Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
Patients frequently have a microcytic anaemia.
Result
low Hb, low Hct
ESR
Test
ESR can be variably elevated even without active infection.
Result
may be elevated
CRP
Test
Elevation of ESR and CRP together provide stronger evidence of active infection. Inflammatory markers may be misleading as they tend to rise and fall in relation to chronic inflammatory processes, even in the absence of infection.
Result
may be elevated
faecal calprotectin
Test
Faecal calprotectin levels correlate with colitis severity and can be used to monitor activity.[45]
Result
elevated with colitis
CT chest
Test
Indicated to identify acute infection or to monitor chronic infections.
During active infection, prompt imaging is useful to localise and evaluate the extent of infection.
CT is also useful to monitor chronic lung disease.
Result
variable pulmonary abnormalities including: nodules, ground-glass opacities, focal consolidations, masses, cavities, abscesses, interlobular septal thickening, and emphysematous changes.[55]
CT or ultrasound for active infection
Test
During active infection, prompt imaging is useful to localise and evaluate the extent of infection.
Result
lesions compatible with infection
whole body PET scan with F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
Test
Whole body FDG PET is helpful in differentiating active infectious processes from past infectious or chronic inflammatory lesions.[43]
Result
increased FDG uptake
MRI scan
Test
Useful to investigate certain types of infection (e.g., suspected osteomyelitis or brain infection). Also to exclude neurological involvement with disseminated Aspergillus or Nocardia infection.
MRI can be used to monitor colitis activity.[45]
Result
changes compatible with infection or colitis
colonoscopy
Test
Endoscopy, especially colonoscopy, may be required to evaluate the activity of inflammatory colitis.
Result
macroscopic and histological signs of inflammation
pulmonary function tests
Test
Abnormal lung function tests can point towards chronic lung disease.[36]
Result
abnormal spirometry and gas transfer
nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test
dihydrorhodamine (DHR) 123 test
Test
Uses flow cytometry to detect the conversion of DHR 123 to fluorogenic rhodamine 123 in activated neutrophils.
Sometimes differentiates between X-linked and autosomal recessive forms as well as identifying X-linked carriers.[48][49][50]
Results should be interpreted by experienced individuals.
Results reported as a percentage of cells displaying an oxidative burst as well as the visual appearance of the histogram. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sample DHR histograms. Neutrophils were incubated with dihydrorhodamine 123 (DHR 123) and then activated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). On activation, DHR 123 is oxidised to highly fluorescent rhodamine 123 in normal neutrophils. Pre-activation histograms are shown on the left and post-activation histograms on the right. Block A shows normal response, with a large rightward shift in mean fluorescent intensity. Block B shows a patient with X-linked CGD lacking a detectable oxidative burst. Block C shows the mother of an affected patient with 2 populations of neutrophils, one normal and one with mutated gp91phox. Block D shows the typical pattern observed in patients with autosomal recessive CGD. Patients with autosomal recessive CGD can also rarely display an absence of oxidative burst activity, as shown in Block E.Permission by CCHMC clinical diagnostic immunology lab [Citation ends].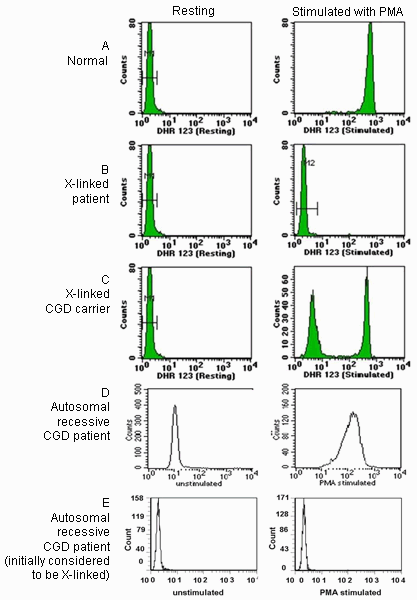
Specific values of the normal range depend on the laboratory performing the test.
In newly diagnosed male patients, testing of the mother should follow.[48]
Result
absent or reduced oxidative burst percentage; abnormal histogram
Investigations to consider
genetic sequencing for genes encoding NADPH oxidase components
Test
Genetic analysis is used to confirm the diagnosis.[51]
Recommended following an abnormal NBT or DHR.
Result
abnormal genetic sequencing consistent with CGD
Western blotting
Test
May be considered following an abnormal NBT or DHR.
Result
absence of one of the NADPH oxidase components
flow cytometric analysis of individual NADPH oxidase components
Test
May be considered following an abnormal NBT or DHR.
Result
absence of one of the NADPH oxidase components
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer