Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) usually evolves insidiously over days to weeks.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Fayfman M, Pasquel FJ, Umpierrez GE. Management of hyperglycemic crises: diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Med Clin North Am. 2017 May;101(3):587-606.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6535398
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28372715?tool=bestpractice.com
The aim of initial laboratory investigations is to establish the diagnosis and assess the severity. Subsequent investigations are used to identify underlying triggers, such as infection or myocardial infarction (MI).
History and physical exam
Patients usually present with polyuria, polydipsia, weakness, and weight loss.[12]Umpierrez GE, Smiley DD. Complications. In: Fonseca V, ed. Clinical diabetes. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2006:101-8. Altered mental status is frequently present on admission, and correlates with the severity of hyperglycemia and serum osmolality.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
Coma is a very rare presentation of HHS and is associated with total serum osmolality levels >340 mOsm/kg.[3]Stoner GD. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Dec 1;96(11):729-36.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/1201/p729.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29431405?tool=bestpractice.com
Important factors to consider in the patient's past or current medical history include changes or omissions of insulin therapy, recent infection, and recent or previous MI or stroke because these may precipitate HHS.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Pasquel FJ, Umpierrez GE. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state: a historic review of the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2014 Nov;37(11):3124-31.
http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/37/11/3124.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25342831?tool=bestpractice.com
It is essential to take a full drug history, in particular looking for recent use of corticosteroids, pentamidine, beta-blockers, thiazide diuretics, phenytoin, or atypical antipsychotics, because these affect carbohydrate metabolism and may participate in the development of hyperglycemic crises.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Alavi IA, Sharma BK, Pillay VK. Steroid-induced diabetic ketoacidosis. Am J Med Sci. 1971 Jul;262(1):15-23.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4327634?tool=bestpractice.com
[27]Nardone DA, Bouma DJ. Hyperglycemia and diabetic coma: possible relationship to diuretic-propranolol therapy. South Med J. 1979 Dec;72(12):1607-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/515777?tool=bestpractice.com
[28]Diamond MT. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar coma associated with hydrochlorothiazide and pancreatitis. N Y State J Med. 1972 Jul 1;72(13):1741-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4504065?tool=bestpractice.com
[29]Podolsky S, Pattavina CG. Hyperosmolar nonketotic diabetic coma: a complication of propranolol therapy. Metabolism. 1973 May;22(5):685-93.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4145086?tool=bestpractice.com
[30]Carter BL, Small RE, Mandel MD, et al. Phenytoin-induced hyperglycemia. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1981 Oct;38(10):1508-12.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7294047?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Newcomer JW. Second generation (atypical) antipsychotics and metabolic effects: a comprehensive literature review. CNS Drugs. 2005;19(suppl 1):1-93.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15998156?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Wilson DR, D'Souza L, Sarkar N, et al. New-onset diabetes and ketoacidosis with atypical antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2003 Jan 1;59(1):1-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12413635?tool=bestpractice.com
Physical signs of volume depletion include dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor, tachycardia, hypotension, and, in severe cases, shock. Volume depletion may be difficult to assess in the form of poor skin turgor in older patients. Assessment of the buccal mucosa for dryness is more informative in these patients.[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
Mild hypothermia may be observed in some patients, as a result of peripheral vasodilation.[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
Severe hypothermia is a poor prognostic sign.[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
Abdominal pain is uncommon in HHS but frequent (>50%) in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Umpierrez GE, Smiley DD. Complications. In: Fonseca V, ed. Clinical diabetes. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2006:101-8. Therefore, in patients with hyperglycemic emergencies, the presence of unexplained abdominal pain should guide the clinician toward a diagnosis of DKA rather than HHS. Occasionally, patients with HHS may present with focal neurologic signs (hemianopia and hemiparesis) and seizures (either focal or generalized).[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Umpierrez GE, Smiley DD. Complications. In: Fonseca V, ed. Clinical diabetes. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2006:101-8.[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
This presentation can be mistaken for acute stroke. However, correction of hyperglycemia with fluid and insulin therapy leads to rapid resolution of these signs in HHS.[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Umpierrez GE, Smiley DD. Complications. In: Fonseca V, ed. Clinical diabetes. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2006:101-8. Epilepsia partialis continua is an unusual form of seizure that is present in 6% of patients with HHS in the early phase of HHS.[49]Harden CL, Rosenbaum DH, Daras M. Hyperglycemia presenting with occipital seizures. Epilepsia. 1991 Mar-Apr;32(2):215-20.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2004625?tool=bestpractice.com
Seizures related to hyperglycemia in HHS are usually resistant to anticonvulsive therapy and phenytoin may further exacerbate HHS.[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
Initial investigations
The aim of initial laboratory investigations is to establish the diagnosis and assess the severity.
Plasma glucose
Blood urea nitrogen and creatinine
Serum electrolytes[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
Serum sodium is usually low owing to the osmotic flux of water from the intracellular to extracellular space in the presence of hyperglycemia. The total sodium deficit is 5-13 mEq/kg. Hypernatremia in the presence of hyperglycemia in patients with HHS indicates profound volume depletion. To assess the severity of sodium and water deficit, the patient's corrected sodium can be calculated by adding 1.6 mEq/L of sodium to the measured value for every 100 mg/dL of glucose above 100 mg/dL.[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
Total potassium deficit is 4-6 mEq/kg, owing to increased loss of potassium by diuresis. In spite of the total body potassium deficit, serum potassium is usually elevated. This is because insulin insufficiency, hypertonicity, and acidemia cause a large extracellular shift of potassium. A low potassium level on admission indicates severe total-body potassium deficit.[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
Serum chloride levels are usually low. There is usually a total chloride deficit of 5-15 mEq/kg; this is secondary to the sodium deficit.
Serum magnesium levels are usually low. There is usually a total magnesium deficit of 1-2 mEq/kg, as a result of increased magnesium loss from diuresis.
Serum phosphate levels are usually low or normal on presentation. The total body phosphate deficit is 3-7 mmol/kg, as a result of increased phosphate loss from diuresis.
Serum osmolality
Total serum osmolality is total concentration of sodium, glucose, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum.
[
Osmolality Estimator (serum)
Opens in new window
]
Effective serum osmolality is calculated from serum concentrations of sodium and glucose.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
BUN concentration is not taken into account, because it is freely permeable and its accumulation does not change the osmotic gradient.[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
Elevated in all patients with HHS (total serum osmolality: >320 mOsm/kg; calculated effective serum osmolality: >300 mOsm/kg).[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
Serum or urinary ketones
Beta-hydroxybutyrate is the main product of ketogenesis, with acetoacetic acids constituting the remainder of the ketones.
Guidelines recommend that direct measurement of beta-hydroxybutyrate by laboratory enzymatic methods or by point-of-care capillary measurement should be undertaken whenever possible.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
[50]Dhatariya KK, Vellanki P. Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)/hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS): novel advances in the management of hyperglycemic crises (UK versus USA). Curr Diab Rep. 2017 May;17(5):33.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5375966
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28364357?tool=bestpractice.com
If beta-hydroxybutyrate measurement is not available, nitroprusside reaction can be used to detect ketones.
Beta-hydroxybutyrate is converted to acetoacetate over time, which is excreted in the urine. When measuring serum ketones, the nitroprusside reaction will not detect beta-hydroxybutyrate. Thus, serum or urine ketones measured by the nitroprusside reaction may be initially negative at the time of presentation, or remain positive when DKA-HSS has resolved (giving the appearance that there are no ketones in the serum, or that DKA-HSS is not resolving).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Expected blood test results in HHSCreated by BMJ Digital Health [Citation ends].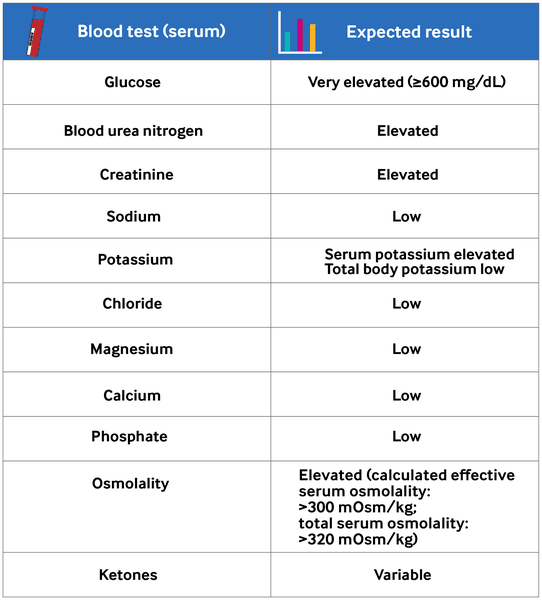
Anion gap
Anion gap is calculated as (Na)-(Cl + HCO₃) (mEq/L).
The normal range of anion gap varies depending on the laboratory. Typically, levels ≥12 mEq/L signify an anion gap acidosis, which may indicate mixed DKA-HHS, lactic acidosis, or other conditions unrelated to HHS.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
[3]Stoner GD. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Dec 1;96(11):729-36.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/1201/p729.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29431405?tool=bestpractice.com
Serum lactate
Lactic acid levels can be elevated in conditions such as sepsis, and in severe volume depletion in patients with diabetes.[2]Mustafa OG, Haq M, Dashora U, et al. Management of hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) in adults: an updated guideline from the Joint British Diabetes Societies (JBDS) for inpatient care group. Diabet Med. 2023 Mar;40(3):e15005.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/dme.15005
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36370077?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
Urinalysis
Urine ketones are usually negative or mildly positive (<2 + on a ketone strip).
Urine glucose is positive.
If infection is present, urine will be positive for leukocytes and nitrites; urinary tract infection is a common precipitant of HHS.[3]Stoner GD. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Dec 1;96(11):729-36.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/1201/p729.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29431405?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Pasquel FJ, Umpierrez GE. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state: a historic review of the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2014 Nov;37(11):3124-31.
http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/37/11/3124.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25342831?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Karslioglu French E, Donihi AC, Korytkowski MT. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome: review of acute decompensated diabetes in adult patients. BMJ. 2019 May 29;365:l1114.
https://www.bmj.com/content/365/bmj.l1114.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31142480?tool=bestpractice.com
Blood gas
Arterial pH is usually ≥7.30 and arterial bicarbonate is ≥15 mEq/L. A venous pH sample is usually 0.03 units lower than arterial pH. Several studies have suggested that the difference between venous and arterial pH samples is not sufficiently significant to change clinical management.[50]Dhatariya KK, Vellanki P. Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)/hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS): novel advances in the management of hyperglycemic crises (UK versus USA). Curr Diab Rep. 2017 May;17(5):33.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5375966
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28364357?tool=bestpractice.com
Furthermore, venous pH sampling is easier, more convenient, and less painful.
Complete blood count
Leukocytosis is a common finding in patients in hyperglycemic crises.[36]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, et al. Management of hyperglycemic crises in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001 Jan;24(1):131-53.
https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/24/1/131/21107/Management-of-Hyperglycemic-Crises-in-Patients
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11194218?tool=bestpractice.com
Leukocytosis of >25,000 per microliter may indicate infection and requires further evaluation.[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
Liver function tests
Additional investigations
Subsequent investigations are used to identify underlying triggers, such as infection or MI, or an alternative diagnosis.
Chest x-ray
Used to exclude pneumonia, a common precipitant of HHS.[3]Stoner GD. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Dec 1;96(11):729-36.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/1201/p729.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29431405?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;30(4):817-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11727401?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Pasquel FJ, Umpierrez GE. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state: a historic review of the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2014 Nov;37(11):3124-31.
http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/37/11/3124.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25342831?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Karslioglu French E, Donihi AC, Korytkowski MT. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome: review of acute decompensated diabetes in adult patients. BMJ. 2019 May 29;365:l1114.
https://www.bmj.com/content/365/bmj.l1114.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31142480?tool=bestpractice.com
ECG
Should be performed if cardiovascular diseases, such as MI, are suspected as the trigger or if severe electrolyte abnormalities are present.[1]Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, et al. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia. 2024 Aug;67(8):1455-79.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11343900
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38907161?tool=bestpractice.com
Evidence of hypokalemia (U waves) or hyperkalemia (tall T waves) may also be present.
Myocardial enzymes
Blood, urine, or sputum cultures
Used to identify precipitating infections. Further workup for sepsis should be performed if clinically indicated.[46]Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32(7):1335-43.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699725
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19564476?tool=bestpractice.com
