Differentials
Common
Axial spondyloarthritis (Ankylosing spondylitis [AS])
History
oligoarticular involving large joints or polyarticular inflammatory joint involvement, inflammatory back pain
Exam
synovitis, spine involvement, enthesitis: dactylitis or tenderness at entheseal insertions such as the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia insertions; extra-articular manifestations: uveitis, psoriasis, keratoderma blennorrhagicum, erythema nodosum
1st investigation
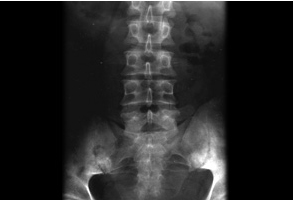
- plain x-rays of the pelvis:
sacroiliitis
More
Psoriatic arthritis
History
scalp or nail problems, joint pain and stiffness, pain at site of tendon attachment, spinal stiffness
Exam
peripheral arthritis, dactylitis, reduction of cervical spine mobility
1st investigation
- plain film x-rays of the hands and feet:
erosion in the distal interphalangeal joint, periarticular new-bone formation; osteolysis, pencil-in-cup deformity in advanced disease
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate and CRP:
normal or elevated
- anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody:
mostly negative
More
Other investigations
Reactive arthritis
History
oligoarticular involving large joints or polyarticular inflammatory joint involvement
Exam
synovitis, spine involvement, enthesitis: dactylitis or tenderness at entheseal insertions such as the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia insertions; extra-articular manifestations: uveitis, psoriasis, keratoderma blennorrhagicum, erythema nodosum; urethritis in males and mucopurulent cervicitis in females with sexually acquired reactive arthritis[89]
1st investigation
- plain film x-rays:
sacroiliitis or enthesopathy
More - erythrocyte sedimentation rate and CRP:
may be elevated
Other investigations
- urethral swab Gram stain:
≥5 polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNLs) per high power (x1000) microscopic field, and/or ≥10 PMNLs per high power (x1000) microscopic field
More - vaginal discharge swab Gram stain:
≥5 PMNLs per high power (x1000) microscopic field, and/or ≥10 PMNLs per high power (x1000) microscopic field
More - nucleic amplification tests:
positive for Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae
More
Undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy
History
oligoarticular involving large joints or polyarticular inflammatory joint involvement, inflammatory back pain
Exam
synovitis, spine involvement, enthesitis: dactylitis or tenderness at entheseal insertions such as the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia insertions; extra-articular manifestations: uveitis, psoriasis, keratoderma blennorrhagicum, erythema nodosum
1st investigation
- plain x-rays of the pelvis:
sacroiliitis
More
Other investigations
- plain x-rays of affected joints:
erosions, periostitis may be seen
- sonography:
synovitis, erosions, and enthesitis
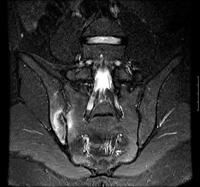
- MRI sacrum:
sacroiliitis
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD)
History
may present in 4 patterns: pseudo-rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis with synovitis, pseudogout, and monoarthropathy
Exam
synovitis, tophaceous deposits at the extensor surfaces and ears
1st investigation
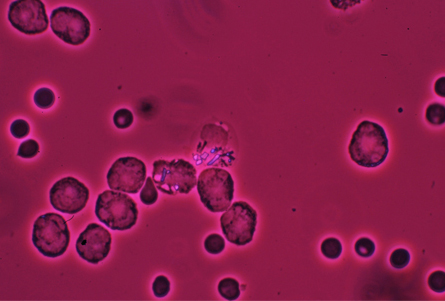
- joint aspiration:
calcium pyrophosphate dehydrated crystals
More
Other investigations
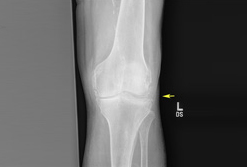
- plain x-rays:
chondrocalcinosis
More - musculoskeletal ultrasound:
chondrocalcinosis
Gout
History
acute onset, <50 years of age, severe joint pain
Exam
synovitis, tophaceous deposits at the extensor surfaces and ears
1st investigation
- joint aspiration:
white blood cell count >2 x 10^9/L (2000/mm^3) (mean: 20 x 10^9/L [20,000/mm^3]); strongly negative birefringent needle-shaped crystals under polarised light
More
Polymyalgia rheumatica
History
fever, night sweats; pain and stiffness of the shoulders and pelvic girdle that are most severe in the morning and last several hours
Exam
palpable synovitis in knees, wrists, metacarpophalangeal joints; oedema, decreased active range of motion of shoulders, neck, hips
Osteoarthritis (OA)
History
pain, functional difficulties, stiffness
Exam
hand, hip, and knee involvement; bony deformities particularly in the hands; tenderness; limited range of motion; bony malalignment is common, particularly in the knee
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
activity-related joint pain, morning stiffness that lasts no longer than 30 minutes, >45 years of age
More
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
History
complaints of multiple joint pain and swelling accompanied by early morning stiffness lasting for more than 1 hour
Exam
symmetrical polyarthritis with wrist and small joint involvement
1st investigation
Other investigations
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
History
young female with arthralgia, photosensitive rash, alopecia, mouth ulcers, pleurisy
Exam
small to medium joint polyarthritis, malar rash, hard palate ulcers, alopecia
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
low platelet count
- peripheral blood smear:
microangiopathy (in severe form)
- serum anti-nuclear andibody, anti-dsDNA, and anti-Smith antibodies:
positive
More - erthrocyte sedimentation rate:
elevated
Other investigations
Septic arthritis
History
usually acute monoarticular joint involvement, fever; risk factors: age >80 years, diabetes mellitus, history of rheumatoid arthritis, joint surgery, hip or knee prosthesis, skin infection, immunodeficiency
Exam
swollen, tender joint; rarely polyarticular
1st investigation
- joint aspirate for cell count, Gram stain, and culture:
synovial fluid white blood cell count >50 x 10^9/L (>50,000/mm^3), identification and growth of causative organism
More
Other investigations
Bacterial endocarditis
History
often insidious onset; chills, malaise, weight loss, night sweats, shortness of breath, leg oedema, hemisensory/motor deficit, arthralgia; history of rheumatic fever, recent dental work, prosthetic valve, intravenous drug use, or prior subacute bacterial endocarditis
Exam
new murmur, signs of congestive heart failure or peripheral emboli (splinter haemorrhages, Osler's nodes, Janeway lesions), Roth's spots, or retinal haemorrhages, focal neurological deficit
1st investigation
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
elevated
More - transthoracic echocardiography:
vegetation, cardiac valve incompetence
Other investigations
Viral arthritis
History
acute polyarthritis, may be fever; parvovirus B19 infection presents acutely with polyarticular symmetrical arthralgia without significant swelling; may be risk factors for specific infections, history of travel in Southeast Asia, the Caribbean, or South America, and mosquito bite with chikungunya virus infection; a minority of people with chikungunya infection go on to develop chronic symptoms
Exam
multiple tender joints without significant synovial effusion; may be skin rash: for example, morbilliform rash, hyperpigmentation, and intertriginous lesions with chikungunya virus infection
1st investigation
- parvovirus B19 serology:
may be positive
More - hepatitis A, B, C serology:
may be positive
- HIV antibodies:
may be positive
- chikungunya serology:
may be positive
Other investigations
- hepatitis B or C polymerase chain reaction (PCR):
may be positive
- HIV PCR:
may be positive
- chikungunya PCR:
may be positive
Uncommon
Enteropathic arthritis
History
abdominal pain, diarrhoea, fever, fatigue, lower gastrointestinal bleeding, altered bowel habit, loss of appetite, weight loss
Exam
joint inflammation, uveitis, abdominal mass or tenderness, rectal fistula, positive faecal occult blood test
1st investigation
- colonoscopy:
ulcerative colitis: erythema, mucosal granularity, friability, oedema, loss of vascularity; Crohn's disease: ulcerations with cobblestone appearance, normal rectum
Other investigations
- barium enema:
ulcerative colitis: diffuse reticulated pattern, microulcerations, loss of haustra, luminal narrowing, polyps; Crohn's disease: extensive ulcerations, nodularity, ileocaecal narrowing, fistula
- upper gastrointestinal series:
inflammation, filling abnormalities, fistula
Remitting seronegative symmetrical synovitis with pitting oedema syndrome
History
men >50 years of age, acute-onset polyarthritis
Exam
bilateral hand pitting oedema, synovitis
1st investigation
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
elevated
Other investigations
- CRP:
elevated
- corticosteroid challenge:
improvement in symptoms
More
Sarcoidosis
History
often in young black women, dyspnoea, cough, uveitis, fever, fatigue, weight loss
Exam
rarely neck lymphadenopathy; otherwise may be normal
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
low platelet count; white blood cell count may be normal or elevated
- peripheral blood smear:
low platelet count; otherwise normal
- CXR:
bilateral hilar and right paratracheal adenopathy, although isolated bilateral hilar adenopathy more frequent; bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, predominantly in the upper lobes; pleural effusions (rare) and egg shell calcifications (very rare) may be seen
More
Other investigations
- serum ACE level:
elevated
More
Juvenile-onset or adult-onset idiopathic arthritis
History
periodic, transient fevers associated with rapid rash onset; rash disappears as the fever remits; arthritis and myalgia commonly present
Exam
fever, salmon-pink macular rash, favours the trunk and sites of pressure; joint pain, inflammation commonly affecting knees, ankles (juvenile), and carpals (adults)
Overlap syndrome
History
arthralgias, myalgias, photosensitive rash, alopecia, mouth ulcers, pleurisy, fatigue, dry eyes, dry mouth, painless loss of function of hands, heartburn, reflux and dysphagia, weight loss, swelling of the hands and feet, dyspnoea, difficulty with motor tasks, fatigue and generalised malaise, proximal muscle weakness, pruritus, fever
Exam
arthritis, basal crepitations, sclerodactyly, sclerodermatous skin changes, lymphadenopathy[12]
1st investigation
- serum anti-nuclear antibody (ANA):
positive
More - anti-ribonucleoprotein antibodies:
positive
- FBC:
may be normal; microcytic anaemia with chronic gastrointestinal bleed; microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia with scleroderma renal crisis
- urea and serum creatinine:
usually normal
More - erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
usually normal, occasionally elevated
- CRP:
usually normal
- urine microscopy:
usually normal
More - ECG:
normal; may show cardiac involvement (arrhythmias)
- CXR:
normal; bibasilar interstitial infiltrates; cardiomegaly or signs of right heart failure may be present
Sjogren's syndrome
History
fatigue, dry eyes, dry mouth, arthralgia, myalgia
Exam
arthritis, dental caries, corneal ulceration, no saliva pool, enlarged salivary glands
1st investigation
- Schirmer's test:
positive
- anti-60 kDa (Sjogren's syndrome A) Ro and anti-La (Sjogren's syndrome B):
positive
Other investigations
Scleroderma
History
painless loss of function of hands, heartburn, reflux and dysphagia, weight loss, arthralgias and myalgias, fatigue, swelling of the hands and feet, dyspnoea
Exam
sclerodactyly, skin thickening, digital pits or ulcers, Raynaud's phenomenon, abnormal nail-fold capillaroscopy, subcutaneous calcinosis
1st investigation
- serum autoantibodies:
positive anti-nuclear antibodies in >90% of patients
- FBC:
may be normal; microcytic anaemia with chronic gastrointestinal bleed; microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia with scleroderma renal crisis
- urea and serum creatinine:
usually normal; elevated serum urea and creatinine with scleroderma renal crisis
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
usually normal, occasionally elevated
- CRP:
usually normal
- urine microscopy:
normal; mild proteinuria with few cells or casts occurs with scleroderma renal crisis
- ECG:
normal; may demonstrate cardiac involvement such as arrhythmias
- CXR:
normal; evidence of interstitial lung disease demonstrated by bibasilar interstitial infiltrates; cardiomegaly or signs of right heart failure may be present
Other investigations
- pulmonary function tests (spirometry, lung volumes and diffusion capacity measurement):
interstitial lung disease: a decrease in forced vital capacity and diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) plus an overall restrictive pattern; pulmonary hypertension: a disproportionate drop in DLCO compared with FVC
- echocardiography:
pulmonary hypertension: a rise in right ventricular systolic pressure; pericardial effusion, right ventricle or left ventricle diastolic dysfunction may be present
Polymyositis
History
difficulty with motor tasks, fatigue and generalised malaise, shortness of breath, weight loss, dysphagia, arthralgia, myalgia
Exam
muscle weakness, muscle atrophy
1st investigation
- serum creatine kinase:
elevated
- electromyography:
short duration, low amplitude, polyphasic units with early recruitment on voluntary activity; diffuse spontaneous activity with fibrillation and positive sharp waves at rest
- aldolase:
elevated
- LDH:
elevated
- alanine transaminases:
elevated
- myoglobin:
elevated
Other investigations
- muscle biopsy:
endomysial inflammatory infiltrates, muscle necrosis, atrophy, muscle fibre regeneration
Dermatomyositis
History
proximal muscle weakness, pruritus, fatigue and malaise, fever, arthralgia, myalgia, dyspnoea, weight loss
Exam
Gottron's papules, heliotrope rash with or without periorbital oedema, macular violaceous erythema; periungual erythema, nail-fold capillary dilation, cuticular overgrowth, 'mechanic's' hands, photosensitivity, poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans
1st investigation
- serum creatine kinase:
high levels
- serum aldolase:
high levels
- electromyography:
abnormal spontaneous activity (fibrillation and positive sharp waves) and abnormal voluntary activity (low-amplitude, short-duration polyphasic motor potentials)
- anti-nuclear antibodies:
positive
Other investigations
- muscle biopsy:
perivascular or interfascicular inflammation; endothelial hyperplasia in the intramuscular blood vessels; perifascicular atrophy
- myositis-specific antibodies and myositis-associated antibodies:
positive
- skin biopsy:
vacuolar alteration of the basal layer of the epidermis; necrotic keratinocytes; vascular dilation; perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate
Systemic vasculitis
History
arthralgia, constitutional symptoms, purpura, abdominal pain, cutaneous ulcers, haemoptysis, headache and scalp tenderness
Exam
asymmetrical brachial pulses, bruit, visual changes, haematuria, foot drop, wrist drop
1st investigation
Other investigations
- liver function test:
may be elevated
More - FBC:
anaemia, schistocytes may be seen
- biopsy of affected tissue:
vessel wall necrosis, fibrinoid necrosis, karyorrhexis, and red blood cell extravasation
Gonococcal arthritis
History
in disseminated gonococcal infection: knees, wrists, ankles, and elbows are most affected; tenosynovitis in hands, ankles, knees, and feet
Exam
swollen, tender joint; rarely polyarticular, dermatitis may present as a maculopapular or a vesicular rash
1st investigation
- nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT):
positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- culture:
positive chocolate agar culture
More
Other investigations
Rheumatic fever
History
fever, migratory arthritis, Sydenham's chorea, epistaxis, abdominal pain; heart involvement may be asymptomatic or cause chest pain, dyspnoea
Exam
joint swelling, ring- or snake-shaped skin eruptions on the trunk and upper arms and legs, skin nodules, pericardial friction rub, murmur
1st investigation
- anti-streptolysin O (ASO) or anti-deoxyribonuclease B (anti-DNase B) titres:
increased or rising ASO or anti-DNase B titres taken at least 2 weeks apart. Fourfold increase or decrease in titres may suggest recent infection.
- throat culture:
growth of beta-haemolytic group A streptococci
More - rapid molecular test:
positive
More - rapid antigen test for group A streptococci:
positive
- ECG:
normal or conductance abnormalities
More
Other investigations
- echocardiography:
carditis, mitral or aortic valve vegetations or regurgitation
Lyme disease
Whipple's disease
History
arthralgia, fever, diarrhoea
Exam
skin hyperpigmentation, lymphadenopathy, oligo- or polyarthritis
1st investigation
- blood and cerebrospinal fluid polymerase chain reaction:
may show Tropheryma whipplei
Other investigations
- duodenal biopsy:
presence of periodic acid-Schiff positive organisms in the lamina propria of the small intestine
Tuberculous arthritis
History
osteoarticular tuberculosis (TB): back pain; hip, knee, or hand pain; or pain due to underlying osteomyelitis
Exam
decreased, painful range of motion of the spine and hip; tender swelling of knee; hand pain and swelling
1st investigation
- synovial smear and culture:
positive for TB
Other investigations
- synovial biopsy and culture:
positive for TB
- plain x-rays of joints:
lytic lesions near joints with sparse periosteal reaction
More
Paraneoplastic arthritis
History
Exam
hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, synovitis
1st investigation
- malignancy screening:
neoplasm
Other investigations
Neoplastic carcinomatosis
History
constitutional symptoms, extreme pain, monoarticular or polyarticular concurrent with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, acute and chronic leukemia; no response to conventional therapy
Exam
asymmetrical distribution, affliction of predominantly lower extremities, synovitis, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- malignancy screening:
neoplasm
Other investigations
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer