Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- symptoms of anaemia (fatigue, weakness, dyspnoea, palpitations)
- constitutional symptoms (weight loss, night sweats, low-grade fever, cachexia, fatigue, and pruritus)
- splenomegaly ± hepatomegaly
- features of extramedullary haematopoiesis
Other diagnostic factors
- features of portal hypertension
- joint and bone pain
- hearing loss
- bleeding
- infections
Risk factors
- radiation exposure
- industrial solvents exposure
- age ≥65 years
- cytogenetic abnormalities
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
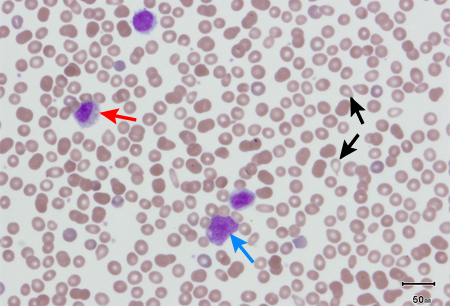
- FBC with differential
- peripheral blood smear
- bone marrow aspiration
- bone marrow biopsy
- fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) or or multiplex reverse transcriptase PCR
- genetic mutation analysis
Investigations to consider
- bone marrow cytogenetic analysis
- echocardiogram
- ultrasound of suspected site
- technetium 99 scan
- CT of suspected site
- MRI of suspected site
- serum uric acid
- antinuclear antibodies
- rheumatoid factor titre
- complement levels
- Coombs' test
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Jerry L. Spivak, MD

Professor of Medicine and Oncology
Division of Hematology
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
JLS is an author of several references cited in this topic and has been reimbursed by GSK for a consultation.
Acknowledgements
Professor Jerry Spivak would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Ashkan Emadi, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
AE declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
John T. Reilly, BSc, MD, FRCP, FRCPATH
Professor and Consultant in Haematology
Royal Hallamshire Hospital
Sheffield
UK
Disclosures
JTR is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Giovanni Barosi, MD
Director of the Laboratory of Clinical Epidemiology
IRCCS Policlinico S. Matteo Foundation
Pavia
Italy
Disclosures
GB declares that he has no competing interests.
Richard Silver, MD
Myeloproliferative Disorders Program Specialist
Department of Medicine
Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology
Weill Cornell Medical College
New York
NY
Disclosures
RS is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Tefferi A. Primary myelofibrosis: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2023 May;98(5):801-21.Full text Abstract
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: myeloproliferative neoplasms [internet publication].Full text
McLornan DP, Godfrey AL, Green A, et al. Diagnosis and evaluation of prognosis of myelofibrosis: a British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2024 Jan;204(1):127-35.Full text Abstract
Kröger N, Bacigalupo A, Barbui T, et al. Indication and management of allogeneic haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in myelofibrosis: updated recommendations by the EBMT/ELN International Working Group. Lancet Haematol. 2024 Jan;11(1):e62-74. Abstract
McLornan DP, Psaila B, Ewing J, et al. The management of myelofibrosis: a British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2024 Jan;204(1):136-50.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available here.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer