History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
vulval/perineal mass
Classically a medially protruding cystic structure at the inferior aspect of the labia majora in the 5 or 7 o'clock position. It is crossed by the labium minus. Occasionally, cysts spread into the labium majus.[2][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bartholin's cystFrom the personal collection of Colleen Kennedy Stockdale [Citation ends].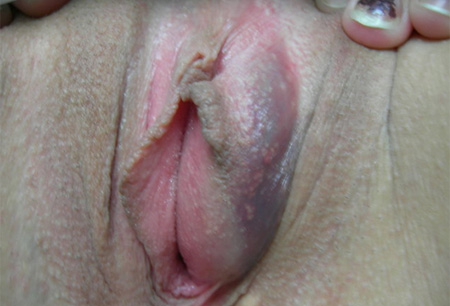
vulval pressure or fullness
Cysts may create a pressure phenomenon at the introitus.[2] While small cysts may be asymptomatic, women note the presence of fullness or pressure with increasing size.
pain during sitting or walking
Larger cysts are more likely to cause discomfort, and pain may be noted when sitting or walking. Pain can be particularly severe with abscess formation.[18]
Other diagnostic factors
common
fever
About 25% of women with abscess have fever.[15]
dyspareunia
With increasing cyst size, women note increasing symptoms. Larger cysts protrude medially, obscuring the introitus, and this may result in painful sexual activity.[2]
vulval erythema and induration
The most severely symptomatic patients present with evidence of infection or abscess formation.
uncommon
spontaneous rupture
Abscesses develop rapidly (within 2 to 3 days) and tend to rupture spontaneously.[6] Evidence of drainage and relief of pain suggests that spontaneous rupture has occurred.
Risk factors
strong
woman of reproductive age
previous Bartholin's cyst/abscess
A risk factor especially if the initial treatment was incomplete (e.g., if a Word catheter dislodges before complete epithelialisation). Repetitive procedures may also result in further duct orifice narrowing and scarring, making recurrence more likely.
sexual activity
Cyst size depends on accumulation of gland secretions, and is exemplified by rapid enlargement during sexual activity and shrinkage or stability of cyst size in women with diminished sexual activity.
weak
direct trauma or surgery
Rarely, cyst or abscess may occur after episiotomy, trauma, or vulvovaginal surgery.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer