Differentials
Common
Polycystic ovary syndrome
History
oligomenorrhoea (<8 periods a year), infertility
Exam
clinical signs of hyperandrogenism other than hirsutism (acne, male-pattern alopecia); obesity (in about 50% of women); acanthosis nigricans may be present
1st investigation
Other investigations
- serum total and free testosterone:
elevated
More
Idiopathic hirsutism
History
regular menstrual cycles, no identifiable aetiology for the excessive hair growth
Exam
mild to moderate hirsutism
1st investigation
- total testosterone:
normal
More
Other investigations
Uncommon
Hyperprolactinaemia
Non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia
History
premature pubarche, short stature, acne, menstrual irregularity, oligomenorrhoea, primary amenorrhoea, infertility, early onset of hirsutism, family history of congenital adrenal hyperplasia[28]
Exam
acne, clitoromegaly (10% of the patients), alopecia (8%)[28]
1st investigation
- serum 17-hydroxyprogesterone:
>6 nanomol/L (200 nanograms/dL)
More
Other investigations
- adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test:
17-hydroxyprogesterone >45 nanomol/L (1500 nanograms/dL)
More
Cushing's syndrome
History
menstrual irregularity, bruising, emotional lability
Exam
hypertension, truncal obesity associated with nuchal fat pad, moon face, facial plethora, purple striae, proximal muscle weakness
Other investigations
- overnight dexamethasone suppression test:
morning cortisol >50 nanomol/L (1.8 micrograms/dL)
More
Androgenic drugs
History
use of androgenic drugs (e.g., anabolic or androgenic steroids, danazol, oral contraceptives with androgenic progestins)
Exam
mild to moderate hirsutism
1st investigation
- stop causative drug:
improvement in hirsutism
Other investigations
Androgen-secreting ovarian tumour
History
older age, rapid progression, virilisation
Exam
signs of virilisation; palpable abdominal mass or palpable mass on vaginal examination
1st investigation
Other investigations
- abdominal/pelvic MRI without and with gadolinium contrast:
presence of vascular vegetations in cystic masses and ascites, suggests malignancy
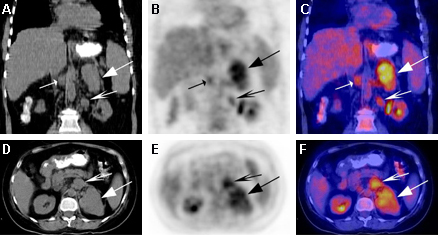
- PET, PET-CT, or PET/MRI:
presence of abnormal lesions; can help distinguish between benign and malignant ovarian tumours
Ovarian hyperthecosis
History
may occur after menopause, intense hirsutism of slow progression, virilisation, amenorrhoea, or irregular menses
Exam
obesity, virilisation (clitoromegaly, temporal balding, deepening of the voice, increased muscle mass), moderate to severe hirsutism, acanthosis nigricans
1st investigation
Other investigations
Adrenocortical carcinoma
History
abdominal pressure or pain, acne, progressive hirsutism, amenorrhoea or oligomenorrhoea, gynaecomastia, diabetes mellitus
Exam
hypertension, virilisation, cushingoid features (bruising, thin skin, facial plethora, purple striae)
1st investigation
- CT abdomen:
large and heterogenous mass, usually >4 cm, with irregular contour and >10 Hounsfield units on unenhanced CT; vascular mass on contrast-enhanced CT with contrast washout <60% at 15 minutes
Other investigations
- MRI abdomen:
hyperintense mass in relation to liver on T2-weighted images
- 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) PET:
focal activity in the lesion, may display central photopenic area surrounded by rim of intense activity if large tumour with necrotic centre
More
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer