Differentials
Generalised morphoea
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Non-systemic type of scleroderma; does not involve the fingers. Absence of Raynaud's phenomenon, GORD, and dilated nailbed capillaries.
INVESTIGATIONS
Serum antinuclear antibody and rheumatoid factor (RF) present, RF especially in children.
Skin biopsy with changes at the dermis and subcutaneous tissues, with an initial inflammatory infiltrate followed by increased collagen bundles, decreased vascularity, atrophy, and an absence of inflammatory infiltrate.
Eosinophilic fasciitis (Shulman's syndrome)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Condition may be more common in men. Woody induration of extremity or trunk. Peau d'orange (skin pitting like an orange peel) present. Raynaud's phenomenon is unusual and there are no dilated nailbed capillaries. The limb may become worse after exercise. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Eosinophilic fasciitis with peau d'orangeFrom the personal collection of Professor J. Pope; used with permission [Citation ends].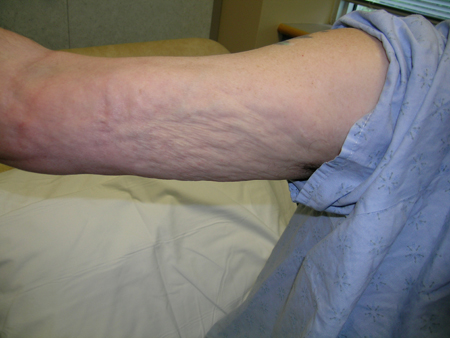
INVESTIGATIONS
Presence of serum antinuclear antibody is uncommon.
Peripheral eosinophilia present.
Fascia biopsy shows inflammatory infiltrates including eosinophils.
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
There is a history of at least one magnetic resonance image with gadolinium enhancement. Cobblestone, nodular, indurated plaques of the lower extremities, trunk, feet, and hands are present. Raynaud's phenomenon and dilated nailbed capillaries are absent.
INVESTIGATIONS
Serum antinuclear antibody is absent and serum creatinine is increased.
Scleroedema
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Diabetes mellitus or a monoclonal gammopathy may coexist. Usually affects only the skin. Skin is indurated, doughy, and involves the neck, back, and face. Raynaud's phenomenon, dilated capillaries, and internal organ involvement is absent.
INVESTIGATIONS
Serum antinuclear antibody is absent.
Skin biopsy shows thickening of the dermis and hyaluronic acid between the collagen fibres.
Scleromyxoedema (or papular mucinosis)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Associated with paraproteinaemias.
Affects the hands, face, and extensor surfaces. Raynaud's phenomenon and dilated capillaries at the nailbeds are absent. Skin dermis can break into solid papules. Due to the deposition in the skin there can be reduced range of motion of the involved areas.
INVESTIGATIONS
Skin deposition is mucinosis material (not collagen).
Diabetic cheiroarthropathy
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Associated with diabetes mellitus. Raynaud's phenomenon, nailbed dilated capillaries, and skin tightness proximal to the fingers are absent. Typically both hands are affected. Limited joint mobility due to thickening of the skin and contracture of the fingers, which cannot fully extend or flatten. Rarely, larger joints are affected (generally in more advanced, long-standing diabetes mellitus).
INVESTIGATIONS
Serum antinuclear antibody is absent.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Generalised disorder that can affect any system. Most commonly affects women during their reproductive years. Symptoms and signs may accumulate over time. Raynaud's phenomenon is invariably bilateral and occurs in as many as 50% of patients at disease onset, although often predating other features of SLE.
SLE has other features such as photosensitivity, malar rash, and oral ulcers.
INVESTIGATIONS
Antinuclear antibody anti-DNA or anti-Smith antibody may be positive.
Red blood cell casts in urine.
Dermatomyositis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
An idiopathic inflammatory myopathy characterised by the presence of hallmark cutaneous lesions (e.g., heliotrope rash, Gottron's papules). Skin lesions are frequently the initial presenting complaint, with muscle involvement developing later. Some patients have cutaneous involvement alone. Raynaud's phenomenon may be present.
INVESTIGATIONS
Serum creatine kinase and aldolase elevated. Skin biopsy shows perivascular or interfascicular inflammation, endothelial hyperplasia in the intramuscular blood vessels, perifascicular atrophy.
Sclerodactyly in other connective tissue diseases
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Other connective tissue diseases (e.g., mixed connective tissue disease) may demonstrate sclerodactyly. Usually involves only the distal half of the fingers.
INVESTIGATIONS
Variable presence of anti-DNA, cytopenias, casts in the urine.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer