Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- presence of polytrauma/multiple injury
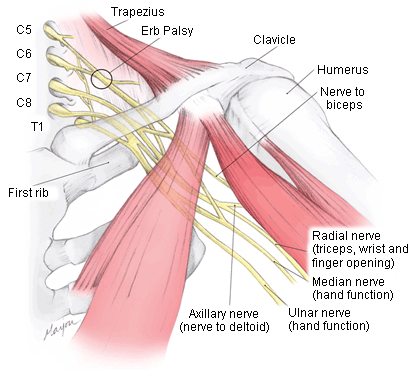
- paralysis of shoulder
- paralysis of bicep
- numbness of radial digits of hand and shoulder
- paralysis of triceps
- paralysis of wrist/finger extensors
- flail/insensate extremity
- absent tendon reflexes
Risk factors
- motor vehicle accident
- neurofibromatosis
- improper positioning during surgery
- age <50 years
- male sex
- Parsonage-Turner syndrome
- tumours (primary and metastatic tumours)
- rib abnormalities
- metabolic disorders
Diagnostic investigations
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Rahul K. Nath, MD

Director
Texas Nerve and Paralysis Institute
Houston
TX
Disclosures
RKN is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Abdelouahed Amrani, MD
Professor
Children's Hospital
Rabat
Morocco
Disclosures
AA declares that he has no competing interests.
S. Raja Sabapathy, MS, MCh, DNB, FRCS, MAMS
Director and Head
Department of Plastic, Hand and Reconstructive Microsurgery and Burns
Ganga Hospital
Coimbatore
India
Disclosures
SRS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Nath RK, Lyons AB, Bietz G. Physiological and clinical advantages of median nerve fascicle transfer to the musculocutaneous nerve following brachial plexus root avulsion injury. J Neurosurg. 2006;105:1-5. Abstract
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: plexopathy. 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available here.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer