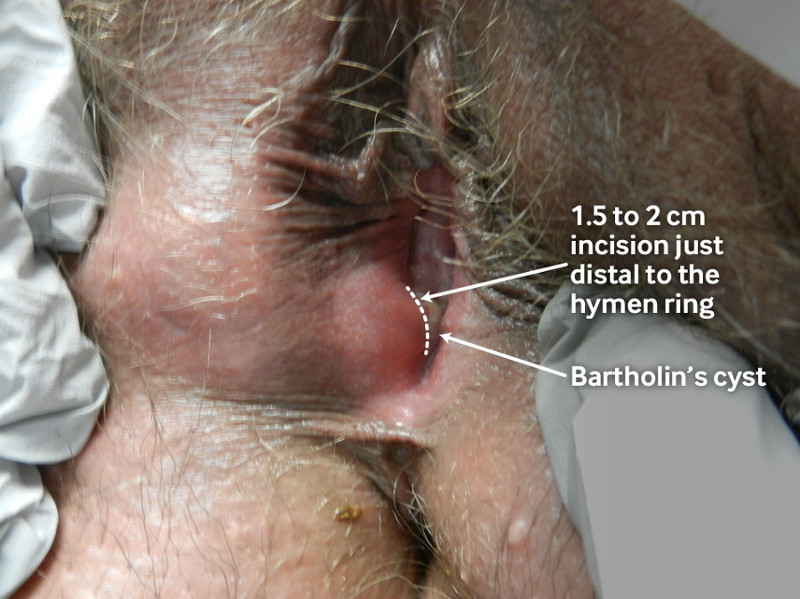
If the initial sutures pull through, a larger suture may be tried. If the larger suture also pulls through, further attempts should not be made. The aperture should be as large as possible, ideally large enough to admit 2 fingers, as it will shrink to half its size within 1 to 3 weeks.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9.[10]Azzan BB. Bartholin's cyst and abscess: a review of treatment of 53 cases. Br J Clin Pract. 1978 Apr;32(4):101-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/666961?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Jacobson P. Marsupialization of vulvovaginal (Bartholin) cysts: report of 140 patients with 152 cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1960 Jan;79:73-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14406421?tool=bestpractice.com
Twice-daily sitz baths are recommended post-operatively.
Variations on this technique have been described, including use of carbon dioxide laser to create a haemostatic cyst defect without use of suture, packing with an iodoform gauze that is removed after 1 week, using rubber drains after placing a linear incision into the cyst cavity, or removing an oval-shaped section of tissue (the window technique).[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Davis GD. Management of Bartholin duct cysts with the carbon dioxide laser. Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Feb;65(2):279-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3918283?tool=bestpractice.com
[27]Cheetham DR. Bartholin's cyst: marsupialization or aspiration? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Jul 1;152(5):569-70.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4014349?tool=bestpractice.com
[28]Di Donato V, Bellati F, Casorelli A, et al. CO2 laser treatment for Bartholin gland abscess: ultrasound evaluation of risk recurrence. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013 May-Jun;20(3):346-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23380446?tool=bestpractice.com
[29]Figueiredo AC, Duarte PE, Gomes TP, et al. Bartholin's gland cysts: management with carbon-dioxide laser vaporization. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2012 Dec;34(12):550-4.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0100-72032012001200004&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=en
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23329284?tool=bestpractice.com
Possible advantages of the window technique include a reduction in recurrence rate.[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
[22]Cho JY, Ahn MO, Cha KS. Window operation: an alternative treatment method for Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;76(5 Pt 1):886-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2216242?tool=bestpractice.com
One small study found that use of a carbon dioxide laser was associated with a more favourable sexual health recovery than surgical incision.[30]Di Donato V, Vena F, Casorelli A, et al. The impact of CO<sub>2</sub> laser for treatment of Bartholin's gland cyst or abscess on female sexual function: a pilot study. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2019 Feb;35(2):150-4.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30132350?tool=bestpractice.com
The use of iodine to identify the optimal site of incision for anatomical placement of the ostium has also been described.[31]Hollyock VE. The use of iodine in the marsupialization of Bartholin's duct cysts. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1979 Nov;19(4):228-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/295642?tool=bestpractice.com
Complications of marsupialisation include moderate pain, haematoma formation, prolonged healing, and dyspareunia due to scarring.[1]Pundir J, Auld BJ. A review of the management of diseases of the Bartholin's gland. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;28(2):161-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18393010?tool=bestpractice.com
[18]Omole F, Kelsey RC, Phillips K, et al. Bartholin duct cyst and gland abscess: office management. Am Fam Physician. 2019 Jun 15;99(12):760-6.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0615/p760.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31194482?tool=bestpractice.com
The recurrence rate is between 2% and 25%.[1]Pundir J, Auld BJ. A review of the management of diseases of the Bartholin's gland. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;28(2):161-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18393010?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
Catheter drainage
The Word catheter is a safe, simple, and effective outpatient treatment and is a reasonable alternative to marsupialisation.[17]Haider J, Condous G, Kirk E, et al. The simple outpatient management of Bartholin's abscess using the Word catheter: a preliminary study. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2007 Apr;47(2):137-40.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17355304?tool=bestpractice.com
The incision for the catheter should be made with a number 11 scalpel blade and placed just exterior to the hymen ring, within the introitus in the region of the normal duct opening. If the cyst is too deep, placing the catheter is difficult and may not be possible. Clinical use is limited by availability and the catheter's tendency to dislodge.[32]Kushnir VA, Mosquera C. Novel technique for management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. J Emerg Med. 2009 May;36(4):388-90.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19038518?tool=bestpractice.com
The catheter is the size of a 10F Foley catheter with a 2 to 3 cm stem. A sealed stopper is attached at one end and a 5-mL capacity latex inflatable balloon at the other.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9. The catheter should be left in place for 4 to 6 weeks to allow epithelialisation of a tract.[2]Wilkinson EJ, Stone IK. Atlas of vulvar disease. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1995:11-13.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9. Continuous pain or discomfort 24 hours after insertion indicates that the bulb is too large. This can be easily corrected by withdrawing some of the fluid in the bulb.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Insertion of a Word catheter to treat a Bartholin’s cyst. The site is cleaned and anaesthetised, and then a small stab incision (3 to 4 mm) is made into the cyst/abscess cavity (parallel to the hymen ring). The Word catheter is introduced into the cyst/abscess cavity after the contents have drained. The balloon is filled with sterile saline and a suture is tied around the catheter to prevent leaking or deflation. The catheter end is then tucked into the vagina.From the personal collection of Colleen Kennedy Stockdale; used with permission [Citation ends].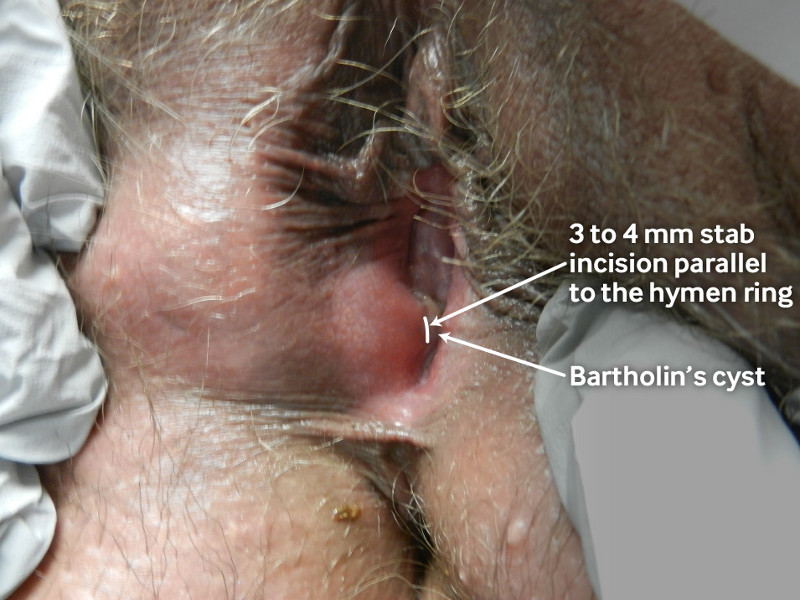
One study looked at quality of life and sexual activity of 30 women with Bartholin's cyst or abscess during treatment with a Word catheter, and found that discomfort and pain during sexual activity decreased significantly from initial presentation to end of treatment.[33]Reif P, Elsayed H, Ulrich D, et al. Quality of life and sexual activity during treatment of Bartholin's cyst or abscess with a Word catheter. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2015 Jul;190:76-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25800788?tool=bestpractice.com
While this is currently the only study to address quality of life and sexual activity during treatment of Bartholin's cyst, the findings are limited by the methodology, including lack of a control group.
Another trial reported similar recurrence rates among women with Bartholin's gland abscess or recurrent cyst who were randomised to treatment with a Word catheter or marsupialisation (12% vs. 10%, respectively within 1 year of treatment, P = 0.70).[34]Kroese JA, van der Velde M, Morssink LP, et al. Word catheter and marsupialisation in women with a cyst or abscess of the Bartholin gland (WoMan-trial): a randomised clinical trial. BJOG. 2017 Jan;124(2):243-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27640367?tool=bestpractice.com
Treatment with a Word catheter was associated with less pain during the 24-hour post-procedural period, and reduced time from diagnosis to intervention.[34]Kroese JA, van der Velde M, Morssink LP, et al. Word catheter and marsupialisation in women with a cyst or abscess of the Bartholin gland (WoMan-trial): a randomised clinical trial. BJOG. 2017 Jan;124(2):243-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27640367?tool=bestpractice.com
A Jacobi ring catheter creates 2 drainage tracts rather than 1 and is thought to be as effective as a Word catheter.[35]Gennis P, Li SF, Provataris J, et al. Jacobi ring catheter treatment of Bartholin's abscesses. Am J Emerg Med. 2005 May;23(3):414-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15915435?tool=bestpractice.com
A similar technique has been described using a small ring catheter made from butterfly Vacutainer tubing. A piece of Vicryl suture is threaded through the lumen, and the tubing is pulled through 2 small stab incisions in the cyst cavity and tied to create a loop.[32]Kushnir VA, Mosquera C. Novel technique for management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. J Emerg Med. 2009 May;36(4):388-90.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19038518?tool=bestpractice.com
Excision
Excision of the cyst duct or gland was standard primary treatment of a Bartholin's cyst until the late 1960s.[1]Pundir J, Auld BJ. A review of the management of diseases of the Bartholin's gland. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;28(2):161-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18393010?tool=bestpractice.com
It is no longer the preferred treatment for primary surgery but may be required for recurrent cysts. Despite this, a 2019 observational study in French university hospitals found that gland excision was the most commonly used treatment for Bartholin's cysts (68.5%), followed by marsupialisation (22.5%).[9]Cardaillac C, Dochez V, Gueudry P, et al. Surgical management of Bartholin cysts and abscesses in French university hospitals. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2019 Oct;48(8):631-5.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jogoh.2019.03.022
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30936026?tool=bestpractice.com
The absence of a Bartholin's gland may lead to dryness of the vulva, with severe itching, burning, and dyspareunia.[10]Azzan BB. Bartholin's cyst and abscess: a review of treatment of 53 cases. Br J Clin Pract. 1978 Apr;32(4):101-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/666961?tool=bestpractice.com
[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Jacobson P. Marsupialization of vulvovaginal (Bartholin) cysts: report of 140 patients with 152 cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1960 Jan;79:73-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14406421?tool=bestpractice.com
[36]Heah J. Methods of treatment for cysts and abscesses of Bartholin's gland. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1988 Apr;95(4):321-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3382606?tool=bestpractice.com
Excision should be performed by an experienced gynaecological surgeon under general anaesthesia, because of the possibility of excessive bleeding from the underlying venous plexus.[1]Pundir J, Auld BJ. A review of the management of diseases of the Bartholin's gland. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;28(2):161-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18393010?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
[16]Ruch RM, Clayton EM Jr. Bartholin cystectomy: paraffin technique. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1958 May;75(5):1055-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13520828?tool=bestpractice.com
[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
Excision can be difficult if multiple previous attempts have been made to drain a cyst or abscess and adhesions have formed. It should not be attempted in the presence of active infection.[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
Liquid paraffin may aid dissection.[16]Ruch RM, Clayton EM Jr. Bartholin cystectomy: paraffin technique. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1958 May;75(5):1055-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13520828?tool=bestpractice.com
Complications of excision include haemorrhage, haematoma formation, cellulitis, sepsis, damage to the rectum, cosmetic disfigurement, and formation of scar tissue.[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
[16]Ruch RM, Clayton EM Jr. Bartholin cystectomy: paraffin technique. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1958 May;75(5):1055-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13520828?tool=bestpractice.com
[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
[22]Cho JY, Ahn MO, Cha KS. Window operation: an alternative treatment method for Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;76(5 Pt 1):886-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2216242?tool=bestpractice.com
Silver nitrate cauterisation
Silver nitrate is a simple, cost-effective germicide and a chemical sclerosing agent. Its use has been described in the outpatient treatment of both cysts and abscesses.[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Yüce J, Zeyneloglu HB, Bükülmez O, et al. Outpatient management of Bartholin gland abscesses and cysts with silver nitrate. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994 Feb;34(1):93-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8053887?tool=bestpractice.com
Benefits of silver nitrate application include low rate of early and late morbidity, low recurrence rate, and avoiding sutures.[37]Yüce J, Zeyneloglu HB, Bükülmez O, et al. Outpatient management of Bartholin gland abscesses and cysts with silver nitrate. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994 Feb;34(1):93-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8053887?tool=bestpractice.com
A prospective randomised controlled trial found that using silver nitrate and marsupialisation were equally effective, with less scar formation noted with the use of silver nitrate.[38]Ozdegirmenci O, Kayikcioglu F, Haberal A. Prospective randomized study of marsupialization versus silver nitrate application in the management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009 Mar-Apr;16(2):149-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19598336?tool=bestpractice.com
Complications include chemical burns of the labial or surrounding mucosa, labial oedema, haemorrhagic or purulent discharge, and cyst recurrence.[12]Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The Bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004 Jul;8(3):195-204.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874863?tool=bestpractice.com
Alcohol sclerotherapy
Compared with aspiration, instillation of alcohol for sclerotherapy reduced treatment time, with a low recurrence rate.[21]Cobellis PL, Stradella L, De Lucia E, et al. Alcohol sclerotherapy: a new method for Bartholin gland cyst treatment. Minerva Ginecol. 2006 Jun;58(3):245-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16783297?tool=bestpractice.com
Complete evacuation of the injected alcohol is essential to avoid necrosis of the cyst wall. Compared with silver nitrate, alcohol sclerotherapy was as effective, with fewer complications and a faster healing time. There were no recurrences at 24-month follow-up.
Bartholin's abscess
If an abscess points and ruptures spontaneously, conservative management with regular sitz baths, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and analgesia is usually all that is required.[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
Small abscesses can be treated with local application of warm, wet dressings or regular sitz baths. This promotes spontaneous drainage of the abscess or development to a stage suitable for incision and drainage.[6]Kaufman RH, Faro S, Brown D. Benign diseases of the vulva and vagina. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2005:240-9.[19]Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. Am Fam Physician. 1998 Apr 1;57(7):1611-6, 1619-20.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/1998/0401/p1611.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9556648?tool=bestpractice.com
Abscess recurs after incision and drainage in up to 15% of cases. Occasionally, early treatment of infection with broad-spectrum antibiotics prevents abscess formation. One 2019 observational study in French university hospitals found that incision and drainage was the most commonly used treatment for Bartholin's abscesses (87%), followed by marsupialisation (13%).[9]Cardaillac C, Dochez V, Gueudry P, et al. Surgical management of Bartholin cysts and abscesses in French university hospitals. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2019 Oct;48(8):631-5.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jogoh.2019.03.022
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30936026?tool=bestpractice.com
After drainage (either spontaneous or surgical), broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage is recommended, and a catheter may be considered. Packing the cavity or leaving a catheter in situ allows a drainage tract to form and may reduce the risk of recurrence.[32]Kushnir VA, Mosquera C. Novel technique for management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses. J Emerg Med. 2009 May;36(4):388-90.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19038518?tool=bestpractice.com
Definitive surgical methods are preferably deferred until active infection and inflammation have resolved. There is a lack of evidence to support a particular management strategy, and abscesses may recur.[24]Illingworth B, Stocking K, Showell M, et al. Evaluation of treatments for Bartholin's cyst or abscess: a systematic review. BJOG. 2020 May;127(6):671-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31876985?tool=bestpractice.com

