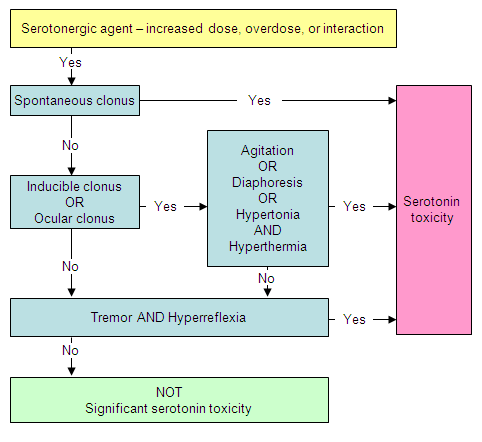
Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria (HSTC)[4]Dunkley EJ, Isbister GK, Sibbritt D, et al. The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria: simple and accurate diagnostic decision rules for serotonin toxicity. QJM. 2003;96:635-642.
http://qjmed.oxfordjournals.org/content/96/9/635.full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12925718?tool=bestpractice.com
A number of clinical diagnostic criteria have been used to diagnose serotonin toxicity. The Sternbach criteria were the first suggested, but they were developed from the literature, did not include some of the most important diagnostic features (e.g., clonus), and included a number of non-specific features.[9]Sternbach H. The serotonin syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148:705-713.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2035713?tool=bestpractice.com
This has led to a number of medications being associated with serotonin toxicity without sufficient evidence: in particular, several antipsychotic drugs.[15]Isbister GK, Downes F, Whyte IM. Olanzapine and serotonin toxicity. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003;57:241-242.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12667176?tool=bestpractice.com
[19]Nisijima K, Yoshino T, Yui K, et al. Potent serotonin (5-HT2A) receptor antagonists completely prevent the development of hyperthermia in an animal model of the 5-HT syndrome. Brain Res. 2001;890:23-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11164765?tool=bestpractice.com
These criteria are generally not used any more.[21]Chiew AL, Buckley NA. The serotonin toxidrome: shortfalls of current diagnostic criteria for related syndromes. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2022 Feb;60(2):143-58.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34806513?tool=bestpractice.com
The best diagnostic criteria, with good sensitivity (84%) and specificity (97%), are the Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria (HSTC).[4]Dunkley EJ, Isbister GK, Sibbritt D, et al. The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria: simple and accurate diagnostic decision rules for serotonin toxicity. QJM. 2003;96:635-642.
http://qjmed.oxfordjournals.org/content/96/9/635.full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12925718?tool=bestpractice.com
These criteria were developed from a large series of overdoses of serotonergic drugs and have now been used in a number of other studies of therapeutic drug use.[5]Taylor JJ, Wilson JW, Estes LL. Linezolid and serotonergic drug interactions: a retrospective survey. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:180-187.
http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/43/2/180.full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16779744?tool=bestpractice.com
[16]Evans RW, Tepper SJ, Shapiro RE, et al. The FDA alert on serotonin syndrome with use of triptans combined with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: American Headache Society position paper. Headache. 2010;50:1089-1099.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01691.x/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20618823?tool=bestpractice.com
These criteria rely on a good focused neurological examination, including assessing tone, clonus, and reflexes.
In the presence of a serotonergic agent, serotonin toxicity exists:
If spontaneous clonus is present OR
If inducible clonus AND agitation or diaphoresis are present OR
If ocular clonus AND agitation or diaphoresis are present OR
If tremor AND hyper-reflexia are present OR
If hypertonia AND pyrexia (temperature >38°C [>100.4°F]) AND ocular clonus or inducible clonus are present.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria (HSTC) algorithmFrom the collection of Dr Geoffrey Isbister [Citation ends].