Differentials
Common
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
History
urinary hesitancy, straining to void, sensation of incomplete emptying, double voiding, weak stream, intermittency, urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia, history of BPH, family history of BPH, prior episode of retention
Exam
enlarged prostate on digital rectal examination, palpable bladder due to urinary retention
1st investigation
- prostate-specific antigen (PSA):
may be raised
More
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
History
dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary urgency, small volume voiding, nocturia, suprapubic pain, prior history of UTI and treatment, history of pyelonephritis, history of antibiotic treatment failure
Exam
fever, suprapubic tenderness, bladder distention in urinary stasis, cystocele on pelvic examination
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
positive leukocyte esterase, positive nitrite, pyuria (>10 white blood cells [WBC] per high power field), bacteriuria
More
Other investigations
- urine culture and sensitivity:
≥100,000 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL
More
Acute pyelonephritis
History
flank pain, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, suprapubic pain, history of nephrolithiasis, Urinary tract infection (UTI) and diabetes, immunosuppression
Exam
costovertebral angle tenderness, suprapubic tenderness, fever, decreased bowel sounds
1st investigation
Other investigations
- renal ultrasound:
stones; structural abnormalities
- contrast CT abdomen:
heterogeneous uptake of contrast
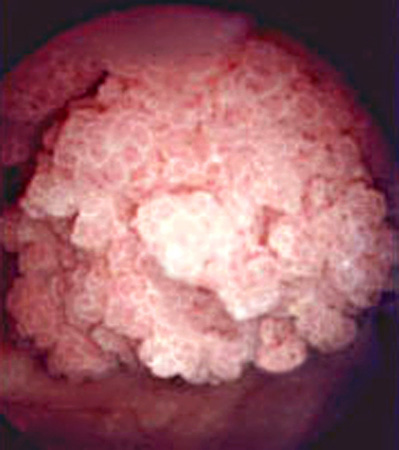
Bladder cancer
History
painless haematuria, dysuria, frequency, urgency; history of pelvic irradiation, history of smoking, weight loss, exposure to environmental/chemical carcinogens; primarily affects those ≥65 years
Exam
pelvic mass, costovertebral angle tenderness from obstruction; frequently no abnormalities detected
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
red blood cells
More - urine cytology:
atypical or malignant cells, signified by increased clustering, increased cellularity, or altered nuclear morphology
More - CT urography or MR urography:
bladder tumour; may show ureteral or renal collecting system mass or filling defect
More - cystoscopy:
bladder tumour
More
Other investigations
Prostate cancer
History
advanced age, family history, obstructive voiding symptoms, weight loss; prior history of treatment with surgery, radiation, or brachytherapy
Exam
abnormal digital rectal examination, prostate nodule or diffuse hardness of the gland
1st investigation
- prostate-specific antigen (PSA):
raised (>4 micrograms/L [>4 ng/mL])
More
Other investigations
- transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy:
confirms adenocarcinoma
- multiparametric MRI:
Can help inform decision to biopsy and help identify target areas for biopsy.
More
Kidney stone
History
abrupt onset of severe flank pain, pain radiating to the groin, haematuria, nausea, vomiting, previous history of calculi, family history of nephrolithiasis, history of gout, history of inflammatory bowel disease
Exam
costovertebral angle tenderness
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
haematuria, pyuria, crystalluria, cysteine crystals, acidic or alkaline pH
- non-contrast CT abdomen:
urolithiasis, hydronephrosis
More
Instrumentation of the urinary tract
History
recent cystoscopy, ureteroscopy, prostate needle biopsy
Exam
presence of a urethral catheter, suprapubic catheter, ureteral stent with retrieval strings in urethra
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
diagnosis is clinical, and further tests are not routinely recommended
Other investigations
- kidney, ureter, bladder (KUB) x-ray:
ureteral stent and drain visualisation
Menstruation
History
current menses, history of cyclical haematuria
Exam
physical examination is normal
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
diagnosis is clinical, and further tests are not routinely recommended
Other investigations
Uncommon
Renal trauma
History
blunt flank trauma, penetrating flank or abdominal wounds (gunshot or stab), fractured lower ribs
Exam
hypotension, tachycardia, flank tenderness, flank contusion, abdominal tenderness, abdominal distention
1st investigation
- intravenous contrast-enhanced CT of the abdomen and pelvis with immediate and delayed images:
lacerations to the renal parenchyma, collecting system, and renal vessels; perinephric haematoma, active bleeding, and urinary extravasation
More
Other investigations
- intraoperative intravenous pyelography ('one-shot IVP'):
confirms contralateral renal function
More
Bladder trauma
History
blunt pelvic trauma, penetrating pelvic or abdominal wounds (gunshot or stab), pelvic fracture, inability to void
Exam
suprapubic tenderness, lower abdominal ecchymoses
1st investigation
- CT pelvis with bladder contrast (CT cystogram):
extravasation of contrast revealing bladder injury
More
Other investigations
- x-ray:
possible fracture of the pelvic ring, lacerating fragments of bone causing injury to the bladder, or a disruption of the symphysis pubis
More
Urethral trauma
History
external genital trauma, straddle injury, bilateral pubic rami fracture and Malgaigne's fracture, perineal lacerations, inability to void, recent complicated colorectal or gynaecological procedure
Exam
blood at penile meatus, bloody urethral discharge, high riding prostate on digital rectal examination, sleeve of ecchymoses limited to the penile shaft, butterfly-ecchymosis of the perineum
1st investigation
- retrograde urethrogram:
contrast extravasation from the urethra
More
Sickle cell anaemia
History
African-American descent, prior episodes of sickle crises, family history of sickle cell disease, migrating, intermittent pain
Exam
hepatosplenomegaly, abdominal tenderness, testicular atrophy, oedema of extremities
1st investigation
- peripheral blood smear:
nucleated red blood cells, sickle-shaped cells, and Howell-Jolly bodies
Other investigations
- Hb electrophoresis (whole blood):
haemoglobin S
More
Coagulopathy
History
easy bruising, propensity to bleed, recurrent epistaxis, family history of bleeding diatheses, history of cirrhosis
Exam
ecchymoses, prolonged bleeding
1st investigation
- prothrombin time, PTT, INR:
may be normal or prolonged/raised
- FBC:
thrombocytopenia or may be normal
More
Other investigations
Cystic kidney disease
History
often asymptomatic, flank pain, self-limiting haematuria, urinary tract infection, renal colic
Exam
costovertebral angle tenderness, palpable flank mass in polycystic kidneys, hypertension
1st investigation
- renal ultrasound:
cystic lesions
More
Other investigations
- serum creatinine:
normal or raised
More - CT abdomen:
well-defined, oval lesions
Arteriovenous malformation
History
passage of long, vermiform clots, flank pain, previous history of renal biopsy or percutaneous renal procedure
Exam
hypertension, cardiomegaly, abdominal or flank bruit
1st investigation
- CT abdomen with contrast:
mass lesion, filling defect, delayed nephrogram, renal vein compression
Other investigations
- renal angiography:
simultaneous filling of the arterial and venous system, delayed nephrogram, demonstration of vascular defect
Renal vein thrombosis
History
sudden flank pain, history of nephrotic syndrome
Exam
evidence of flank trauma, oedema
1st investigation
- Doppler ultrasonography:
enlarged, oedematous, echogenic kidney with absent venous signal
More
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
loss of corticomedullary differentiation, low-attenuation thrombus in the renal vein, renal enlargement with parenchymal opacification
More
Alport syndrome
History
recurrent, persistent non-visible haematuria with episodes of visible haematuria, hearing impairment, family history of haematuria, hearing loss, or renal disease
Exam
hypertension, oedema, sensorineuronal hearing loss, anterior lenticonus, corneal erosions
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
dysmorphic red cells, red cell casts, proteinuria, increase in urinary albumin excretion
More - urea and creatinine:
raised (creatinine >2.0 mg/dL, urea >20 mg/dL)
- 24-hour urine collection for protein:
may indicate proteinuria
Other investigations
- skin biopsy:
positive immunohistochemistry
- renal biopsy:
diffuse thickening and splitting of the basement membrane, focal glomerulosclerosis and tubular atrophy; negative immunohistochemistry
Extrapulmonary tuberculosis
History
irritative voiding symptoms, nocturia, weight loss, malaise, history of tuberculosis (TB) exposure, history of cystitis unresponsive to antibiotics, history of epididymitis, recurrent urinary tract infections with Escherichia coli, fever, night sweats
Exam
orchalgia with reactive hydrocele, nodular prostate on digital rectal examination
1st investigation
- urine dipstick:
leukocyte esterase-positive; positive for red blood cells
- acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear and culture of extrapulmonary biopsy specimen:
positive
More - chest x-ray:
may demonstrate atelectasis from airway compression, pleural effusion, consolidation, pulmonary infiltrates, mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy, upper zone fibrosis
More - sputum acid-fast bacilli smear and culture:
presence of acid-fast bacilli (Ziehl-Neelsen stain) in specimen
More - nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT):
positive for M tuberculosis
More
Other investigations
- CT urography:
moth-eaten calyces with ulceration, calyceal obliteration, hydronephrosis, calcification, calculi, small bladder
- lateral flow urine lipoarabinomannan (LF-LAM) assay:
positive
More
Benign familial haematuria (thin basement membrane nephropathy)
History
recurrent, persistent visible and non-visible haematuria, family history of haematuria
Exam
oedema and hypertension
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
dysmorphic red cells, red cell casts, proteinuria, increase in urinary albumin excretion
More - :
raised (creatinine >2.0 mg/dL, BUN >20 mg/dL)
- urea and creatinine:
- 24-hour urine collection for protein:
>1 g/24 hours
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
thinning of the glomerular basement membrane
More
Post-infectious glomerulonephritis
History
abrupt onset of oedema, weakness, malaise, visible haematuria, headache, 1-2 weeks post-pharyngitis, 2-4 weeks after streptococcal dermatitis, most common from age 2-10 years
Exam
periorbital and peripheral oedema, hypertension, skin rashes
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
dysmorphic red cells, red cell casts, proteinuria, increase in urinary albumin excretion
More - urea and creatinine:
raised (creatinine >177 micromol/L, urea >7.1 mmol/L)
- 24-hour urine collection for protein:
may indicate proteinuria
Other investigations
- serum antistreptolysin O titre:
raised, or normal
More
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
History
abrupt onset of dependent or periorbital oedema, fatigue, recurrent visible haematuria, headache from hypertension, oliguria
Exam
periorbital and peripheral oedema, hypertension, conjunctival pallor, retinal drusen
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
dysmorphic red cells, red cell casts, proteinuria, increase in urinary albumin excretion
More - urea and creatinine:
raised (creatinine >177 micromol/L, urea >7.1 mmol/L)
- 24-hour urine collection for protein:
may indicate proteinuria
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
History
prodromal symptoms of malaise, fever, arthralgias, anorexia, and myalgias; abdominal pain, painful skin nodules or ulcerations
Exam
hypertension, painful cutaneous nodules, conjunctivitis, uveitis, oliguria
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
dysmorphic red cells, red cell casts, proteinuria, increase in urinary albumin excretion
More - urea and creatinine:
raised (creatinine >177 micromol/L, urea >7.1 mmol/L)
- 24-hour urine collection for protein:
may indicate proteinuria
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
hypercellular, sclerotic glomeruli with crescentic inclusions
More
IgA nephropathy
History
recurrent macroscopic haematuria associated with upper respiratory tract infections
Exam
generally asymptomatic, occasional hypertension
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
red blood cell casts, mild proteinuria
More - urea and creatinine:
raised (creatinine >177 micromol/L, urea >7.1 mmol/L)
- 24-hour urine collection for protein:
may indicate proteinuria
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
IgA deposition in the mesangium, proliferative crescents in severe cases
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
History
arthralgias, low-grade fever, fatigue, malaise, anorexia, nausea, weight loss, seizures, pleuritic pain, photosensitivity
Exam
malar, butterfly or discoid rash, oral or vaginal ulcers, retinal vasculitis, systolic murmur
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
pyuria, red blood cells, granular casts, proteinuria
More - urea and creatinine:
raised (creatinine >177 micromol/L, urea >7.1 mmol/L)
- 24-hour urine collection for protein:
may indicate proteinuria
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
mild glomerulitis to widespread immunoglobulin deposition and proliferative crescent formation
- lupus serologies (ANA, anti-dsDNA, antiphospholipid antibody):
raised
- serum complement (C3, C4):
low
- activated partial thromboplastin time:
may be prolonged in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies
More - chest x-ray:
pleural effusion, infiltrates, cardiomegaly
More - ECG:
may exclude other causes of chest pain
More
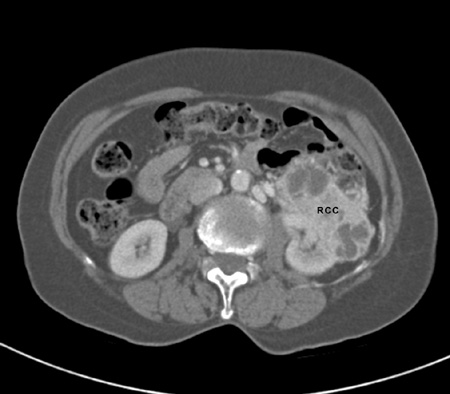
Renal cancer
History
flank fullness, history of dialysis, history of smoking, family history of renal cell carcinoma, polycystic kidney disease, weight loss, exposure to environmental/chemical carcinogens; most cases detected incidentally on imaging
Exam
hypertension, flank mass, adenopathy, new onset of left varicocele, lower extremity oedemas
1st investigation
Metastatic renal cancer
History
history of primary lung, breast, or gastrointestinal malignancy, weight loss
Exam
cachexia, anaemia, cough, right upper quadrant pain, neurological deficits, lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- CT abdomen with and without intravenous contrast:
contrast enhancing renal mass
More
Other investigations
- MRI abdomen/pelvis:
renal mass, regional lymphadenopathy, and/or visceral/bone metastases
More
Urethral cancer
History
more common in men, African-Americans, and those aged over 50 years; frequency, hesitancy, obstructive urinary symptoms
Exam
palpable mass, hard stricture
1st investigation
- CT urography:
filling defect, mass
- voiding cystourethrogram:
filling defect, mass
More
Other investigations
- urethroscopy:
visible urethral mass
- MRI:
will help determine the depth of invasion and the stage of disease
Penile cancer
History
history of penile lesion, history of condyloma
Exam
erythematous patch, induration, palpable mass, inguinal lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- skin biopsy:
squamous cell carcinoma
Other investigations
- MRI/CT pelvis:
will effectively stage the extent of disease
Placenta percreta
History
painless vaginal bleeding in the first or second trimester, history of prior caesarean section, advanced age during pregnancy
Exam
haemodynamic instability, sudden abdominal pain, distention
1st investigation
- pelvic ultrasound with Doppler studies:
placental erosion through uterine wall, loss of hypo-echoic boundary between the placenta, bladder wall, and surrounding organs; sonolucent spaces, representing placental lacunae, adjacent to myometrium and surrounding structures
- MRI:
placental erosion through uterine wall
Other investigations
Endometriosis
History
cyclic haematuria following menses, women of reproductive age, nulliparous women with short menstrual cycles, dysmenorrhoea, chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, pain responsive to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and oral contraceptives
Exam
abdominal or suprapubic tenderness especially during palpation of the uterosacral ligaments and adnexa
1st investigation
- transvaginal pelvic ultrasound:
pelvic mass, endometrial cysts
Other investigations
- CT urography:
filling defect, mass
More - cystoscopy:
bladder endometrioid tissue
- hysterosalpingography:
endometrioid tissue
Bladder stone
History
suprapubic pain, haematuria, bladder outlet obstructive symptoms, previous surgery
Exam
suprapubic tenderness
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
haematuria, leukocyte esterase, nitrites
More - non-contrast CT abdomen:
bladder stone
Other investigations
- kidney, ureter, bladder x-ray:
radio-opaque bladder stone
More
Radiation cystitis
History
history of pelvic radiation, dysuria, urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia, haematuria, timing and dosage of prior radiation
Exam
suprapubic tenderness
1st investigation
- cystoscopy:
inflamed bladder mucosa
Other investigations
Nephrotoxic/cytotoxic drugs
History
history of analgesic use or misuse, aminoglycosides, cyclophosphamide, ciclosporin, chemotherapy, cabazitaxel, penicillins, sulfonamides, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, recurrent haematuria, flank pain, dysuria
Exam
hypotension, oedema, suprapubic pain
1st investigation
Other investigations
- cystoscopy:
amyloid deposits, haemorrhagic inflammation
Anticoagulation
History
history of atrial fibrillation, mechanical valve, stroke, bruising, bleeding gums
Exam
pelvic mass, costovertebral angle tenderness, bruising, bleeding gums
1st investigation
- coagulation studies:
abnormal
More
Exercise-induced haematuria
History
recent history of vigorous exercise
Exam
physical examination is usually normal
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
red blood cells
Other investigations
Loin pain haematuria syndrome
History
young women, intermittent haematuria, intermittent flank pain ranging from mild to severe, oral contraceptive use
Exam
low-grade fever
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
diagnosis is clinical, and further tests are not routinely recommended
Other investigations
Pseudohaematuria
History
consumption of certain foods such as beetroot, blackberries, rhubarb or drugs (such as rifampicin, phenytoin, levodopa, methyldopa, quinine) known to discolour urine
Exam
physical examination is normal
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
diagnosis is clinical, and further tests are not routinely recommended
Other investigations
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer