Investigations
1st investigations to order
microscopical examination with potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation
Test
Undertaken in the doctor's office. Always confirm a diagnosis of PV by direct microscopical examination of scale from lesions with a KOH preparation. In preparing the specimen, obtain scale and debris from skin lesions by light scraping with a #15 surgical blade (no need to draw blood with the blade) or stripping off scale with tape or a cotton swab when patient cooperation (e.g., in young children) might make a sharp instrument unsafe. Specimen is placed on a glass slide and examined after application of 10% KOH solution with or without Parker ink (which quickly stains the fungi blue) or chlorazol black (which quickly stains the fungi green).[13][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: KOH and chlorazol black preparation showing short hyphae and sporesFrom the collection of Brian L. Swick, MD [Citation ends].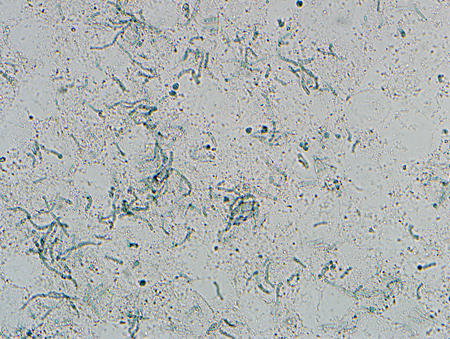
Result
short hyphae and budding yeast with spaghetti-and-meatballs appearance
Investigations to consider
skin biopsy
Test
Only required if hx or physical examination findings are atypical. In most cases, a KOH preparation is adequate for diagnosis. However, if adequate scale cannot be obtained or if the results are inconclusive, a skin biopsy can be obtained to confirm diagnosis and exclude other conditions with a similar presentation, especially pityriasis alba, seborrhoeic dermatitis, confluent and reticulate papillomatosis, and vitiligo.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Skin biopsy showing short hyphae and yeastFrom the collection of Brian L. Swick, MD [Citation ends].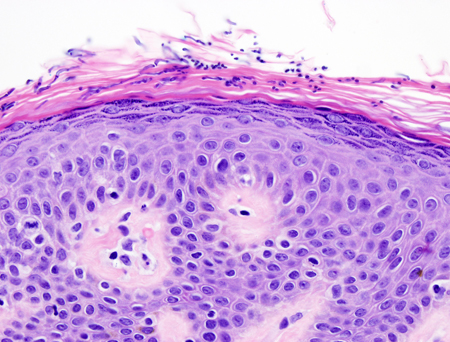
Result
abundant short hyphae and budding yeast forms within the stratum corneum
culture
Test
Identification by culture is difficult and not necessary for routine diagnosis of PV. Special media, other than typical Sabouraud mycological media, is needed to grow and isolate the fungus.[1]
Result
white to cream-coloured colonies 2 to 3 days after inoculation on modified Dixon's and Leeming's or Dixon's media
Gram stain
Test
Gentian violet is applied directly to the affected skin as a diagnostic adjunct to distinguish PV from other scaly eruptions that can be associated with hyper- or hypopigmented macules and patches.[32]
Result
purple-coloured accentuation of the infected patches with gentian violet
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer