A history of sun and ultraviolet (UV) exposure may be observed as sun-damaged skin. Ask patients about their history of UV exposure; questioning about X-ray and arsenic exposure is advised.
A medical history of xeroderma pigmentosum, nevoid basal cell carcinoma (Gorlin-Goltz) syndrome, or transplantation (particularly solid organ) significantly increases risk for basal cell carcinoma (BCC).[31]Lambert WC, Lambert MW. Development of effective skin cancer treatment and prevention in xeroderma pigmentosum. Photochem Photobiol. 2015 Mar-Apr;91(2):475-83.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/php.12385
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25382223?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Bresler SC, Padwa BL, Granter SR. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome). Head Neck Pathol. 2016 Jun;10(2):119-24.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4838974
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26971503?tool=bestpractice.com
[40]Kanitakis J, Alhaj-Ibrahim L, Euvrard S, et al. Basal cell carcinomas developing in solid organ transplant recipients: clinicopathologic study of 176 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2003 Sep;139(9):1133-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12975154?tool=bestpractice.com
Skin examination
Perform a thorough skin examination; use good lighting and possibly handheld lenses or a dermoscope.[42]Nasr I, McGrath EJ, Harwood CA, et al; British Association of Dermatologists' Clinical Standards Unit. British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of adults with basal cell carcinoma 2021. Br J Dermatol. 2021 Nov;185(5):899-920.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bjd.20524
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34050920?tool=bestpractice.com
[43]Mogensen M, Jemec GB. Diagnosis of nonmelanoma skin cancer/keratinocyte carcinoma: a review of diagnostic accuracy of nonmelanoma skin cancer diagnostic tests and technologies. Dermatol Surg. 2007 Oct;33(10):1158-74.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17903149?tool=bestpractice.com
Undertake a full skin (whole body) examination for all patients with confirmed BCC, and consider performing one at initial presentation, especially if history or clinical evidence suggests a higher risk of skin cancer. People with BCC have an increased risk of developing other skin tumours (both keratinocyte carcinomas and melanoma), and patients may present with additional, concurrent precancers or cancers at other sites.[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
[45]Peris K, Fargnoli MC, Kaufmann R, et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma-update 2023. Eur J Cancer. 2023 Oct;192:113254.
https://www.ejcancer.com/article/S0959-8049(23)00356-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37604067?tool=bestpractice.com
Recognition of different types of BCC is essential, as the therapy will vary according to type.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Nodular basal cell carcinoma on the cheek, on background of diffuse solar damage with marked solar elastosisFrom the collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz [Citation ends].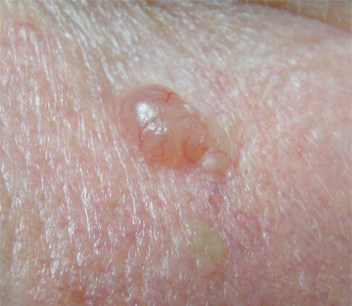 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Superficial BCC: A plaque somewhat translucent with focal crusting and ulceration, enlarging with a nodular qualityFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Superficial BCC: A plaque somewhat translucent with focal crusting and ulceration, enlarging with a nodular qualityFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends].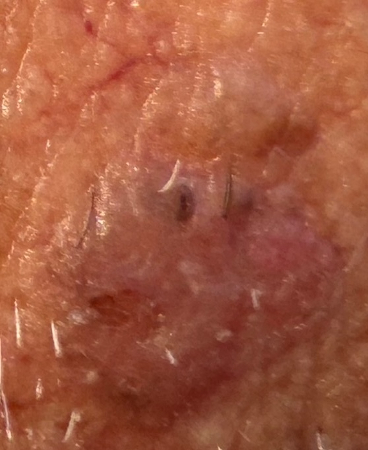 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Digital dermoscopy image of above superficial basal cell carcinoma utilizing Sklip PRO dermatoscopeFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Digital dermoscopy image of above superficial basal cell carcinoma utilizing Sklip PRO dermatoscopeFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends].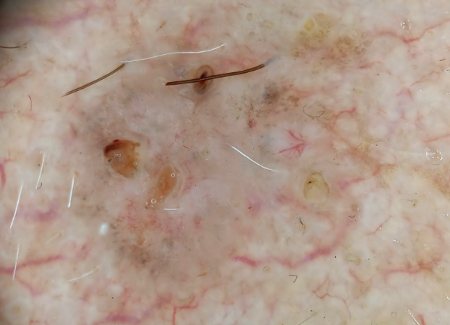
Seek the following characteristics of BCC:[3]Raasch BA, Buettner PG, Garbe C. Basal cell carcinoma: histological classification and body-site distribution. Br J Dermatol. 2006 Aug;155(2):401-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16882181?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Lear W, Dahlke E, Murray CA. Basal cell carcinoma: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and associated risk factors. J Cutan Med Surg. 2007 Jan-Feb;11(1):19-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17274935?tool=bestpractice.com
[45]Peris K, Fargnoli MC, Kaufmann R, et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma-update 2023. Eur J Cancer. 2023 Oct;192:113254.
https://www.ejcancer.com/article/S0959-8049(23)00356-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37604067?tool=bestpractice.com
Pearly papules and/or plaques
Non-healing scabs
Small crusts and non-healing wounds
Plaques, nodules, and tumours with rolled borders
Papules with associated telangiectasias.
Additionally, stretching skin under a good light source (the 'stretch test') will accentuate the pearly nature of the tumour and has been shown to improve diagnostic accuracy.[42]Nasr I, McGrath EJ, Harwood CA, et al; British Association of Dermatologists' Clinical Standards Unit. British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of adults with basal cell carcinoma 2021. Br J Dermatol. 2021 Nov;185(5):899-920.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bjd.20524
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34050920?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Newlands C, Currie R, Memon A, et al. Non-melanoma skin cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines. J Laryngol Otol. 2016 May;130(S2):S125-32.
https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-laryngology-and-otology/article/nonmelanoma-skin-cancer-united-kingdom-national-multidisciplinary-guidelines/EC5EF7B3A87F26984E49F02239E1AD31
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27841126?tool=bestpractice.com
Biopsy
Either a shave biopsy or punch biopsy, depending on size and location of tumour, can be performed.[42]Nasr I, McGrath EJ, Harwood CA, et al; British Association of Dermatologists' Clinical Standards Unit. British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of adults with basal cell carcinoma 2021. Br J Dermatol. 2021 Nov;185(5):899-920.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bjd.20524
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34050920?tool=bestpractice.com
[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
[45]Peris K, Fargnoli MC, Kaufmann R, et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma-update 2023. Eur J Cancer. 2023 Oct;192:113254.
https://www.ejcancer.com/article/S0959-8049(23)00356-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37604067?tool=bestpractice.com
[47]Kim JYS, Kozlow JH, Mittal B, et al; Work Group, Invited Reviewers. Guidelines of care for the management of basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Mar;78(3):540-59.
https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(17)32529-X/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29331385?tool=bestpractice.com
Deep reticular dermis should be included in the biopsy to avoid missing an infiltrative histology, which may sometimes be present only at the deeper, advancing margins of a tumour.[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
A punch biopsy is best used in cosmetically non-challenging areas, as it requires closure with stitches. An advantage of punch biopsy is that the tools may be available in sizes of up to 12 mm, and therefore lesions smaller than this can be removed in a single procedure, facilitating simultaneous diagnosis and treatment.[48]Stulberg D, Crandell B, Fawcett RS. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. Am Fam Physician. 2004 Oct 15;70(8):1481-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15526735?tool=bestpractice.com
Reserve a shave biopsy for cosmetically challenging areas such as the face.
Dermatohistopathology
The histopathological diagnosis of BCC is often straightforward. Occasionally, distinction from other neoplasms, such as a trichoepithelioma, may be challenging. A BCC manifests dermal masses of varying sizes and shapes composed of uniform basophilic cells with large oval nuclei and scant cytoplasm. These masses are often tightly associated with epidermis or a follicular opening, and have a peripheral cell layer demonstrating a palisading pattern of nuclei.[3]Raasch BA, Buettner PG, Garbe C. Basal cell carcinoma: histological classification and body-site distribution. Br J Dermatol. 2006 Aug;155(2):401-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16882181?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Lear W, Dahlke E, Murray CA. Basal cell carcinoma: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and associated risk factors. J Cutan Med Surg. 2007 Jan-Feb;11(1):19-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17274935?tool=bestpractice.com
[5]Barnhill RL, ed. Textbook of dermatopathology, 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2004.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histological appearance of basal cell carcinoma (20x, H-E stain); characteristic peripheral nuclear palisading, stroma-epithelium split, and so-called mucinous nature of the stroma are seenFrom the collection of Drazen M. Jukic, MD, PhD [Citation ends].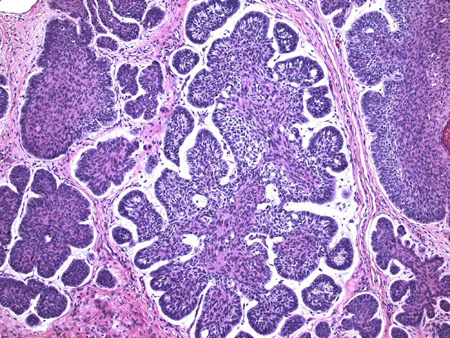
BCC is one of the human neoplasias with the highest mitotic rate (high mitotic activity), but it also has a high apoptotic rate. Thus, the neoplasm is overall slow-growing, and both features (mitotic and apoptotic figures) are used as one of the distinguishing criteria for diagnosis of BCC. In a small percentage, BCCs are pigmented and might resemble a melanoma clinically.[3]Raasch BA, Buettner PG, Garbe C. Basal cell carcinoma: histological classification and body-site distribution. Br J Dermatol. 2006 Aug;155(2):401-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16882181?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Lear W, Dahlke E, Murray CA. Basal cell carcinoma: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and associated risk factors. J Cutan Med Surg. 2007 Jan-Feb;11(1):19-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17274935?tool=bestpractice.com
Imaging for high risk or advanced disease
Consider magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) for:[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
Imaging studies are also indicated in rare instances where patients present with metastatic BCC.[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
Choice of imaging modality and targeted area depends on the suspected extent of disease after multidisciplinary discussion.[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
[45]Peris K, Fargnoli MC, Kaufmann R, et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma-update 2023. Eur J Cancer. 2023 Oct;192:113254.
https://www.ejcancer.com/article/S0959-8049(23)00356-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37604067?tool=bestpractice.com
MRI may be preferred for suspected perineural invasion or to gauge the extent of local disease. CT may be preferred for suspected bone involvement or to confirm and gauge the extent of nodal or distant metastasis.[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
Patients with low-risk BCC do not require imaging.[44]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: basal cell skin cancer [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1
[45]Peris K, Fargnoli MC, Kaufmann R, et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma-update 2023. Eur J Cancer. 2023 Oct;192:113254.
https://www.ejcancer.com/article/S0959-8049(23)00356-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37604067?tool=bestpractice.com
For details on risk stratification, see Criteria.
Emerging tests
In vivo multiphoton microscopy uses non-invasive, label-free, in vivo imaging to reveal several characteristic features of BCC lesions that may help facilitate diagnosis.[49]Balu M, Zachary CB, Harris RM, et al. In vivo multiphoton microscopy of basal cell carcinoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Oct;151(10):1068-74.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/2278674
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25909650?tool=bestpractice.com
Reflectance confocal microscopic technologies have become a popular method for non-invasive approaches to aid in the diagnosis of basal cell carcinomas.[45]Peris K, Fargnoli MC, Kaufmann R, et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma-update 2023. Eur J Cancer. 2023 Oct;192:113254.
https://www.ejcancer.com/article/S0959-8049(23)00356-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37604067?tool=bestpractice.com
[50]Foltz EA, Witkowski A, Becker AL, et al. Artificial intelligence applied to non-invasive imaging modalities in identification of nonmelanoma skin cancer: a systematic review. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;16(3):629.
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/3/629
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38339380?tool=bestpractice.com
[51]Verzì AE, Russo A, Castellino N, et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography of eyelid margin growths: A case series. Skin Res Technol. 2024 Jan;30(1):e13559.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/srt.13559
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38174775?tool=bestpractice.com
Adding artificial intelligence to non-invasive imaging has tremendous potential and is the subject of active investigation.[50]Foltz EA, Witkowski A, Becker AL, et al. Artificial intelligence applied to non-invasive imaging modalities in identification of nonmelanoma skin cancer: a systematic review. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;16(3):629.
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/3/629
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38339380?tool=bestpractice.com
However, further research is needed to isolate pooled diagnostic accuracy.[50]Foltz EA, Witkowski A, Becker AL, et al. Artificial intelligence applied to non-invasive imaging modalities in identification of nonmelanoma skin cancer: a systematic review. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;16(3):629.
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/3/629
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38339380?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Superficial BCC: A plaque somewhat translucent with focal crusting and ulceration, enlarging with a nodular qualityFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Superficial BCC: A plaque somewhat translucent with focal crusting and ulceration, enlarging with a nodular qualityFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Digital dermoscopy image of above superficial basal cell carcinoma utilizing Sklip PRO dermatoscopeFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Digital dermoscopy image of above superficial basal cell carcinoma utilizing Sklip PRO dermatoscopeFrom the personal collection of Prof. Robert A. Schwartz; used with permission [Citation ends].
