Tests
1st tests to order
serum electrolytes
Test
Performed to evaluate severity and to guide supportive treatment.
A nonspecific test.
Elevated BUN and creatinine may be present in the dehydrated patient.
Result
hypokalemia, hypochloremia, alkalosis; elevated blood urea and serum creatinine may occur with dehydration
serum magnesium
Test
Electrolyte imbalance, particularly hypermagnesemia, has been associated with ileus.[82]
Result
hypermagnesemia may be present
CBC
Test
Performed to evaluate for evidence of infection.
A significantly elevated WBC, especially if accompanied by abdominal tenderness or peritoneal signs, is a sign that a more severe condition (e.g., sepsis, peritonitis) is present.
Result
normal or slightly elevated WBC
abdomen and pelvis CT scan (with intravenous contrast and oral water soluble contrast)
Test
Performed to exclude other causes of distention and obstipation, and to exclude a mechanical obstruction.[77][80][81] CT scan shows fluid-filled intestines and no evidence of transition zone indicating mechanical bowel obstruction, bowel perforation, intra-abdominal abscess, or other gastrointestinal pathology. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan with intravenous and oral contrast showing fluid-filled small intestine and cecum in ileusFrom the personal collection of Dr Paula I. Denoya [Citation ends].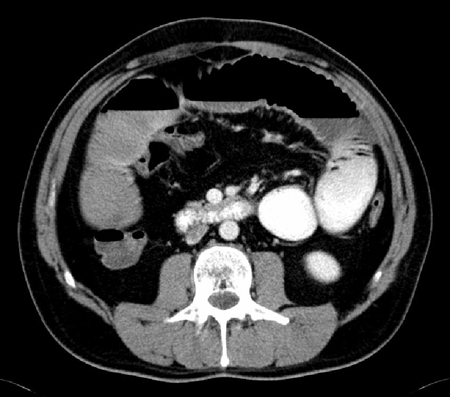 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan with intravenous and oral contrast showing fluid-filled small intestine in ileusFrom the personal collection of Dr Paula I. Denoya [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan with intravenous and oral contrast showing fluid-filled small intestine in ileusFrom the personal collection of Dr Paula I. Denoya [Citation ends].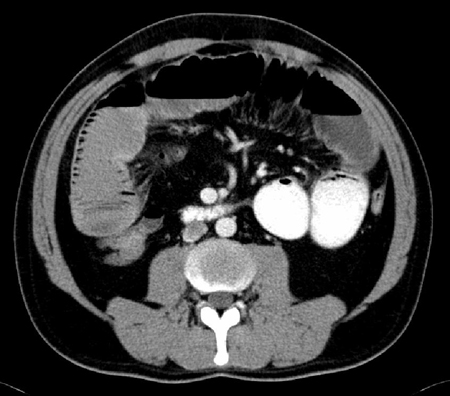
In postoperative patients, a CT scan should be performed if the presumed ileus has not resolved in 5-7 days, or the clinical condition of the patient worsens.[32]
In the immediate postoperative period, CT scan with oral contrast is the method of choice in differentiating prolonged ileus and mechanical obstruction.[80][81]
Contrast-enhanced CT acquisition is sufficient for the assessment of possible small bowel obstruction; use of unenhanced CT alongside contrast-enhanced imaging does not add diagnostic information and should be avoided.[79]
In patients with renal insufficiency, caution should be exercised prior to administering intravenous contrast, which can be avoided if necessary.
Water-soluble contrast should be used in place of barium, which is contraindicated if there is a possible perforation.
Result
fluid-filled intestines; distended stomach
Tests to consider
serum LFTs
Test
To exclude other conditions that may contribute to ileus, such as cholecystitis or pancreatitis.
Result
normal in ileus
serum amylase
Test
To exclude other conditions that may contribute to ileus, such as cholecystitis or pancreatitis.
Result
normal in ileus
serum lipase
Test
To exclude other conditions that may contribute to ileus, such as cholecystitis or pancreatitis.
Result
normal in ileus
small bowel series
Test
Performed if CT scan is not diagnostic but there is still suspicion of intestinal obstruction.
To exclude a point of mechanical obstruction in patients with prolonged postoperative ileus. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Small bowel series showing dilated small bowel loops in ileus; nasogastric tube is seen curled in the stomachFrom the personal collection of Dr Paula I. Denoya [Citation ends].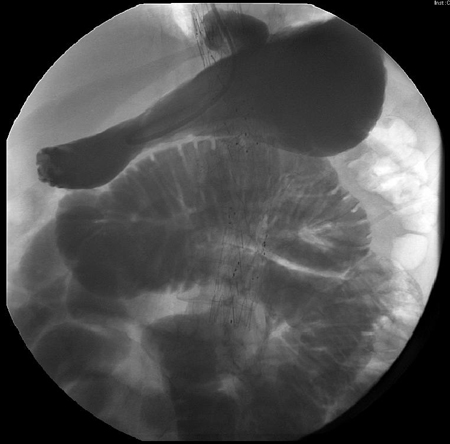 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Small bowel series showing dilated contrast-filled small bowel loops in ileus; some contrast is visible in the right colonFrom the personal collection of Dr Paula I. Denoya [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Small bowel series showing dilated contrast-filled small bowel loops in ileus; some contrast is visible in the right colonFrom the personal collection of Dr Paula I. Denoya [Citation ends].
Care should be taken, as there is a risk of aspiration.
Result
no evidence of obstruction or bowel leak
gastric emptying study
Test
Consider performing this test in cases of prolonged ileus, especially in patients with comorbidities such as long-standing diabetes mellitus, which is associated with gastroparesis.
Result
delayed gastric emptying
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer