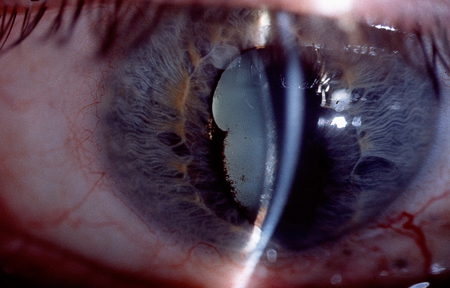
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- pain (anterior uveitis)
- decreased vision
- synechiae
- flare
- keratic precipitates
Other diagnostic factors
- tearing
- photophobia
- floaters
- eye redness without discharge
- constricted or non-reactive pupil
- decreased intra-ocular pressure
- retinal exudates and oedema, optic nerve oedema
- retinal vascular sheathing
- macular oedema
- optic disc swelling
- retinal haemorrhages
- ciliary flush
- corneal oedema
- cataract
Risk factors
- inflammatory diseases of the joints, bowel, or skin
- human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B27 positive
- ocular trauma
- age 20-60 years
Diagnostic investigations
Investigations to consider
- visual field testing
- optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- fluorescein angiography
- FBC
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- CRP
- fluorescent treponemal antibody (FTA-ABS), Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL), and rapid plasma reagin (RPR)
- serum ACE
- antinuclear antibodies (ANAs)
- HLA-B27
- Lyme titre
- purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test
- cytoplasmic anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (c-ANCA)
- perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (p-ANCA)
- antidouble-stranded DNA antibody (anti-dsDNA)
- rheumatoid factor
- anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies
- Bartonella henselae titre
- toxoplasma serological titre
- other HLA antigens
- biochemistry screen
- chest x-ray
- real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for ocular infectious disease
- diagnostic vitrectomy biopsy
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
John J. Huang, MD
President
Connecticut Uveitis Foundation
Associate Clinical Professor
Yale University
New Haven
New England Retina Associates
Hamden
CT
Disclosures
JJH declares that he has no competing interests.
Maxwell Elia, MD
Uveitis and Retina Specialist
Medical Eye Center of New Hampshire
Manchester
NH
Disclosures
ME declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr John J. Huang and Dr Maxwell Elia would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Richard Gale, Dr Zsolt Varga, Dr Victor L. Perez, and Dr Carlos A. Medina, the previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
RG, ZV, VLP, and CAM declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Jessica Ackert, MD
Assistant Professor
Ophthalmology
Mount Sinai Hospital
New York
NY
Disclosures
JA declares that she has no competing interests.
Anthony J. Hall, MD, FRANZCO
Director of Ophthalmology
Alfred Hospital
Melbourne
Australia
Disclosures
AJH has been reimbursed by Novartis, the manufacturer of Lucentis, for lecture fees. AJH's employer, the Alfred Hospital, has received research funding from Novartis, the manufacturer of Lucentis, and from Bayer, the manufacturer of Eylea.
Daniel A. Johnson, MD
Chairman
Department of Ophthalmology
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio
San Antonio
TX
Disclosures
DAJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Deschenes J, Murray PI, Rao NA, et al; International Uveitis Study Group. International Uveitis Study Group (IUSG): clinical classification of uveitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2008 Jan-Feb;16(1):1-2. Abstract
Jabs DA, Nussenblatt RD, Rosenbaum JT; Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group. Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data: results of the First International Workshop. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005 Sep;140(3):509-16. Abstract
Foster CS, Kothari S, Anesi SD, et al. The Ocular Immunology and Uveitis Foundation preferred practice patterns of uveitis management. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan-Feb;61(1):1-17. Abstract
Dick AD, Rosenbaum JT, Al-Dhibi HA, et al. Guidance on noncorticosteroid systemic immunomodulatory therapy in noninfectious uveitis: Fundamentals Of Care for UveitiS (FOCUS) Initiative. Ophthalmology. 2018 May;125(5):757-73.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available here.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer