Investigations
1st investigations to order
lymphoscintigram
Test
A highly accurate diagnostic test to identify lymphoedema (96% sensitive and 100% specific).[56]
Radiographical images are taken after Tc99m-labelled antimony, sulfur, or albumin is injected into the dorsal web space of the affected extremity or genitalia. Images are obtained at 45 minutes and 2 hours after injection.[61]
Lymphoscintigraphy evaluates lymphatic function and is often used as the first imaging modality to confirm the diagnosis.[47]
A normal examination shows visualisation of the proximal lymph nodes, normal proximal migration of the radiolabelled protein, and absence of dermal backflow after contrast injection.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lymphoscintigraphy showing dermal back-flow and absent uptake of radiolabelled colloid in lymph nodes of left lower extremity consistent with lymphoedemaFrom the collection of Dr Arin K. Greene [Citation ends].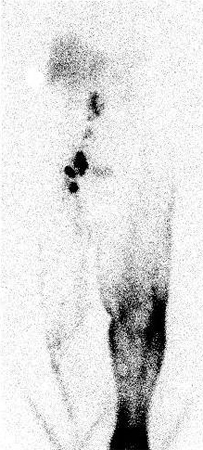
Result
dermal backflow, delayed or absent transport, or lack of visualisation of lymph nodes
Investigations to consider
MRI scan of affected extremity
Test
MRI may help differentiate lipoedema, venous disease, and other vascular anomalies from lymphoedema, and is essential if malignancy is suspected.[3] MRI techniques encompassing MR lymphography (MRL) and MR angiography (MRA) both with and without contrast (peripheral or intranodal) are being increasingly utilised at specialist centres globally, and provide high resolution imaging with no ionising radiation.[47][57][58]
Result
thickened skin; honeycombing of fluid and fibrous tissue above the muscle fascia
CT scan of affected extremity
Test
CT is less useful than MRI because it has inferior soft-tissue resolution and exposes the patient to radiation.[59]
Lymphoscintigraphy combined with single photon emission CT (LAS-SPECT-CT) can produce higher resolution images, and improve spatial localisation.[47]
Result
thickened skin; honeycombing of fluid and fibrous tissue above the muscle fascia
near infrared fluorescence imaging
Test
Uses fluorescent dye (indocyanine green) to visualise lymphatic vessels.[5] Requires equipment that is currently only found in some specialist lymphatic surgical centres. This technique is increasingly being used by lymphatic surgeons to refine assessment of clinical stages and find suitable vessels for lymphatic-venous anastomosis surgery.[1]
Result
fluorescent dye remains in the lymphatic system, allowing real-time visualisation of lymphatic function
lymphangiography
Test
Involves injecting lymphatic channels with radio-opaque contrast dye. Rarely used because of its morbidity (has been associated with lymphangitis [19%] and disease exacerbation [32%]).[18]
May be used to determine the location of a specific anatomical obstruction for preoperative planning of a bypass procedure.[18]
Result
location of a specific anatomical obstruction
blood smear for filariasis
Test
Indicated if history arouses suspicion of filariasis.
Result
presence of microfilariae
genetic testing
Test
May be ordered in patients with primary lymphoedema.
Primary lymphoedema is mostly sporadic; however, approximately 10% to 15% of patients have familial or syndromic lymphoedema.[3]
A causative mutation has been identified in some lymphoedema-associated syndromes: examples include (but are not limited to) Milroy's disease (VEGFR3), lymphoedema-distichiasis syndrome (FOXC2), hypotrichosis-lymphoedema-telangiectasia (SOX18), and Hennekam syndrome (CCBE1).[22][23][24][25][26]
Typically, next-generation sequencing techniques are used to screen blood-derived DNA using gene panels. Whole exome sequencing is another increasingly used option.[2]
Result
presence of mutation: VEGFR3 (Milroy's disease); FOXC2 (lymphoedema-distichiasis syndrome); SOX18 (hypotrichosis-lymphoedema-telangiectasia); CCBE1 (Hennekam syndrome)
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer