Aetiology
Aetiology
The causes of acute red eye can be considered within the following categories:[3]
Adnexal causes
Trichiasis: posterior misdirection of the eyelashes from the normal site of origin [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: TrichiasisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Entropion: inward turning of the eyelid margin [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EntropionPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Ectropion: outward turning of the eyelid margin [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EctropionPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
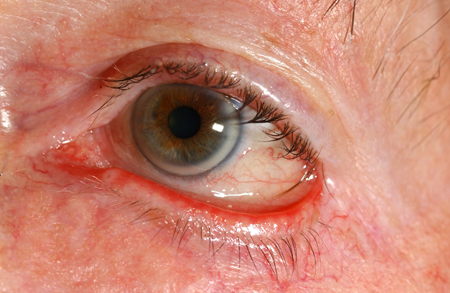
Blepharitis: inflammation of the eyelid margin [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: BlepharitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
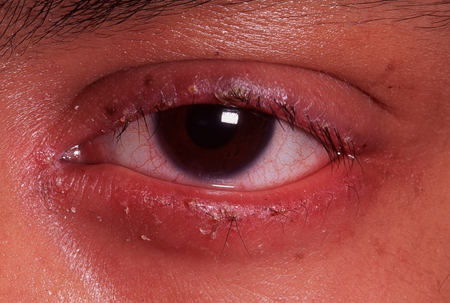
Dry eye: symptoms or signs consistent with a deficiency of the precorneal tear film. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Dry eye (stained with fluorescein)From the personal collection of Dr Jonathan Smith; used with permission [Citation ends].
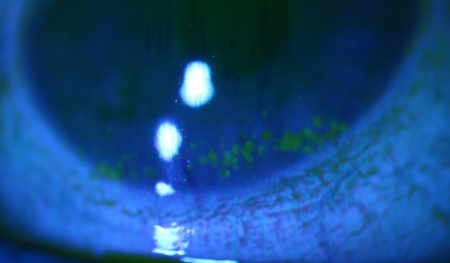
Conjunctival causes
Bacterial conjunctivitis: inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by bacterial infection [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bacterial conjunctivitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
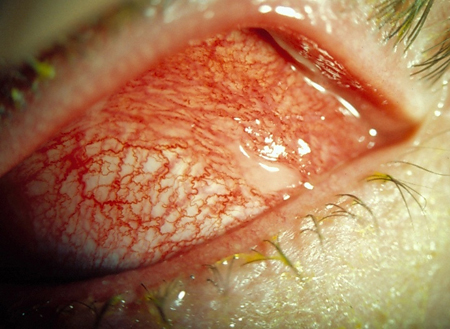
Viral conjunctivitis: inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by viral infection. Some patients with COVID-19 may present with features typical of viral conjunctivitis.[4] Primary care physicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for this uncommon presentation[5][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Viral conjunctivitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
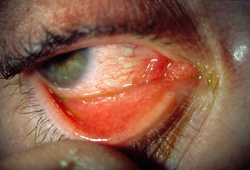
Allergic (vernal) conjunctivitis: inflammation of the conjunctiva occurring during an allergic response [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Allergic (vernal) keratoconjunctivitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
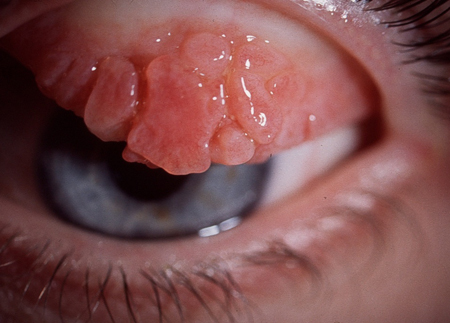
Neonatal conjunctivitis: inflammation of the conjunctiva within the first month of life
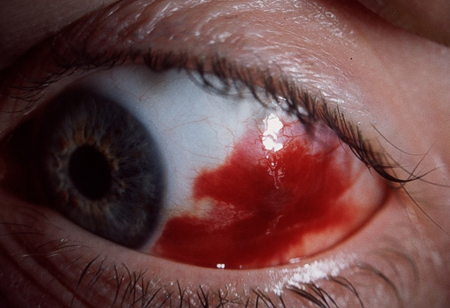
Subconjunctival haemorrhage [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Subconjunctival haemorrhagePrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
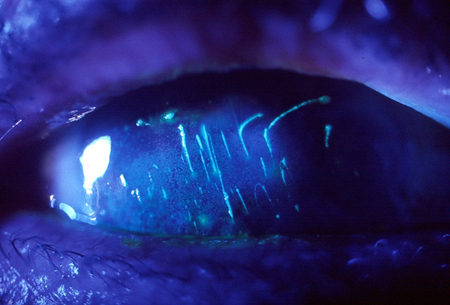
Subtarsal foreign body [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Subtarsal foreign body: vertical corneal abrasions seen with fluorescein stainPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
Conjunctival foreign body.
Corneal causes
Bacterial corneal ulcer: corneal epithelial defect caused by bacterial infection [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal ulcer seen with fluorescein stainPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
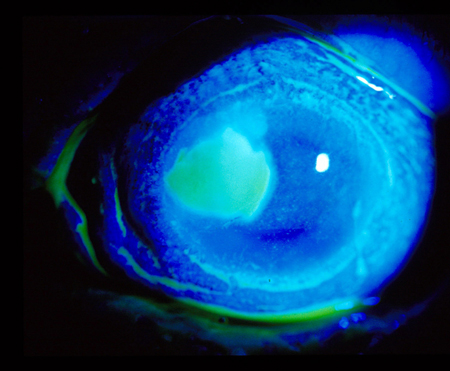
Viral corneal ulcer: corneal epithelial defect caused by viral infection [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Dendritic ulcer seen with fluorescein stainPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Fungal corneal ulcer: corneal epithelial defect caused by fungal infection
Contact lens-related
Corneal foreign body [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal foreign bodyPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
Corneal abrasion: corneal epithelial defect usually caused by trauma. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal abrasion seen with fluorescein stainPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Inflammatory causes
Anterior uveitis: inflammation of the anterior portion of the uveal tract [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Anterior uveitis with posterior synechiaePrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

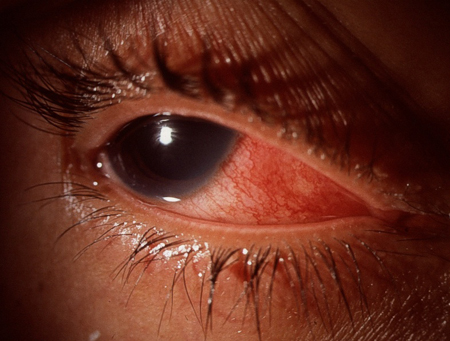
Scleritis: inflammation of the sclera [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ScleritisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
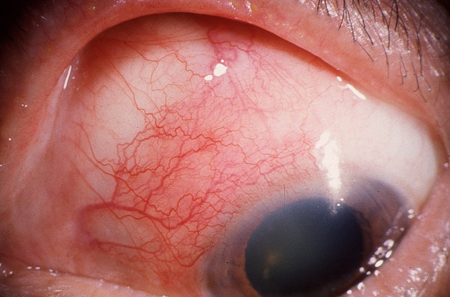
Episcleritis: inflammation of the episclera. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EpiscleritisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
Traumatic causes
Physical [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Penetrating corneal injury with iris prolapsePrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
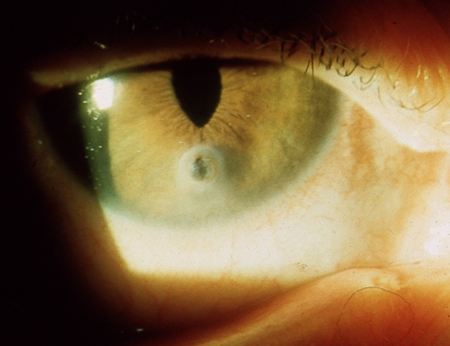
Chemical.
Other
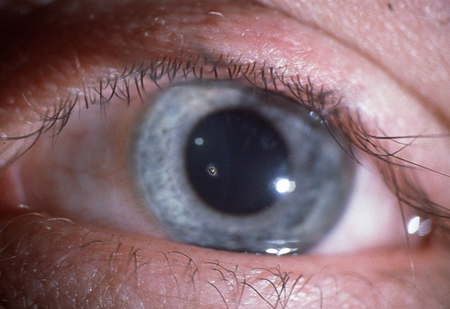
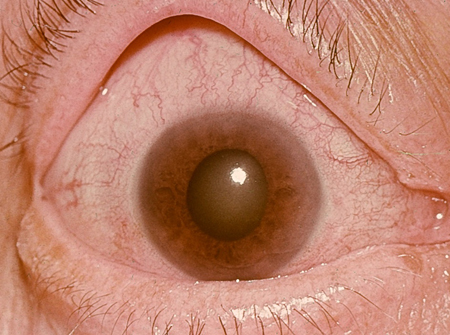
Angle-closure glaucoma: closure of the iridocorneal angle leading to an acute rise in intra-ocular pressure. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Angle-closure glaucoma: central corneal oedema with an oval-shaped mid-dilated pupil.Private collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
Most common conditions
Those commonly presenting to a primary care physician are:
Infective conjunctivitis[6][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bacterial conjunctivitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Allergic conjunctivitis [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Allergic (vernal) keratoconjunctivitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Dry eye and other adnexal problems.[7][8][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: TrichiasisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EntropionPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EntropionPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EctropionPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EctropionPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: BlepharitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: BlepharitisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Dry eye (stained with fluorescein)From the personal collection of Dr Jonathan Smith; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Dry eye (stained with fluorescein)From the personal collection of Dr Jonathan Smith; used with permission [Citation ends].
Sight-threatening causes
Causes of red eye that can threaten vision by leading to reduced visual acuity include:
Angle-closure glaucoma [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Angle-closure glaucoma: central corneal oedema with an oval-shaped mid-dilated pupil.Private collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Chemical injuries
Conditions affecting the cornea
Trauma
Anterior uveitis. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Anterior uveitis with posterior synechiaePrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Causes of red eye that can threaten vision by leading to globe rupture or perforation include: [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Penetrating corneal injury with iris prolapsePrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
Scleritis [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ScleritisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].

Physical trauma
Corneal ulceration
High-velocity foreign bodies.
These are discussed further with initial management in Emergencies: Urgent Considerations.
Risk factors
Risk factors associated with specific causes of red eye include:
Anterior uveitis: [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Anterior uveitis with posterior synechiaePrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
 human leukocyte antigen-B27 histocompatibility complex-positive patients, tuberculosis, syphilis, Lyme disease, sarcoidosis, Behcet's disease, and pauciarticular juvenile chronic arthritis.
human leukocyte antigen-B27 histocompatibility complex-positive patients, tuberculosis, syphilis, Lyme disease, sarcoidosis, Behcet's disease, and pauciarticular juvenile chronic arthritis.Scleritis: [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ScleritisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
 connective tissue disorders including rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and relapsing polychondritis.
connective tissue disorders including rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and relapsing polychondritis.Episcleritis: [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EpiscleritisPrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
 connective tissue disorders including rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis), and SLE.
connective tissue disorders including rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis), and SLE.Angle-closure glaucoma: [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Angle-closure glaucoma: central corneal oedema with an oval-shaped mid-dilated pupil.Private collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
 hypermetropia, drugs (e.g., therapeutic mydriatics, drugs with unwanted mydriatic effects such as systemic anticholinergics and topiramate).
hypermetropia, drugs (e.g., therapeutic mydriatics, drugs with unwanted mydriatic effects such as systemic anticholinergics and topiramate).Subconjunctival haemorrhage: [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Subconjunctival haemorrhagePrivate collection - courtesy of Mr Hugh Harris [Citation ends].
 hypertension, systemic anticoagulation, bleeding abnormalities (leukaemia, clotting disorders), conjunctival vascular lesion, trauma (including contact lens-related injury), and diabetes.
hypertension, systemic anticoagulation, bleeding abnormalities (leukaemia, clotting disorders), conjunctival vascular lesion, trauma (including contact lens-related injury), and diabetes.Dry eye: [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Dry eye (stained with fluorescein)From the personal collection of Dr Jonathan Smith; used with permission [Citation ends].
 connective tissue disorders including Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and SLE.
connective tissue disorders including Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and SLE.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer