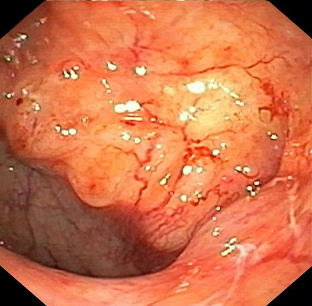
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- neck mass
- epistaxis or bloody nasal discharge
- nasal obstruction
- tinnitus or impaired hearing
- unilateral otitis media with effusion
- cranial nerve palsy
Other diagnostic factors
- headaches
- diplopia or strabismus
- facial numbness
- fever
- night sweats
- unintentional weight loss
Risk factors
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection
- diet high in salted fish
- first-degree relative with nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC)
- smoking
- human papilloma virus (HPV) infection
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- nasopharyngoscopy
- tumour biopsy
- MRI of the nasopharynx, skull base, and neck (to clavicles)
- 18F-FDG-PET/chest CT
Investigations to consider
- plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA
- Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNA in situ hybridisation (EBER ISH)
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Hyunseok Kang, MD, MPH
Professor
Department of Medicine
University of California
San Francisco
CA
Disclosures
HK has been paid by Coherus Biosciences, and HLB Group for serving their scientific advisory board. HK is a paid consultant for PIN therapeutics and Bayer. HK has been paid by MitoImmune for serving the data safety monitoring board. HK's institution has been paid by PDS Biotechnology, NeoImmuneTech, Lilly, Remix Therapeutics, and Merus for contracted research. HK's institution has been paid by NRG Oncology's grant program. HK has been paid by Wiley, OncLive, Massachusetts Medical Association, and AXIS medical education for developing educational content.
Jason Chan, MD
Assistant Professor
Department of Radiation Oncology
University of California
San Francisco
CA
Disclosures
JC declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Kevin J. Harrington, PhD, FRCP, FRCR
Head of Division of Radiotherapy and Imaging
The Institute of Cancer Research
London
UK
Disclosures
KJH has received honoraria for Scientific Advisory Boards and/or Lectures/Symposia from Arch Oncology, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Codiak, F-Star, Inzen, Johnson and Johnson, Merck-Serono, MSD, Pfizer, and Replimune.
Lawrence R. Lustig, MD
BMJ Best Practice ENT expert panel member
Professor and Chair
Department of Otolaryngology
Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons
New York
NY
Disclosures
LRL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Chen YP, Ismaila N, Chua MLK, et al. Chemotherapy in combination with radiotherapy for definitive-intent treatment of stage II-IVA nasopharyngeal carcinoma: CSCO and ASCO guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Mar 1;39(7):840-59.Full text Abstract
Bossi P, Chan AT, Licitra L, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2021 Apr;32(4):452-65.Full text Abstract
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: head and neck cancers [internet publication].Full text
Maghami E, Ismaila N, Alvarez A, et al. Diagnosis and management of squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary in the head and neck: ASCO guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Aug 1;38(22):2570-96.Full text Abstract
Lee AWM, Lee VHF, Ng WT, et al. A systematic review and recommendations on the use of plasma EBV DNA for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2021 Aug;153:109-22. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available here.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer