Investigations
1st investigations to order
serum chromogranin A/B
Test
Specialised test, not performed routinely in many laboratories.
Blood samples need to be stored immediately on ice. Sensitivity 60% to 90%. False-positives arise due to impaired renal function, chronic atrophic gastritis, and treatment with proton pump inhibitors.
Useful as a marker for monitoring disease burden and progression.
Result
elevated
urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid
Test
24-hour collection of urine is required.
Patients should avoid certain foods and drugs that can affect the test results during the 48-hour period prior to collection, and during the 24-hour collection period. Examples include: avocados, cantaloupe, eggplant, pineapples, plums, tomatoes, hickory nuts/pecans, plantains, kiwi, dates, grapefruit, honeydew, walnuts, bananas, cough and cold treatments containing guaifenesin, paracetamol, ephedrine, diazepam, nicotine, and phenobarbital).[2]
Urine should be collected in a bottle containing acid so that pH is <3. In midgut carcinoid patients, sensitivity is approximately 60% to 70%, although higher rates have been reported.
Result
elevated
metabolic panel
Test
Used routinely as part of the initial work-up. Enzymatic assays are used to measure plasma creatinine levels.
Result
elevated creatinine if dehydrated from diarrhoea
liver function tests
Test
Used routinely as part of the initial work-up. Levels of alanine aminotransferase(ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) are measured. One small study has shown that only 28.6% of patients with carcinoid tumours have abnormal liver test results, and so other investigations such as imaging tests are also needed for diagnosis.[21]
Result
variable, changes include aminotransferase elevation depending on site of tumour
full blood count
Test
Should be ordered in all patients with suspected carcinoid syndrome as part of the initial evaluation.
Result
usually normal
Investigations to consider
CT chest, abdomen, and pelvis with dual-phase liver
Test
Routine staging should be performed every 4 to 6 months.
Used to monitor progression of the disease.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing multiple liver metastasesFrom the collection of Dr R. Srirajaskanthan and Dr M. Caplin; used with permission [Citation ends].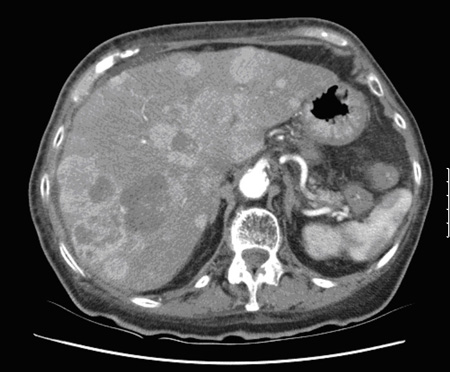
Result
identifies location of primary tumour, presence of liver metastases
bronchoscopy
Test
Result
identifies location of primary tumour
endoscopy
Test
Result
identifies location of primary tumour
somatostatin receptor scintigraphy ± somatostatin single photon emission CT (SPECT)
Test
Somatostatin receptor type 2 is present in 70% to 90% of carcinoid tumours. Most commonly used ligand is indium-111-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA)-octreotide.
Available in most nuclear medicine departments. Referral to a specialist centre may be required.
SPECT can be used where available. Sensitivity of 80% to 100% is reported when 111-In-DTPA-octreotide SPECT is used.
Result
identifies areas of somatostatin receptor-positive tumour
iodine I-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scintigraphy
Test
The compound is taken up and concentrated in endocrine cells. MIBG has a sensitivity of 50% in patients with carcinoid syndrome. The test can be requested from a nuclear medicine department but may require consultant referral. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Iodine I 123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) uptake image showing multiple metastasesFrom the collection of Dr R. Srirajaskanthan and Dr M. Caplin; used with permission [Citation ends].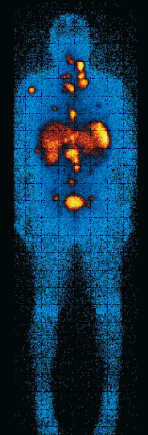
Result
identifies areas of tumour through MIBG take-up
histology
Test
Biopsy of either a liver metastasis or primary lesion is helpful in determining the underlying type of tumour and stage of tumour.
Result
identifies tumour type and stage
somatostatin receptor positron emission tomography (SSTR-PET) or fludeoxyglucose F-18 (FDG)
Test
Somatostatin receptor imaging is required for all patients with a histologically proven neuroendocrine tumour (NET) or suspected lesions on cross sectional imaging. The preferred method is SSTR-PET. Commonly used tracers include gallium (Ga)-68 dotatate, gallium Ga-68 dotanoc, and GA-68 dotatoc.
FDG PET is of use in patients with intermediate- and high-grade NETs. There are other tracers in development that are potentially of interest.
Result
identifies areas of somatostatin receptor-positive tumour
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer