Differentials
Common
Hamartoma
History
usually asymptomatic
Exam
no physical findings are attributable to hamartomas
1st investigation
- CT chest:
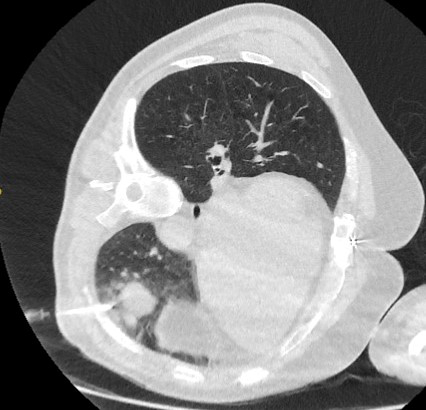
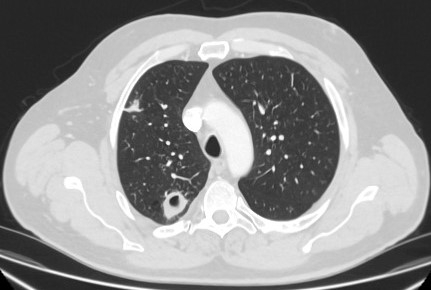
well-demarcated peripheral nodule, average diameter of 15 mm with heterogeneous appearance due to its content of mesenchymal tissue; fat attenuation is common, with or without calcification; popcorn calcifications can occur in some cases[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography (CT) section with soft tissue configuration, showing a right lung hamartoma, as incidental finding in an asymptomatic patient. Note the central calcification and several small spots of fat within the nodule. This nodule was stable over a 12 year period and no intervention requiredFrom the collection of Dr George Tsaknis, MD, PhD, FRCP(London), MRQA, MAcadMEd, PGCert; used with permission [Citation ends].
More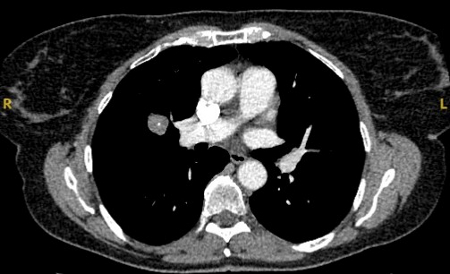
Other investigations
Infectious
History
intravenous drug use, bacteraemia due to extra-thoracic infection, travel to endemic areas, pet/animal exposures, and specific leisure activities (e.g., caving) or occupations (e.g., grain farmers); cough, dyspnoea, haemoptysis, weight loss, fever, joint aches, skin lesions, and night sweats; possible exposure to Histoplasma capsulatum, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Coccidioides immitis, Cryptococcus neoformans, Aspergillus, Pseudallescheria boydii, Fusarium, Zygomycetes, and others
Exam
non-specific skin findings may be seen in atypical mycobacteria and cryptococcosis; lymphadenopathy often present in active disease
1st investigation
- CT chest:
usually <20 mm diameter and round, with smooth borders; may have central, laminated, or diffuse calcification patterns if old; sometimes mediastinal lymphadenopathy with or without lymph node calcifications
More
Primary lung cancer
History
new cough, haemoptysis, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss, paraneoplastic syndromes (e.g., general, renal, endocrine, neurological, cutaneous, rheumatological, haematological)
Exam
clubbing, focal wheezing, rales, decreased breath sounds and dullness to percussion, dilated neck/chest veins
1st investigation
- CT chest:
nodule typically in upper lobe, with irregular or spiculated borders, and largely non-calcified; the larger the nodule, the higher the probability of malignancy
More
Other investigations
Metastatic cancer
History
symptoms related to the primary site and general symptoms of pain, weight loss, malaise, cough, dyspnoea
Exam
clubbing, focal wheezing; abnormal physical findings may or may not be present
1st investigation
- CT chest:
one or multiple nodules of variable sizes from diffuse micronodular shadows (miliary) to well-defined masses; often irregular and often in the periphery of the lower lung zones
More
Intrapulmonary lymph node
History
history is non-specific (considered an anatomical variant); more commonly a history of smoking
Exam
no specific findings
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
smooth marginated, round or ovoid nodule, 5-12 mm in diameter with soft-tissue attenuation
More - CT chest:
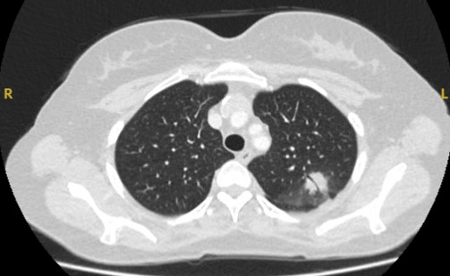
5-12 mm subpleural nodule[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography (CT) showing a small peripheral triangular nodule in the right lower lobe, consistent with an intrapulmonary lymph nodeFrom the collection of Dr George Tsaknis, MD, PhD, FRCP(London), MRQA, MAcadMEd, PGCert; used with permission [Citation ends].
Other investigations
Sarcoidosis
History
cough, dyspnoea, fatigue, weight loss, fever, night sweats, rash, eye pain, photophobia, blurred vision, red eye
Exam
pulmonary examination is usually unrevealing; can affect any organ, so physical findings depend on specific organs affected; skin lesions, including maculopapular eruptions, subcutaneous nodular lesions, red-purple skin lesions
1st investigation
- CT chest:
adenopathy often present with sarcoid; sarcoid nodules have a predilection for the upper zones, though can be located throughout the lung
More
Other investigations
- flexible bronchoscopy/CT-guided TTNA:
presence of non-caseating granulomas
More
Rheumatoid arthritis
History
arthralgias, pain, skin nodules
Exam
pleural effusions, pleuritis, joint pain and deformity, skin nodules
1st investigation
- CT chest:
shows lung nodule 3 mm to 70 mm, predominantly in peripheral upper and mid lung zones[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography (CT) showing a right upper lobe apical solid nodule with a surrounding ‘ground glass’ halo, in a patient with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis on methotrexate. Other similar nodules were seen throughout both lungs, and remain stable for >2 years, consistent with inflammatory benign rheumatoid nodulesFrom the collection of Dr George Tsaknis, MD, PhD, FRCP(London), MRQA, MAcadMEd, PGCert; used with permission [Citation ends].
More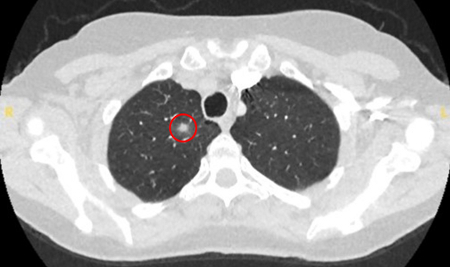
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis)
History
cough, chest pain, dyspnoea, haemoptysis, rhinorrhoea, epistaxis, ear/sinus pain, hoarseness, fever, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss
Exam
palpable purpura, painful ulcers, uveitis, wheezing, sinus tenderness
1st investigation
- CT chest:
solitary or multiple lung nodules; airways are frequently affected
More
Uncommon
Carcinoid tumour
History
often asymptomatic; may cause cough, dyspnoea, haemoptysis, and/or wheezing if nodule is endobronchial; carcinoid syndrome (flushing/diarrhoea/abdominal cramping/swelling of peripheries/wheezing) is uncommon, occurring mainly in patients with liver metastases
Exam
often normal examination; may present with unilateral wheezing
1st investigation
- CT chest:
80% appear as an endobronchial nodule, 20% as a parenchymal nodule, with smooth borders, rounded and highly vascularised
More
Other investigations
- flexible bronchoscopy with biopsy:
usually shows raised, pinkish, vascular, lobulated lesions; presence of malignant cells from biopsy is diagnostic
More
Lymphoma
History
non-productive cough, chest pain, fever, haemoptysis, dyspnoea, night sweats, weight loss; >50% of patients with disease limited to the thorax are asymptomatic
Exam
often normal; may present with respiratory crackles and non-resolving pneumonia
1st investigation
- CT chest:
variable pattern with unilateral or bilateral disease, and isolated or multiple opacities; air bronchograms are a characteristic feature, with haloes of ground-glass shadowing around the lesion margins
More
Arteriovenous malformation
History
dyspnoea is uncommon; arteriovenous malformation may be identified in the work-up of stroke, right-to-left shunt, or haemoptysis
Exam
pulmonary bruit; arteriovenous communications, or haemorrhagic telangiectasia in the skin, mucous membranes, and other organs; cyanosis, clubbing, and dyspnoea; neurological signs from cerebral aneurysms, cerebral emboli, or metastatic abscess
1st investigation
- CT chest:
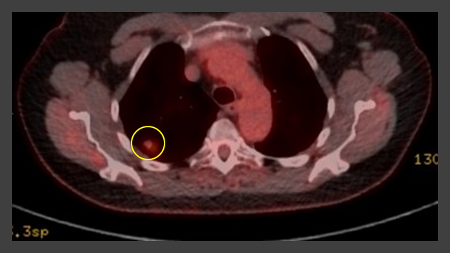
round or oval nodule(s) with feeding artery and draining vein often identified[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography (CT) showing a left upper lobe peripheral elongated nodule, with contrast enhancement and a clear feeding and draining side, consistent with a small arteriovenous malformationFrom the collection of Dr George Tsaknis, MD, PhD, FRCP(London), MRQA, MAcadMEd, PGCert; used with permission [Citation ends].
More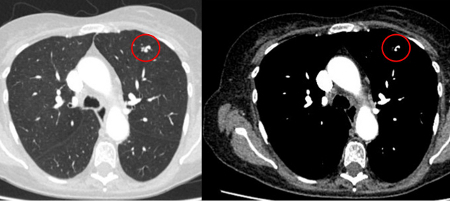 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography (CT) showing a right lower lobe large nodule, with contrast enhancement and a clear feeding and draining side, consistent with an arteriovenous malformationFrom the collection of Dr George Tsaknis, MD, PhD, FRCP(London), MRQA, MAcadMEd, PGCert; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography (CT) showing a right lower lobe large nodule, with contrast enhancement and a clear feeding and draining side, consistent with an arteriovenous malformationFrom the collection of Dr George Tsaknis, MD, PhD, FRCP(London), MRQA, MAcadMEd, PGCert; used with permission [Citation ends].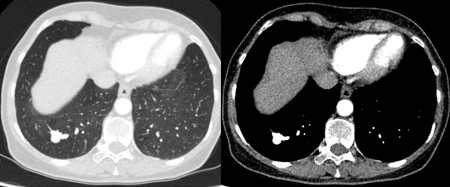
Pulmonary amyloidosis
History
non-specific features such as weight loss or weakness; may present with symptoms of an underlying systemic disease such as nephrotic syndrome, or manifestation of the amyloid such as a restrictive cardiomyopathy; amyloidosis limited to the lung is very rare and is usually an incidental finding on imaging studies
Exam
physical findings are non-specific and depend on the organs involved by amyloid; some common findings in systemic amyloidosis include macroglossia, orthostatic hypotension, peripheral neuropathy, purpura, papular skin rash, and arthropathy
1st investigation
- CT chest:
solitary or multiple lung nodules
More
Mucoid impaction
History
usually asymptomatic; occasionally presents with recurrent infection, cough, dyspnoea, or wheezing; rarely haemoptysis
Exam
focal wheeze; if associated infection present, there may be localised dullness to percussion
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
mass may appear round or oval; may show small blunted protrusions, giving a gloved-fingers appearance
More
Other investigations
- CT scan:
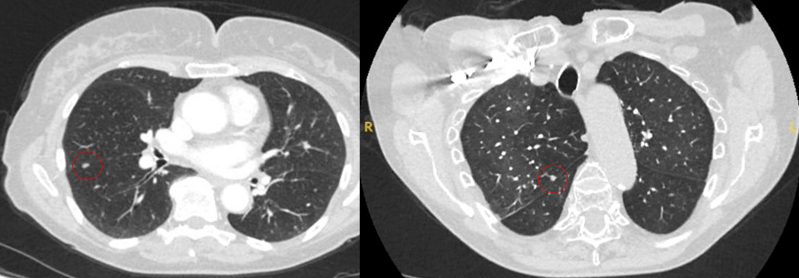
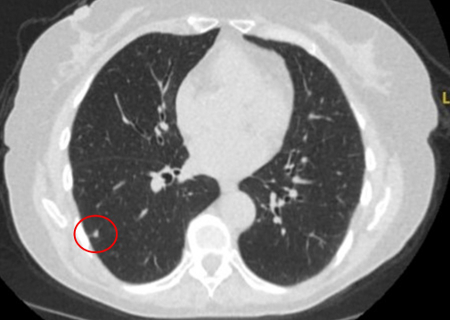
mass may appear homogeneous or non-homogeneous, possibly with cystic changes[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography (CT) showing two areas (red circles) of mucoid impaction of the left upper lobe subsegmental bronchi, resulting in appearance that mimics a noduleFrom the collection of Dr George Tsaknis, MD, PhD, FRCP(London), MRQA, MAcadMEd, PGCert; used with permission [Citation ends].
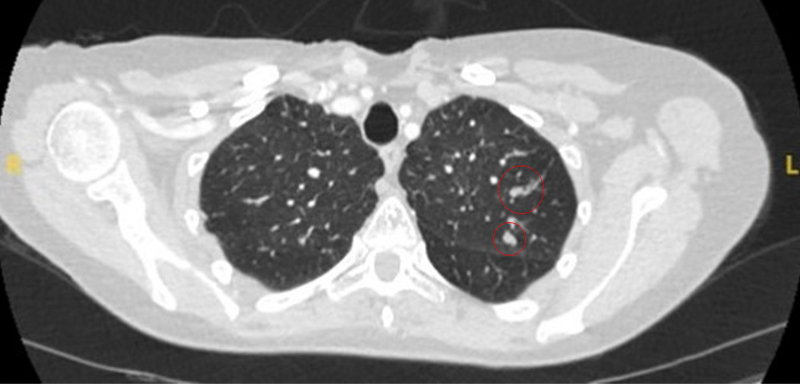
- flexible bronchoscopy:
visualisation of mucous plug
More
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer