Differentials
Common
Septic non-gonococcal arthritis
History
acute onset, severe pain, fever, malaise; patients at risk include intravenous drug users, those with recent bacteraemia, immunocompromised patients (e.g., those with HIV disease, on immunosuppressive agents, or with other immunocompromised states), patients with sickle cell disease or other hemoglobinopathies, patients with rheumatoid arthritis or those with prosthetic joints, those who have had recent arthroscopy or arthrocentesis, patients with a cardiovascular implantable electronic device
Exam
joint is warm and swollen, with severely limited range of motion
1st investigation
- needle joint aspiration:
identification and recovery of pyogenic bacteria on microscopic examination (Gram stain) of synovial fluid and culture; WBC count in synovial fluid is often >100 x 10⁹/L (>100,000/mm³) (polymorphonuclear leukocytes >75%)
More
Other investigations
- blood cultures:
growth of causative organism - positive in 50% of cases[108]
- ultrasound-guided joint aspiration:
WBC count in synovial fluid is often >100 x 10⁹/L (>100,000/mm³) (polymorphonuclear leukocytes >75%)
- CT-guided joint aspiration:
WBC count in synovial fluid is often >100 x 10⁹/L (>100,000/mm³) (polymorphonuclear leukocytes >75%)
Gonococcal arthritis
History
fever, chills, malaise, involvement of predominantly lower-extremity joints (knees, ankles), urethritis
Exam
mono- or oligoarthritis, tenosynovitis (wrists, fingers, ankles, toes), pustular or vesiculo-pustular skin lesions
1st investigation
- needle joint aspiration:
identification and recovery of Neisseria gonorrhoeae from synovial fluid (extremely uncommon); microscopic examination and culture of synovial fluid in Thayer-Martin medium
More - blood cultures:
recovery of N gonorrhoeae
More - culture of skin lesion aspirate; urethral, cervical, rectal, or oropharyngeal cultures:
recovery of N gonorrhoeae
- urethral discharge Gram stain:
gram-negative diplococci
Other investigations
Rheumatoid arthritis
History
pain, swelling, and morning stiffness for at least 30-60 minutes
Exam
swelling and tenderness of metacarpo-phalangeal (MCP) and proximal inter-phalangeal (PIP) joints; symmetrical polyarthritis of small and large joints; rheumatoid nodules; later characteristic deformities include subluxations at wrist and MCP joints, ulnar deviation of fingers, swan-neck and boutonniere deformities of fingers, Z-deformities of thumbs
1st investigation
- serum rheumatoid factor (RF):
positive
More - serum antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP):
positive
More - ESR:
elevated in untreated cases
- serum CRP:
elevated in untreated cases
- hand x-ray:
soft tissue swelling, periarticular osteopenia, joint space narrowing, erosions of cartilage and bone around metacarpo-phalangeal (MCP) and proximal inter-phalangeal (PIP) joints
More
Other investigations
- ultrasound scan:
synovial proliferation; joint effusion; joint erosion; increased power Doppler signal (increased vascularity in synovitis)[102][109]
- hand MRI scan:
bone oedema; synovial enhancement; bone erosion
- multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) score:
predicts radiographic joint damage at baseline and during disease course; low disease activity (<30), moderate disease activity (30-44), and high disease activity (>44)[110][111]
Gout
History
acute onset, aged <50 years, severe joint pain
Exam
redness, warmth, swelling, and exquisite tenderness of the affected joint(s)
1st investigation
Other investigations
- ultrasound scan:
synovial proliferation; joint effusion; joint erosion; increased power Doppler signal (increased vascularity in synovitis); characteristic 'double contour' sign, indicating chronic urate frosting on the surface of articular cartilage; intra-articular and extra-articular (tendons, ligaments, and soft tissues) tophi ('wet sugar clumps' or 'snow storm' appearance)[86][112][113]
- dual energy CT (DECT) scan:
distinct attenuation of MSU deposits colour-coded in green[86][114]
Pseudogout
History
acute onset; mono- or oligoarthralgia; may be preceded by trauma, surgery, intercurrent illness
Exam
knee most often affected; also wrists, metacarpo-phalangeal joints, shoulders, elbows; joints are warm, swollen, often with effusions
1st investigation
- needle joint aspiration:
WBC 15 x 10⁹/L to 30 x 10⁹/L (15,000-30,000/mm³), 90% neutrophils
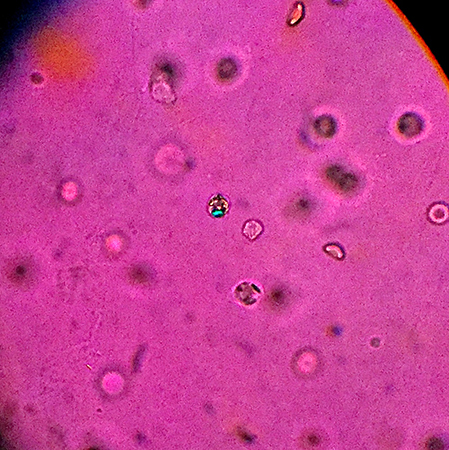
- compensated polarised light microscopy of synovial fluid:
weakly positively birefringent crystals of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD), crystals phagocytosed within polymorphonuclear leukocytes
More - x-ray of joint:
chondrocalcinosis (calcification in fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage)
More
Other investigations
- ultrasound scan:
synovial proliferation; joint effusion; joint erosion; increased power Doppler signal (increased vascularity in synovitis); characteristic 'pseudo double contour' sign, indicating chronic calcium pyrophosphate deposition within the substance of the articular cartilage; hyperechoic sparkling spots within articular fibrocartilage or mobile intra-articular hyperechoic deposits also suggest calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease[115]
Psoriatic arthritis
History
joint pain and swelling, morning stiffness lasting >30 minutes
Exam
asymmetrical small and/or large joint oligo- or polyarthritis (clinical synovitis), nail pitting, and hyperkeratosis, onycholysis
1st investigation
- x-ray of hand, foot:
acro-osteolysis, fluffy periostitis, and new bone formation at the site of entheses; gross destruction of isolated joints, 'pencil-in-cup' appearance (arthritis mutilans), both joint lysis and ankylosis[121]
Other investigations
- ultrasound scan:
proliferative synovitis shows as joint space widening with clusters of soft echoes (bushy and villous appearance) and/or homogeneous synovial thickening; bone erosion shows as intra-articular discontinuity of the bone surface visible in two perpendicular planes[121][122][123]
- MRI:
subchondral bone oedema is characteristically observed[121]
More
Uncommon
Indolent infections
History
chronic infection, joint pain and swelling
Exam
joint swelling and tenderness, usually monoarthropathy
1st investigation
- joint aspiration:
may show acid-fast bacillus with special preparation and stains, fungal elements
More - blood culture:
growth of causative organism
Other investigations
- synovial biopsy:
identification of organism (on special stains and culture); caseating or non-caseating granulomas may be seen
Parvoviral syndrome
History
acute onset, pain in multiple joints, flu-like prodrome, rash
Exam
arthralgia in symmetrical rheumatoid arthritis-like distribution, erythematous macular rash
1st investigation
- serum IgM and IgG antibodies:
positive
More
Lyme disease
History
intermittent knee pain and swelling, antecedent tick bite, rash
Exam
bull's-eye rash (erythema migrans), central clearing, vesicles; monoarthritis involving knee, shoulder, ankle, elbow, temporomandibular joint, wrist
1st investigation
- sensitive enzyme immunoassay or immunofluorescence assay:
positive for Borrelia antibodies. A positive result should be confirmed by a Western blot immunoassay or a second sensitive enzyme immunoassay[87]
Other investigations
- Western blot testing for Borrelia burgdorferi:
positive (confirmatory)
More
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (oligo-articular type)
History
more likely to be female, joint pain >6 weeks' duration, seen in childhood
Exam
≤4 joints, rash, enthesitis, uveitis
1st investigation
- FBC:
normal or reduced haemoglobin and elevated platelets
- ESR:
normal or elevated
- CRP:
normal or elevated
- serum antinuclear antibodies (ANA):
positive or negative
Other investigations
- x-ray of affected joint:
soft-tissue swelling; joint-space narrowing or erosions
Acute rheumatic fever (ARF)
History
latent period following sore throat; adult or child; joints affected serially in quick succession
Exam
joint pain and swelling; knees and ankles are usually involved first; subcutaneous nodules, rash (erythema marginatum)
1st investigation
- throat culture for group A beta-haemolytic streptococci or rapid streptococcal antigen test:
positive for group A beta-haemolytic Streptococcus
- serum antistreptolysin O (ASO):
elevated or rising titre
More - x-ray of chest:
cardiomegaly
Other investigations
- ECG:
heart block, prolonged PR interval
- echocardiography:
cardiomegaly[80]
- serum anti-DNAse B, antistreptokinase, and antihyaluronidase:
positive
Sarcoidosis
History
joint pain in knees or ankles
Exam
warm, swollen, and tender joints; tendinitis, enthesopathy (inflammation of the entheses, the location where a bone has an insertion to a tendon or a ligament), dactylitis (sausage digit); erythema nodosum
1st investigation
- serum ACE:
level elevated
- x-ray of chest:
bilateral hilar adenopathy, right paratracheal adenopathy, pulmonary reticular opacities
More
Other investigations
- PET scan:
may reveal occult sarcoid lesions
- synovial biopsy:
may be non-specific, or show typical sarcoid granulomata
Undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy
History
oligoarticular involving large joints or polyarticular inflammatory joint involvement, inflammatory back pain
Exam
synovitis, spine involvement, enthesitis: dactylitis or tenderness at entheseal insertions such as the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia insertions; extra-articular manifestations: uveitis, psoriasis, keratoderma blennorrhagicum, erythema nodosum
1st investigation
- x-ray of pelvis:
sacroiliac joint irregularity (especially lower part), widening, erosions, and ankylosis at a later stage
More
Other investigations
- plain x-rays of affected joints:
erosions, periostitis may be seen
- sonography:
synovitis, erosions, and enthesitis
- MRI scan of pelvis:
evidence of sacroiliitis (bone oedema, erosions)[118]
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
History
commonly females (typical onset at age 20-30 years), polyarthralgia, with minimal swelling
Exam
moderate tenderness and stiffness with joint manipulation, malar rash, discoid rash, alopecia, oral ulcers
1st investigation
Other investigations
- x-ray of hand:
ulnar deviation of the MCP joints, swan neck deformities, but no erosions (Jaccoud's arthropathy)
- urinalysis:
presence of blood and protein (in lupus nephritis)
- urine microscopy:
RBC or mixed casts, dysmorphic RBCs (in lupus nephritis)
Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD)
History
daily fever ≥39°C (≥102°F); sore throat, joint pain and swelling
Exam
non-pruritic, macular or maculo-papular truncal rash of salmon pink colour with Koebner's phenomenon; pericardial rub
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
WBC ≥100 x 10⁹/L (10,000/mm³), with at least 80% neutrophils; thrombocytosis, anaemia
- serum albumin:
hypoalbuminaemia
- serum hepatic enzymes:
often there is elevation in aspartate and alanine aminotransferase and lactate dehydrogenase
- serum ferritin:
>6741 picomol/L (>3000 nanograms/mL [normal 40-200 nanograms/mL])
More - x-ray of wrist:
non-erosive narrowing of carpo-metacarpal and inter-carpal joint spaces of wrist
More - x-ray of chest:
pleural effusion and/or transient pulmonary infiltrate
More
Other investigations
- bone marrow biopsy:
numerous, well-differentiated macrophages (histiocytes) that are involved in phagocytosis of haematopoietic elements
More
Reactive arthritis
History
lag period between infection and onset of arthralgia; dysuria, pelvic pain
Exam
asymmetrical mono- or oligoarthritis, most commonly in lower extremities; dactylitis, conjunctivitis, anterior uveitis, oral ulcers, keratoderma blennorrhagica, circinate balanitis
1st investigation
Other investigations
- HLA-B27 testing:
positive
More
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS)
History
low back pain for >3 months, stiffness, improves with exercise but not with rest
Exam
stiffness of spine with kyphosis, limited range of movement of lower spine, tenderness on palpation; extra-articular signs may be present, including enthesitis, uveitis, dactylitis, psoriasis, crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis
1st investigation
- x-ray of sacroiliac (SI) joint:
SI joint irregularity, widening, erosions, sclerosis; ankylosis in advanced disease, with complete obliteration of SI joint space
Other investigations
- MRI of sacroiliac (SI) joint:
increased T2-weighted signal from bone and bone marrow adjacent to SI joint (bone marrow oedema)
More - HLA-B27 testing:
positive
More - x-ray of lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spine:
squaring of vertebral bodies, bridging syndesmophytes, ankylosis of facet joints and calcification of anterior longitudinal ligament, anterior atlantoaxial (C1-C2) subluxation
Osteoarthritis
History
joint pain, age commonly >50 years, functional difficulties, stiffness
Exam
hand, hip, and knee involvement; bony deformities particularly in the hands; tenderness; limited range of motion; bony malalignment is common, particularly in the knee
1st investigation
- CRP:
normal
- ESR:
normal
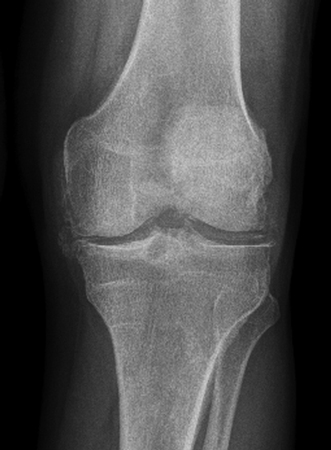
- x-ray of affected joint:
joint-space narrowing, new bone formation (osteophytes), subchondral sclerosis, cysts; in erosive osteoarthritis: erosions, gull-wing deformity; saw-tooth deformity; ankylosis
Other investigations
Trauma
History
prior trauma, joint pain and swelling
Exam
joint swelling, ecchymosis, tenderness with manipulation of extremity, restricted and painful range of motion
1st investigation
- x-ray of affected joint:
fracture through joint line, subluxation, soft-tissue swelling
- needle aspiration of joint:
haemorrhagic effusion (red, pink, or brown)
- MRI of affected joint:
may demonstrate cartilage injury, ligament rupture
Other investigations
- aspiration of joint:
lipohaemarthrosis (presence of lipid globules and blood)
- CT of affected joint:
may show bony and/or soft-tissue injury
- MRI of affected joint:
may show bony and/or soft-tissue injury; better visualisation of soft tissues than CT
Non-traumatic haemarthrosis
History
joint pain; may be history of underlying bleeding disorder, sickle cell anaemia, pigmented villonodular synovitis, synovioma, ruptured aneurysm, AV fistula, haemangioma, Charcot's joint, anticoagulant therapy, scurvy
Exam
swollen, warm, very painful joint; restricted and painful range of motion
1st investigation
- needle aspiration of joint:
haemorrhagic effusion (red, pink, or brown)
Other investigations
- arthroscopy and synovial biopsy:
intra-articular abnormality
More
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
History
painful and swollen joints (wrists, ankles, knees), distal long bone pain
Exam
clubbing, roughening of skin, swollen joints, pachydermoperiostosis
1st investigation
- FBC:
may show anaemia
- x-ray of affected joint:
periosteal reaction; hypervascularisation of digits
Other investigations
- isotope bone scan:
increased uptake in areas of periosteal reaction
Intra-articular metastatic cancer
History
joint pain and swelling >6 weeks, known malignancy
Exam
joint swelling, warmth, and tenderness; typically monoarthritis
1st investigation
- joint fluid cytology:
positive
Other investigations
- synovial biopsy:
pathology of underlying malignancy
Synovial sarcoma
History
aged 30-40 years, slow growing mass in lower extremities; may have pain and numbness (if nerve involvement); in advanced disease: weight loss, fatigue, and anorexia
Exam
joint swelling in lower extremities
1st investigation
- joint fluid cytology:
positive
Other investigations
- synovial biopsy:
synovial sarcoma
Arbovirus infections (e.g., chikungunya)
History
history of travel to endemic areas; fever, rash, myalgias, headache, and arthralgias 2-10 days after mosquito bite (typically Aedes albopictus)
Exam
fever and rash at early stage; arthritis resembling rheumatoid arthritis involving small joints of hands, feet, wrists, and ankles
1st investigation
Other investigations
- antibody tests:
positive
More
Inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease)
History
abdominal pain, bloody diarrhoea, tenesmus, mucus in stool, peripheral large joint oligoarthritis, inflammatory back pain (sacroiliitis) may be present, enthesitis, dactylitis
Exam
pallor, abdominal tenderness and distension, perianal and abdominal wall fistulas; peripheral large joint clinical synovitis (knees, ankles); clinical evidence of sacroiliitis joint pain, enthesitis, dactylitis
1st investigation
- colonic biopsy and/or small bowel biopsy:
continuous distal disease, mucin depletion, basal plasmacytosis, diffuse mucosal atrophy, absence of granulomata, and anal sparing (ulcerative colitis); mucosal bowel biopsies demonstrate transmural involvement with non-caseating granulomas (Crohn's disease)
Other investigations
- ESR:
elevated
- CRP:
elevated
- FBC:
reduced haemoglobin and elevated platelets
- faecal calprotectin:
may be elevated
More
Coeliac disease
History
weight loss, fatigue, bloating, failure to thrive, diarrhoea, fatty stools, blistering itchy rash
Exam
low BMI, pallor, abdominal distension; blistering rash over elbows, knees, sacral area, and buttocks (dermatitis herpetiformis)
1st investigation
- serum anti-transglutaminase, anti-endomysial, and anti-gliadin antibodies:
positive
Other investigations
- small bowel (duodenal) biopsy:
subtotal villous atrophy, reversible with gluten-free diet
More
Whipple's disease
History
arthralgias, oligo- or polyarthritis, hyperpigmentation, weight loss, abdominal pain, fatigue, bloating, failure to thrive, diarrhoea, neurological manifestations
Exam
low BMI, pallor, abdominal distension, hyperpigmentation, lymphadenopathy, joint tenderness with or without frank clinical synovitis in multiple joints
1st investigation
- upper endoscopy with duodenal biopsy:
duodenal mucosa may appear macroscopically pale yellow with clumsy and dilated villi and ectatic lymph vessels
More
Other investigations
- Tropheryma whipplei PCR on blood:
positive
Bowel-associated dermatosis arthritis syndrome
History
Exam
1st investigation
- ESR and CRP:
elevated
- rheumatoid factor (RF) and antinuclear antibodies (ANA):
usually negative
Other investigations
- x-rays:
may rarely show erosive arthritis
- skin biopsy:
evidence of neutrophilic dermatosis
- synovial fluid analysis:
mild to moderate inflammation (with lymphocyte or neutrophil predominance)
Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome
Drug-induced
History
history of exposure to relevant drugs: procainamide, hydralazine, minocycline, isoniazid, tumour necrosis factor inhibitors, etc. (drug-induced lupus); various oral and parenteral pharmacological agents, including plasma-derived products and biologicals (serum sickness-like reaction); aromatase inhibitors, clopidogrel, quinolone antibiotics, statins, and dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors (arthralgia, inflammatory arthritis, and tendinitis); immune checkpoint inhibitors (inflammatory arthritis and tenosynovitis)
Exam
rash, fever, urticaria (serum sickness); other features of lupus (if drug-induced lupus); tendinitis and tendon rupture (quinolone antibiotics); inflammatory arthritis and tenosynovitis (immune checkpoint inhibitors)
1st investigation
- ANA:
positive in drug-induced lupus
- anti-histone antibodies:
positive in drug-induced lupus
- double-stranded DNA:
negative
More
Other investigations
Remitting seronegative symmetrical synovitis with pitting oedema (RS3PE) syndrome
History
acute-onset polyarthritis; males ≥50 years of age
Exam
clinical synovitis; significant pitting oedema of the dorsal surface of hands and feet
1st investigation
- ESR:
elevated
- CRP:
elevated
- serum rheumatoid factor (RF):
negative
Other investigations
- x-ray of affected joint:
usually no erosions
Ebola disease
History
history of residence in or travel to an Ebola-endemic area in the 21 days before onset of illness; secondary exposure (human-to-human or primate-to-human exposure)
Exam
fever, pharyngitis, myalgia, severe headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea, or unexplained bleeding or bruising; maculopapular rash on trunk (may be present around day 5 of infection); bilateral conjunctival infection; bleeding from intravenous puncture sites and mucous membranes
1st investigation
- reverse transcriptase (RT)- PCR to detect viral DNA:
positive
More
Other investigations
- antigen-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA):
positive for Ebola virus RNA
More - FBC:
thrombocytopenia; marked lymphopenia; decreased haemoglobin (if bleeding manifestations)
- IgM and IgG antibodies:
positive
Diffuse tenosynovial giant cell tumour (formerly, diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis)
History
twice as common in males; age 20-50 years; sudden onset; entire synovium affected; typically occurs in large joints such as the knee (80% of cases) or hip
Exam
unexplained joint swelling (effusion), pain, warmth, and tenderness; decreased motion; increased pain and locking of the joint occur with disease progression
1st investigation
- MRI scan:
nodular intra-articular masses that demonstrate low signal intensity on T1-, T2-, and proton-density sequences
Other investigations
- plain x-ray:
detects calcifications
- CT:
hyperdense soft-tissue mass in the joint or tendon sheath
- histopathology:
nodules and/or villi with abundant (pigmented) hemosiderin-laden macrophages
Localised tenosynovial giant cell tumour (formerly, localised pigmented villonodular synovitis)
History
predominantly occurs in females; age 20-50 years; sudden onset; typically occurs in small joints such as the hands and feet
Exam
slow-growing mass; painless, becoming symptomatic
1st investigation
- MRI scan:
nodular intra-articular masses that demonstrate low signal intensity on T1-, T2-, and proton-density sequences
Other investigations
- plain x-ray:
detects calcifications
- CT:
hyperdense soft-tissue mass in the joint or tendon sheath
- histopathology:
nodules and/or villi with abundant (pigmented) hemosiderin-laden macrophages
Synovial osteochondromatosis
History
chronic, progressive pain; swelling of the affected joint exacerbated by physical activity; locking of the affected joint can occur
Exam
joint effusion; tenderness; limited range of motion; clicking, grating, or locking (due to intra-articular bodies within the affected joint); grinding and popping; osteochondral nodules (close to the skin) in knee, ankle, or elbow
1st investigation
- CT scan with radiography:
multiple, smooth, oval-shaped calcified masses within the joint space or bursa
Other investigations
- histopathology:
cartilaginous bodies or osteocartilaginous bodies with central ossification, typically spherical
Amyloid arthropathy
History
commonly presents as shoulder pain or carpal tunnel syndrome
Exam
juxta-articular soft-tissue swelling; osteolytic bone lesions (amyloidomas); symptoms commonly bilateral
1st investigation
- synovial biopsy and synovial fluid analysis:
positive on Congo red staining
Other investigations
- x-ray:
demonstrates erosive and destructive arthropathy; osteolytic bone lesions (amyloidomas)
- MRI:
extensive deposition of an abnormal soft tissue that has low or intermediate signal intensity on T1- and T2-weighted images
Fibroblastic rheumatism
History
Exam
multiple erythematous cutaneous nodules; multiple joint swelling, tenderness, and flexion contractures
1st investigation
- skin and synovial biopsy:
fibroblastic proliferation associated with a collagenous stroma
Other investigations
- x-ray of small joints of hands and feet:
demonstrates an erosive arthropathy
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH)
History
progressive painful and deforming arthropathy of hands and feet and more proximal joints; multiple skin nodules.[127]
Exam
tender and swollen MCP, PIP, and DIP joints; multiple firm reddish-brown papules and nodules over the dorsum of the hands and in the fingers, with the classical 'coral beads' appearance around the nailbeds.
1st investigation
Other investigations
- skin and synovial biopsy:
biopsy of cutaneous nodules shows mononuclear histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells 50–100 mm in diametre, with eosinophilic, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) positive cytoplasm, that has a fine granular appearance
- x-ray of small joints of hands and feet:
demonstrates a severe erosive arthropathy affecting wrists, MCP, PIP, and DIP joints
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer