Investigations
1st investigations to order
urinalysis with microscopy and culture
Test
Should be one of the first tests ordered when considering a diagnosis. Not in itself diagnostic, but is one of the most commonly used differentiating tests.[1][3]
The result is usually normal in these patients, but pyuria, or microscopic or gross haematuria with benign or malignant potential, may be seen, suggesting a differential diagnosis.
Cultures should be negative for fungi, gonorrhoea, chlamydia, and trichomonal species. A positive result points toward an infectious aetiology.
Result
normal
vaginal wet prep
Test
Bacterial vaginosis, yeast infection, or low pH from oestrogen withdrawal may mimic pelvic or bladder pain.
Sexually transmitted infections (trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc) may also cause similar symptoms and warrant prompt treatment of the patient and all sexual partners.
Result
normal
voiding diary
Test
Initial evaluation should aim to quantify the patient's symptoms and assess any response to further treatment. A small maximum voided volume may predict for ulcerative IC, especially if haematuria is present on urinalysis.
Result
small, frequent voids; urgency; nocturia
urine cytology
Test
Should be ordered when considering a diagnosis and haematuria is present. No findings specifically suggest a diagnosis, but results rule out other disease entities such as bladder, urethral, or renal carcinoma.
Result
normal
Investigations to consider
cystoscopy with hydro-distension of bladder
Test
Findings include glomerulations (discrete, tiny, raspberry-like lesions appearing as minuscule mucosal tears and haemorrhages), submucosal petechiae, mucosal tears, and a low anaesthetic bladder capacity.[32][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Glomerulations: haemorrhages seen after diagnostic cystoscopic hydro-distensionFrom the personal collection of Serge P. Marinkovic, MD [Citation ends].
Gross inflammatory disease (i.e., Hunner's ulcers) may be detected, described as circumscriptive, reddened mucosal areas with small vessels radiating toward a central scar, with fibrin deposits or coagulum attached.[31][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hunner's ulcers: larger mucosal haemorrhages seen after diagnostic cystoscopic hydro-distensionFrom the personal collection of Serge P. Marinkovic, MD [Citation ends].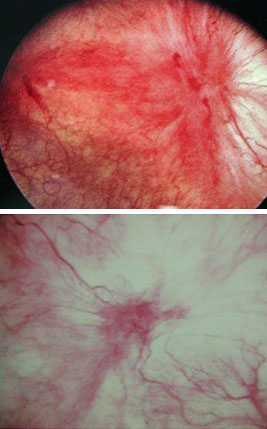
Done with hydro-distension of bladder under local anaesthesia. Clinic cystoscopy can be performed without anaesthesia, but bladder hypersensitivity with filling and pelvic pain may limit the examination considerably.
Biopsies may be taken from suspicious areas.
It is important to note that a negative result does not rule out diagnosis.
Result
glomerulations, submucosal petechiae, mucosal tears, presence of Hunner's ulcers, low anaesthetic bladder capacity
bladder biopsy
Test
Not a compulsory procedure unless gross abnormalities of the bladder wall are found on cystoscopy. Mainly ordered to exclude urothelial carcinoma in patients with initial diagnosis of ulcerative IC.
Result
normal
Emerging tests
stress protein gene assay
Test
For example, mast cell tryptase, glycosaminoglycans, and Tamm-Horsfall protein auto-antibodies. Used primarily in research studies and do not play a role in the diagnosis. Not recommended unless part of experimental protocols.
Result
positive
urine anti-proliferative factor
Test
Found in the urine of some patients with IC/bladder pain syndrome (BPS).[33]
Inhibits bladder epithelial growth, and contributes to significantly decreased levels of HB-EGF and increased levels of epidermal growth factor (EGF).
While the results may be promising, these assays are experimental and thus not yet commercially available.
Result
anti-proliferative factor activity, decreased heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) level, increased EGF level
urine nerve growth factor (NGF)
Test
A small signalling protein produced by urothelial and detrusor muscle cells. NGF promotes growth and survival of sympathetic fibres and sensory nerves and is required for normal bladder functioning.
Increasing levels have been seen in patients with overactive bladder (OAB) as well as IC/BPS. NGF levels decrease with successful treatment of both conditions, though it is non-specific when differentiating between the 2 conditions.
Result
increased levels of NGF over controls, with decreasing levels after treatment success
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer