Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- polyuria
- polydipsia
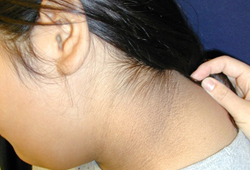
- acanthosis nigricans
- nocturia
Other diagnostic factors
- hypertension
- yeast infections
- skin infections
- urinary tract infections
- fatigue
- blurred vision
- weight loss
Risk factors
- obesity
- genetic predisposition/family history
- high-risk ethnic background
- puberty
- female sex
- diabetic in-utero environment
- small for gestation age
- rapid growth in infancy
- bottle feeding
- high protein intake in infancy
- polycystic ovaries
- intra-myocellular lipid content
- fat deposition in the liver
- learning disability
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- urine dipstick
- random plasma glucose
- fasting plasma glucose
- HbA1c
- autoantibodies to insulin, islet antigen 2 (IA-2), glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), and zinc transporter 8 (ZnT8)
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Jennifer Miller, MD

Professor
Department of Pediatrics
University of Florida
Gainesville
FL
Disclosures
JM declares that she has received research funding from Soleno Therapeutics, Harmony Biosciences, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. JM is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Chelsea Zimmerman, MD
Clinical Physician
Pediatric Endocrinology
Endocrinology and Metabolism of East Alabama
Opelika
AL
Disclosures
CZ declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Jennifer Miller and Dr Chelsea Zimmerman would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Arlan Rosenbloom and Dr Paul Hiers, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
AR is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. Unfortunately, we have since been made aware that AR is deceased. PH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Philip Zeitler, MD, PhD
Professor of Pediatrics and Clinical Science
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Aurora
CO
Disclosures
PZ declares that he has no competing interests.
Julian P. Hamilton-Shield, MB, ChB, MD(Bristol), MRCP, FRCPCH, FRCPCH
Professor
Diabetes and Metabolic Endocrinology
School of Clinical Sciences
University of Bristol
UK
Disclosures
In the past, JPHS received speaking honoraria from Sanofi-Aventis, Roche, Abbott, Novo-Nordisk, and Nutricia. None of these talks were directly pertinent to the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Kristen Nadeau, MD
Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Aurora
CO
Disclosures
KN declares that she has no competing interests.
Dennis Styne, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Rumsey Chair of Pediatric Endocrinology
University of California
Sacramento
CA
Disclosures
DS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes - 2025. Diabetes care. 2025 Jan;48(suppl 1):S1-352.Full text
Shah AS, Barrientos-Pérez M, Chang N, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2024: type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Horm Res Paediatr. 2024;97(6):555-83.Full text Abstract
Glaser N, Fritsch M, Priyambada L, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2022: diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022 Nov;23(7):835-56. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available here.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer