Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- fever
- lymphadenopathy
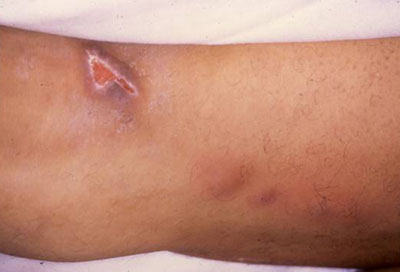
- painful skin ulcer
- unilateral conjunctivitis
Other diagnostic factors
- headache
- malaise/fatigue
- myalgia
- anorexia
- abdominal pain
- vomiting
- rales
- non-productive cough/dyspnoea
- sore throat
- photophobia
- vision impairment/loss
- jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, diarrhoea
- positive Kernig's/Brudzinski's sign, stiff neck
Risk factors
- tick exposure
- biting fly exposure
- contact with infected animals
- outdoor work in areas where infected animals live
- spring or summer season
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- FBC
- serum electrolyte levels
- LFTs
- serum creatine kinase
- urine dipstick for blood
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- serology
- blood culture
- specimen culture
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of ulcer swab or lymph node aspirate
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
William A. Petri, Jr., MD, PhD, FACP

Wade Hampton Frost Professor of Epidemiology
Professor of Medicine, Microbiology, and Pathology
Chief, Division of Infectious Diseases and International Health
University of Virginia
Charlottesville
VA
Disclosures
WAP declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Christopher Huston, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases
University of Vermont College of Medicine
Burlington
VT
Disclosures
CH declares that he has no competing interests.
Beth Kirkpatrick, MD
Assistant Professor
Infectious Diseases
University of Vermont College of Medicine
Burlington
VT
Disclosures
BK declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tickborne diseases of the United States: a reference manual for health care providers, sixth edition. Aug 2022 [internet publication].Full text
World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Guidelines on tularaemia. 2007 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available here.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer