Treatment algorithm
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups: see disclaimer
Look out for this icon: for treatment options that are affected, or added, as a result of your patient's comorbidities.
active epistaxis: major haemorrhage
follow local major haemorrhage protocol
After assessing the patient using the Airway, Breathing, Circulation (ABC) approach, if the patient is haemodynamically unstable:[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [22]ENT UK. Nose bleed (epistaxis): global ENT guideline. March 2023 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/184/nose_bleed_epistaxis
Call for help immediately so that you can start resuscitation urgently and also, if possible, apply nasal first aid.
Signs of acute hypovolaemia might include tachycardia, syncope, or orthostatic hypotension.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com [16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com
Tachycardia may be due to hypovolaemia, anaemia, anxiety, or pain (from packing placement or cautery)
See Shock.
The British Society for Haematology defines major haemorrhage as either:[23]Stanworth SJ, Dowling K, Curry N, et al. Haematological management of major haemorrhage: a British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2022 Aug;198(4):654-67. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bjh.18275 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35687716?tool=bestpractice.com
Acute major blood loss associated with haemodynamic instability (e.g., heart rate >110 beats per minute and/or a systolic blood pressure <90 mmHg), or
Bleeding that appears controlled but still requires 'massive' transfusion, or is significant due to the patient’s clinical status, physiology, or response to resuscitation therapy.
Manage major haemorrhage according to your local major haemorrhage protocol.[23]Stanworth SJ, Dowling K, Curry N, et al. Haematological management of major haemorrhage: a British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2022 Aug;198(4):654-67. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bjh.18275 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35687716?tool=bestpractice.com
Seek senior or ENT help early in children and elderly patients with severe bleeding as these patients may require aggressive resuscitation and specialist input.
Seek early case-specific guidance from haematology for any patient who:[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Is on anticoagulation
Has a coagulopathy
Needs blood transfusion.
Practical tip
Visual quantification of blood loss, either from the patient’s history or blood-stained clothing, is unreliable and blood loss can be underestimated by both medical and non-medical staff.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Protect yourself from the high risk of contamination associated with epistaxis due to direct bleeding into the airway and the increased likelihood of droplet spread. Follow your local protocol, but as a minimum, you should don the following:[16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com
Gloves
Mask
Visor (face shield)
Lab coat.
resuscitation and supportive care ± admission
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
In addition to stopping the bleeding, monitor vital signs, supplement oxygen, obtain intravenous access, maintain the airway, and support breathing and circulation if required.
For more information on resuscitation, see Shock.
Blood, fresh frozen plasma, and platelet transfusion, and fibrinogen supplementation may be needed.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
See your local resuscitation protocol for management and admission criteria.
If the patient presents in primary care, arrange for transfer to secondary care by emergency ambulance if any of the following factors exist:[29]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Clinical Knowledge Summaries. Scenario: management of acute epistaxis. September 2019 [internet publication]. https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/epistaxis-nosebleeds/management/acute-epistaxis
Signs of haemodynamic instability
Bleeding is profuse
Bleeding site appears to be posterior.
nasal first aid
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
If possible during resuscitation, firmly pinch the soft part of the nose compressing both nostrils (and possible anterior bleeding sites) for at least 10 minutes.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com
Practical tip
Use a swimmer’s nose clip as an alternative technique to apply external pressure on the nostrils.[30]Turner P. The swimmer's nose clip in epistaxis. J Accid Emerg Med. 1996 Mar;13(2):134. https://www.doi.org/10.1136/emj.13.2.134 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8653239?tool=bestpractice.com
tranexamic acid
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Consider administering tranexamic acid according to local protocols.[22]ENT UK. Nose bleed (epistaxis): global ENT guideline. March 2023 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/184/nose_bleed_epistaxis
Practical tip
When deciding whether to administer tranexamic acid you should consider the benefit and risk to the individual patient, seek senior advice, and consult local protocols where appropriate. Practice varies widely. The British Society for Haematology recommends tranexamic acid for major haemorrhage due to trauma but makes no specific recommendations for epistaxis.[23]Stanworth SJ, Dowling K, Curry N, et al. Haematological management of major haemorrhage: a British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2022 Aug;198(4):654-67. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bjh.18275 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35687716?tool=bestpractice.com
Primary options
tranexamic acid: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 1 g orally three times daily for 7 days
More tranexamic acidTranexamic acid may be administered by other routes in certain settings; consult your local protocols.
These drug options and doses relate to a patient with no comorbidities.
Primary options
tranexamic acid: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 1 g orally three times daily for 7 days
More tranexamic acidTranexamic acid may be administered by other routes in certain settings; consult your local protocols.
Drug choice, dose and interactions may be affected by the patient's comorbidities. Check your local drug formulary.
Show drug information for a patient with no comorbidities
Primary options
tranexamic acid
active epistaxis: no major haemorrhage
nasal first aid
After assessing the patient, start first aid measures to control bleeding from the nose if the patient is haemodynamically stable.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Ask the patient to lean forward but remain upright and firmly pinch the soft part of the nose compressing both nostrils (and possible anterior bleeding sites) for at least 10 minutes.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com
Encourage the patient to spit out, rather than swallow, any blood passing into the throat (blood is irritating to the stomach and may make the patient nauseous).
Provide an oral ice pack.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Alternative, practical options include an ice cube for the patient to suck, or applying an ice pack directly to the nose to reduce nasal blood flow.
Children
Children should sit comfortably, possibly on their parent’s lap so that the parent can assist if necessary with firm compression of the lower part of both nostrils for at least 10 minutes. Encourage the child to breathe through their mouth.
Practical tip
Use a swimmer’s nose clip as an alternative technique to apply external pressure on the nostrils.[30]Turner P. The swimmer's nose clip in epistaxis. J Accid Emerg Med. 1996 Mar;13(2):134. https://www.doi.org/10.1136/emj.13.2.134 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8653239?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider – vasoconstrictor ± local anaesthetic nasal spray
vasoconstrictor ± local anaesthetic nasal spray
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
If nasal first aid doesn’t stop the bleeding, clear blood using suction, gentle nose blowing, or forceps (be careful not to injure the nasal mucosa). Then apply a topical vasoconstrictor (e.g., oxymetazoline) ± local anaesthetic (e.g., lidocaine) using any of the following methods:[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com [26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Spray
Soaked cotton wool ball
Pledget.
Consult local protocols for appropriate dose.
Practical tip
Use topical vasoconstrictors cautiously in patients who may experience adverse effects associated with peripheral vasoconstriction due to alpha-1-adrenergic agonists, for example those with:[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Hypertension
Cardiac disease
Cerebrovascular conditions.
Practical tip
Active bleeding may prevent proper evaluation, so mucosal vasoconstriction (decongestion) is helpful for diagnosis and management. If bleeding makes administration difficult, ENT doctors may attempt rapidly alternating nasal suction (or nose blowing) with intranasal spraying of oxymetazoline. This may exceed the typical dosage on the manufacturer's label, however active bleeding prevents absorption of much of the medicine, and these larger doses are routinely used without difficulty in nasal surgery via spray and on pledgets.
In practice, if bleeding is severe enough to preclude adequate assessment, avoid persisting too long with repeated alternations between suction and vasoconstrictor administration, and seek senior assistance.
Practical tip
A vasoconstrictor (decongestant) reduces blood flow, shrinks mucosal thickness, and increases nasal space should pack placement be required. This can reduce mucosal trauma and decrease secondary bleeding from disrupted mucous membrane.
Effective pack placement may be compromised if the procedure is painful. Prepare a mixture of lidocaine and oxymetazoline according to local protocols. Some clinicians simply remove the top from a spray bottle of oxymetazoline, add an equal volume of the lidocaine, and replace the top; however, consultant advice is recommended.
Next, saturate small neurosurgical pledgets or strips of cotton with the mixture and place them horizontally in the nose using bayonet forceps. Leave for 10 to 15 minutes while the patient compresses the nose if necessary.
Children
Use vasoconstrictors and anaesthetics with caution in young children, whether used to improve visualisation or to control the bleeding.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com [44]Béquignon E, Teissier N, Gauthier A, et al. Emergency Department care of childhood epistaxis. Emerg Med J. 2017 Aug;34(8):543-8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27542804?tool=bestpractice.com
Adequate nasal first aid usually stops epistaxis in children and examination of the anterior nasal cavity will commonly reveal either crusting of the anterior nasal mucosa or a visible vessel, which can be treated accordingly.
supportive care ± admission
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
In addition to stopping the bleeding, monitor vital signs, supplement oxygen, obtain intravenous access, maintain the airway, and support breathing and circulation if required.
For more information on resuscitation, see Shock.
Allocate patients with epistaxis to an area of the emergency department where they can be observed closely, as dislodgement of blood clot may sometimes lead to catastrophic bleeding.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Establish intravenous access
Establish intravenous access with a large-bore cannula at the same time as taking bloods, if indicated, in:
Older patients
Patients on anticoagulants
Haemodynamic compromise
Profuse bleeding
Bleeding >20 minutes.
Control raised blood pressure
The relationship between epistaxis and hypertension is complex and remains unclear.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com There is a paucity of evidence and guidance on how and when to treat hypertension in patients with epistaxis.
In practice, if the patient is hypertensive, consider treatment according to hypertension guidelines and discuss a treatment plan with a senior colleague. See Assessment of hypertension.
Practical tip
In the absence of hypertensive urgency/emergency, US guidelines do not recommend routinely lowering blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleed. Interventions to acutely reduce blood pressure can have adverse effects and may cause or worsen renal, cerebral, or coronary ischaemia.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Monitor blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleeds, and base decisions about blood pressure control on:[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
The severity of the patient's nosebleed
The inability to control the bleeding
Individual patient comorbidities
The potential risks of blood pressure reduction.
If hypertension persists after severe epistaxis, request cardiovascular evaluation to screen for underlying hypertensive disease.[31]Michel J, Prulière Escabasse V, Bequignon E, et al. Guidelines of the French Society of Otorhinolaryngology (SFORL). Epistaxis and high blood pressure. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2017 Feb;134(1):33-5. https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2016.09.011 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27726975?tool=bestpractice.com
Children
Seek an early senior or ENT opinion for any child with epistaxis that is severe or difficult to stop.
Consider admission
Decide whether your patient needs admission depending on what measures are needed to control the bleeding. In practice, if bleeding is controlled by first aid measures and topical agents, most patients can be discharged home.
If the patient presents in primary care, arrange for transfer to secondary care if any of the following factors exist:[29]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Clinical Knowledge Summaries. Scenario: management of acute epistaxis. September 2019 [internet publication]. https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/epistaxis-nosebleeds/management/acute-epistaxis
Epistaxis continues after nasal first aid and the facilities and expertise are not available for nasal cautery or packing
Epistaxis continues after nasal cautery and/or anterior packing (when appropriate expertise and facilities for cautery and packing are available in primary care)
A nasal pack is in place (even if bleeding has stopped)
The patient is on anticoagulant therapy (as a clotting screen will be needed)
The cause provokes concern (e.g., leukaemia/tumour)
An underlying cause is likely (e.g., conditions predisposing to bleeding, such as haemophilia or leukaemia)
Significant comorbidity (e.g., coronary artery disease, severe hypertension, severe anaemia)
Child aged <2 years
Frailty or old age.
safeguarding (in children)
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Consider the possibility of injury, including asphyxiation (unintentional or intentional), in children aged <2 years with epistaxis.[25]Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health. Child protection evidence: systematic review on ear, nose and throat. July 2021 [internet publication]. https://childprotection.rcpch.ac.uk/child-protection-evidence/ear-nose-and-throat-systematic-review
In practice:
Treat the epistaxis in the first instance, but start assessment and procedures with respect to non-accidental injury in parallel
Immediately inform your senior and the nurse in charge if a child aged <2 years presents with epistaxis and no known trauma or haematological disorders, or if you have any concern about non-accidental injury.
persistent epistaxis despite initial measures
electrocautery or chemical cautery
Consider cautery as first-line treatment for all acute epistaxis with obvious bleeding points, provided you are suitably trained and facilities allow.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Only perform cautery:
On a visually identified bleeding point[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
If you have been suitably trained.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
If you can’t identify an anterior bleeding point, rigid endoscopy or microscopy (by a suitably trained and experienced practitioner) may be needed.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
In practice, this may require referral to the ENT department, but do not wait for nasendoscopy; pack the nose as soon as possible to control the haemorrhage. The patient can then be referred to ENT for further assessment.
Clear blood in the front of the nose using suction, gentle nose blowing, or forceps.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults A soft suction catheter is less likely to cause trauma to the nasal lining.
Practical tip
Do not cauterise both sides of the septum during the same episode; septal perforation may occur due to decreased perichondrial blood supply.[16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com
Cauterise any visible vessel or localised area of bleeding in an adult patient with either one of:
Silver nitrate (75% strength) applied directly to the vessel[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Apply for no more than 30 seconds in any one spot.[35]Lloyd S, Almeyda J, Di Cuffa R, et al. The effect of silver nitrate on nasal septal cartilage. Ear Nose Throat J. 2005 Jan;84(1):41-4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15742773?tool=bestpractice.com
In practice, most junior doctors in the emergency department can become proficient in silver nitrate cautery.
Electrical cautery.[16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com [26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Electrocautery should be used in preference to silver nitrate cautery if a suitably trained clinician is available.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com In the UK, this procedure is usually reserved for the ENT consultant and is generally performed in theatre.
The preference for electrocautery is based on lower treatment failure and recurrence rates, reduced need for nasal packing, and reduced rates of hospital admission when compared with silver nitrate cautery, although the quality of evidence for this is very low.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Practical tip
What is meant by 'localised area' for nasal cautery has not been clearly defined. In practice, the aim is to identify an active bleeding point and precisely cauterise this area. If bleeding is brisk, ‘doughnutting’ may be an option: cauterise the four quadrants immediately surrounding the vessel to isolate the source and disrupt supply to the bleeding point. Do not cauterise a large area of the mucosa.
Cautery of a vessel that is not part of the Kiesselbach's plexus is not contraindicated, but bleeding from outside this area is rare.
Observe the patient for 15 minutes after cautery to ensure bleeding is controlled before discharge.
Practical tip
Silver nitrate (75%):
Is applied via commercially manufactured sticks or applicators (note that sticks may not be licensed for use on the face in some countries)
Degrades over time, so lack of activity may indicate the need to use fresher silver nitrate
Can stain the skin for weeks or months after nasal cautery if it is not dried adequately, or if there is subsequent nasal discharge.[36]Royal College of Emergency Medicine. A runny nose - localised cutaneous argyria after nasal cautery. August 2020 [internet publication]. https://res.cloudinary.com/studio-republic/images/v1635677125/Safety_Flash_complication_silver_nitrate_epistaxis_2020/Safety_Flash_complication_silver_nitrate_epistaxis_2020.pdf?_i=AA After spraying or applying the vasoconstrictor ± anaesthetic, reduce the risk of staining by:[36]Royal College of Emergency Medicine. A runny nose - localised cutaneous argyria after nasal cautery. August 2020 [internet publication]. https://res.cloudinary.com/studio-republic/images/v1635677125/Safety_Flash_complication_silver_nitrate_epistaxis_2020/Safety_Flash_complication_silver_nitrate_epistaxis_2020.pdf?_i=AA
Drying the area with a cotton bud
Applying silver nitrate from the outside edge of the bleeding point and continuing round in a spiral towards the centre of the bleeding point
Drying around the area after application
Protecting the skin in and around the nostril with antibiotic ointment or soft paraffin.
Children
In children, chemical cautery is preferred to electrocautery because electrocautery is more painful and requires a general anaesthetic.[16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com
Consult a senior colleague if cautery is required.
Do not attempt cautery in a child aged <4 years as cooperation is unlikely and sedation is not recommended due to risk of inhalation of clots, packing, or local anaesthetic agents.
Consider – vasoconstrictor ± local anaesthetic nasal spray
vasoconstrictor ± local anaesthetic nasal spray
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Be aware that patients may have received a topical vasoconstrictor (e.g., oxymetazoline) ± local anaesthetic (e.g., lidocaine) during initial treatment. However, ensure adequate application and allow this to take effect before starting cautery; in addition to providing pain relief, this should improve visualisation of the anterior nasal cavity.
Consult local protocols for appropriate dose.
supportive care ± admission
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
In addition to stopping the bleeding, monitor vital signs, supplement oxygen, obtain intravenous access, maintain the airway, and support breathing and circulation if required.
For more information on resuscitation, see Shock.
Allocate patients with epistaxis to an area of the emergency department where they can be observed closely, as dislodgement of blood clot may sometimes lead to catastrophic bleeding.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Establish intravenous access
Establish intravenous access with a large-bore cannula at the same time as taking bloods, if indicated, in:
Older patients
Patients on anticoagulants
Haemodynamic compromise
Profuse bleeding
Bleeding >20 minutes.
Control raised blood pressure
The relationship between epistaxis and hypertension is complex and remains unclear.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com There is a paucity of evidence and guidance on how and when to treat hypertension in patients with epistaxis.
In practice, if the patient is hypertensive, consider treatment according to hypertension guidelines and discuss a treatment plan with a senior colleague. See Assessment of hypertension.
Practical tip
In the absence of hypertensive urgency/emergency, US guidelines do not recommend routinely lowering blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleed. Interventions to acutely reduce blood pressure can have adverse effects and may cause or worsen renal, cerebral, or coronary ischaemia.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Monitor blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleeds, and base decisions about blood pressure control on:[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
The severity of the patient's nosebleed
The inability to control the bleeding
Individual patient comorbidities
The potential risks of blood pressure reduction.
If hypertension persists after severe epistaxis, request cardiovascular evaluation to screen for underlying hypertensive disease.[31]Michel J, Prulière Escabasse V, Bequignon E, et al. Guidelines of the French Society of Otorhinolaryngology (SFORL). Epistaxis and high blood pressure. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2017 Feb;134(1):33-5. https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2016.09.011 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27726975?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider admission
Consider whether your patient needs admission. Do not routinely admit.
Discharge patients if they are stable 4 hours after cautery.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
If the patient presents in primary care, arrange for transfer to secondary care if any of the following factors exist:[29]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Clinical Knowledge Summaries. Scenario: management of acute epistaxis. September 2019 [internet publication]. https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/epistaxis-nosebleeds/management/acute-epistaxis
Epistaxis continues after nasal cautery and the facilities and expertise are not available for anterior packing
The patient is on anticoagulant therapy (as a clotting screen will be needed)
The cause provokes concern (e.g., leukaemia/tumour)
An underlying cause is likely (e.g., conditions predisposing to bleeding, such as haemophilia or leukaemia)
Significant comorbidity (e.g., coronary artery disease, severe hypertension, severe anaemia)
Child aged <2 years
Frailty or old age.
treatment of underlying cause
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Seek senior or haematological advice to manage any risk factors that could contribute to ongoing or recurrent bleeding, such as:[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Hypertension
Anticoagulation
Coagulopathies.
Refer patients with an underlying condition predisposing to epistaxis (including primary bleeding disorders, haematological malignancies, intranasal tumours, or vascular malformations) for appropriate follow-up.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider referring patients with recurrent epistaxis to the ENT clinic for further assessment and management.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Consultation may be necessary with haematology and appropriate specialities if the patient requires long-term anticoagulant therapy and epistaxis is difficult to control.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
anterior nasal packing
Consider nasal packing if bleeding continues despite first aid measures, topical vasoconstriction ± local anaesthesia, and cautery (if available), if you can’t identify a specific bleeding point, or if there is bilateral bleeding.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Ensure that you have been trained to use nasal packing.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
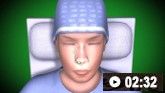
Demonstrates insertion of an inflatable anterior nasal pack and a nasal tampon.
There are two types of packing:
Dissolvable, which in the UK is generally reserved for ENT departments
Non-dissolvable, which is available as compressed sponge and inflatable balloon tampons. Products commonly used in the UK are:
Rapid Rhino®, an inflatable coated nasal balloon catheter
Merocel®, an absorbent dry sponge tampon.
Practical tip
In practice, do not insert nasal packing in a patient with nasal polyps. If nasal first aid and cautery do not stop the bleeding, refer to ENT.
Non-dissolvable nasal packing
Depending on bleeding severity, pack the actively bleeding nostril or both nostrils.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults Seek the advice of a senior colleague if bleeding is severe.
In practice:
Different institutions will have experience with specific nasal packs. Follow local preferences.
As epistaxis generally originates on one side, packing is usually unilateral.
However, when the history and examination fail to identify whether the bleeding is from the right or the left, or when packing one nostril does not control the bleeding, both sides of the nose can be packed to provide some counter pressure to the nasal septum.
Seek senior input if you are inexperienced, or not confident with bilateral packing, as nasal septal perforation may occur.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
If anterior non-dissolvable nasal packing does not control the bleeding, seek senior advice on further management.
Practical tip
Follow the points below to ensure optimal use of anterior nasal packs.
Place all anterior packs as horizontally as possible to avoid misplacement.
Rapid Rhino® and Merocel® packs are equally effective, but Rapid Rhino® may be less painful to insert and easier to remove than Merocel®.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [40]Badran K, Malik TH, Belloso A, et al. Randomized controlled trial comparing Merocel and RapidRhino packing in the management of anterior epistaxis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2005 Aug;30(4):333-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16209675?tool=bestpractice.com [41]Singer AJ, Blanda M, Cronin K, et al. Comparison of nasal tampons for the treatment of epistaxis in the emergency department: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2005 Feb;45(2):134-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15671968?tool=bestpractice.com
Traditional ribbon gauze soaked in bismuth iodoform paraffin paste (BIPP) is as effective as nasal tampons, but is more difficult to insert.
Observe the patient for at least 30 minutes to check there is no bleeding from the nose or into the pharynx.
Re-examine the oropharynx after inserting the nasal pack as blood may divert posteriorly or you may have missed a posterior source for the epistaxis.
Do not prescribe routine systemic antibiotics after insertion of anterior nasal packs unless they are in place for longer than 48 hours.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Pack removal
Non-dissolvable nasal packs should be removed within 24 hours of insertion if there is no evidence of active bleeding (with leeway for daylight hours).[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
The nose should then be re-examined and an assessment made as to the need for cautery.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
If necessary, rigid endoscopy should be performed to identify and cauterise the bleeding point if this is not evident from anterior rhinoscopy.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Practical tip
When removing a nasal pack:
Apply a mixture of topical vasoconstrictor, such as oxymetazoline, and lidocaine (according to local protocols) to the sponge pack
The vasoconstrictor shrinks adjacent mucosa
The lidocaine provides analgesia
Saturate the pack to promote softening and lubrication to discourage mucosal trauma and re-bleeding.
analgesia
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Prescribe adequate analgesia according to your local pain score or pain ladder protocol.
Paracetamol is usually appropriate.
DO NOT prescribe a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen to a patient on anticoagulation or to older people.
In practice, you can prescribe a single dose of an NSAID for most other patient groups with epistaxis.
Opioid analgesics may be necessary in some patients.
Use opioid analgesics with caution in older and shocked patients.
Avoid medications containing aspirin.
Primary options
paracetamol: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 500-1000 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
Secondary options
ibuprofen: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 300-600 mg orally (immediate-release) every 6-8 hours when required, maximum 2400 mg/day
Tertiary options
codeine phosphate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 30-60 mg orally every 4 hours when required, maximum 240 mg/day
OR
morphine sulfate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 5-10 mg orally (immediate-release)/subcutaneously/intravenously/intramuscularly every 4 hours initially, adjust dose according to response
These drug options and doses relate to a patient with no comorbidities.
Primary options
paracetamol: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 500-1000 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
Secondary options
ibuprofen: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 300-600 mg orally (immediate-release) every 6-8 hours when required, maximum 2400 mg/day
Tertiary options
codeine phosphate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 30-60 mg orally every 4 hours when required, maximum 240 mg/day
OR
morphine sulfate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 5-10 mg orally (immediate-release)/subcutaneously/intravenously/intramuscularly every 4 hours initially, adjust dose according to response
Drug choice, dose and interactions may be affected by the patient's comorbidities. Check your local drug formulary.
Show drug information for a patient with no comorbidities
Primary options
paracetamol
Secondary options
ibuprofen
Tertiary options
codeine phosphate
OR
morphine sulfate
supportive care ± admission
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
In addition to stopping the bleeding, monitor vital signs, supplement oxygen, obtain intravenous access, maintain the airway, and support breathing and circulation if required.
For more information on resuscitation, see Shock.
Allocate patients with epistaxis to an area of the emergency department where they can be observed closely, as dislodgement of blood clot may sometimes lead to catastrophic bleeding.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Establish intravenous access
Establish intravenous access with a large-bore cannula at the same time as taking bloods, if indicated, in:
Older patients
Patients on anticoagulants
Haemodynamic compromise
Profuse bleeding
Bleeding >20 minutes.
Control raised blood pressure
The relationship between epistaxis and hypertension is complex and remains unclear.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com There is a paucity of evidence and guidance on how and when to treat hypertension in patients with epistaxis.
In practice, if the patient is hypertensive, consider treatment according to hypertension guidelines and discuss a treatment plan with a senior colleague. See Assessment of hypertension.
Practical tip
In the absence of hypertensive urgency/emergency, US guidelines do not recommend routinely lowering blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleed. Interventions to acutely reduce blood pressure can have adverse effects and may cause or worsen renal, cerebral, or coronary ischaemia.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Monitor blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleeds, and base decisions about blood pressure control on:[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
The severity of the patient's nosebleed
The inability to control the bleeding
Individual patient comorbidities
The potential risks of blood pressure reduction.
If hypertension persists after severe epistaxis, request cardiovascular evaluation to screen for underlying hypertensive disease.[31]Michel J, Prulière Escabasse V, Bequignon E, et al. Guidelines of the French Society of Otorhinolaryngology (SFORL). Epistaxis and high blood pressure. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2017 Feb;134(1):33-5. https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2016.09.011 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27726975?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider admission
Consider whether your patient needs admission. Most patients with epistaxis controlled by cautery or anterior tampon packing do not need hospital admission.[42]Upile T, Jerjes W, Sipaul F, et al. The role of surgical audit in improving patient management; nasal haemorrhage: an audit study. BMC Surg. 2007 Sep 13;7:19. https://www.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2482-7-19 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17854499?tool=bestpractice.com
Some patients requiring non-dissolvable packing because of ineffective earlier measures or profuse bleeding may need admission.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults Consult your local protocol.
Admission and further observation may be needed in patients with anterior packs in place and:[43]Royal College of Emergency Medicine (RCEM). Epistaxis. February 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.rcemlearning.co.uk/reference/epistaxis
Shock
Haemodynamic instability
Haemoglobin <10 g/dL
Anticoagulant medication
Recurrent epistaxis following a previous episode requiring nasal packing within the last 7 days
Uncontrolled hypertension
Significant comorbid illness
Difficult social circumstances
Suspected posterior bleed (bleeding is profuse, from both nostrils, and the bleeding site cannot be identified on examination).
In UK practice, all children with nasal packs are admitted for observation because of the risk of airway compromise.
Admit for 48 hours and remove the nasal pack prior to discharge.
If the patient presents in primary care, arrange for transfer to secondary care if any of the following factors exist:[29]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Clinical Knowledge Summaries. Scenario: management of acute epistaxis. September 2019 [internet publication]. https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/epistaxis-nosebleeds/management/acute-epistaxis
Epistaxis continues after anterior packing (if the facilities and expertise are available for anterior packing)
A nasal pack is in place (even if bleeding has stopped)
The patient is on anticoagulant therapy (as a clotting screen will be needed)
The cause provokes concern (e.g., leukaemia/tumour)
An underlying cause is likely (e.g., conditions predisposing to bleeding, such as haemophilia or leukaemia)
Significant comorbidity (e.g., coronary artery disease, severe hypertension, severe anaemia)
Child aged <2 years
Frailty or old age.
treatment of underlying cause
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Seek senior or haematological advice to manage any risk factors that could contribute to ongoing or recurrent bleeding, such as:[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Hypertension
Anticoagulation
Coagulopathies.
Refer patients with an underlying condition predisposing to epistaxis (including primary bleeding disorders, haematological malignancies, intranasal tumours, or vascular malformations) for appropriate follow-up.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider referring patients with recurrent epistaxis to the ENT clinic for further assessment and management.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Consultation may be necessary with haematology and appropriate specialities if the patient requires long-term anticoagulant therapy and epistaxis is difficult to control.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
3rd line – referral to ENT specialist for posterior packing
referral to ENT specialist for posterior packing
If epistaxis continues after unilateral or bilateral anterior nasal packing, the bleeding is most likely to be coming from the posterior nasal cavity.
Refer patients with posterior epistaxis to the ENT department for posterior packing, endoscopy with cauterisation, or ligation of the sphenopalatine artery.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Practical tip
If the patient is becoming haemodynamically unstable and there is likely to be a delay before ENT consultation, use two Foley catheters to temporarily control blood loss in the emergency department. Seek senior assistance if you are not experienced in this procedure.
Insert size 12 catheters one at a time through the nostril, along the floor of the nose, and into the nasopharynx until you can see them in the pharynx.
Inflate each balloon with 5 to 10 mL of water and then apply gentle traction to compress the bleeding vessels in the posterior nasal cavity.
Combined non-dissolvable anterior and posterior nasal packs should be considered.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Uncertainty exists about the need for routine antibiotic cover for posterior packs.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com Consult your local protocol.
A variety of posterior packing options exist. UK ENT departments commonly use:
A double balloon epistaxis device, or
A traditional gauze anterior pack with a posterior size 12 French urinary catheter.
Surgery and interventional radiology are effective in managing epistaxis that has not responded to first aid and nasal packing, or if bleeding recurs when adequate packing is removed.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com Options include:[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Endoscopic examination of the nose with or without cautery, as appropriate
Sphenopalatine artery ligation
Anterior ethmoid artery ligation (if traumatic)
Embolisation.
analgesia
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
An intravenous opioid analgesic is usually required before posterior packing because it can be very painful or uncomfortable.
Use opioid analgesics with caution in older and shocked patients.
After the procedure, prescribe adequate analgesia according to your local pain score or pain ladder protocol.
Paracetamol may be appropriate.
DO NOT prescribe a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen to a patient on anticoagulation or to older people.
In practice, you can prescribe a single dose of an NSAID for most other patient groups with epistaxis.
Opioid analgesics may be necessary in some patients.
Avoid medications containing aspirin.
Primary options
paracetamol: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 500-1000 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
Secondary options
ibuprofen: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 300-600 mg orally (immediate-release) every 6-8 hours when required, maximum 2400 mg/day
Tertiary options
codeine phosphate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 30-60 mg orally every 4 hours when required, maximum 240 mg/day
OR
morphine sulfate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 5-10 mg orally (immediate-release)/subcutaneously/intravenously/intramuscularly every 4 hours initially, adjust dose according to response
These drug options and doses relate to a patient with no comorbidities.
Primary options
paracetamol: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 500-1000 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
Secondary options
ibuprofen: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 300-600 mg orally (immediate-release) every 6-8 hours when required, maximum 2400 mg/day
Tertiary options
codeine phosphate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 30-60 mg orally every 4 hours when required, maximum 240 mg/day
OR
morphine sulfate: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 5-10 mg orally (immediate-release)/subcutaneously/intravenously/intramuscularly every 4 hours initially, adjust dose according to response
Drug choice, dose and interactions may be affected by the patient's comorbidities. Check your local drug formulary.
Show drug information for a patient with no comorbidities
Primary options
paracetamol
Secondary options
ibuprofen
Tertiary options
codeine phosphate
OR
morphine sulfate
anti-emetic
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Administer with an intravenous opioid to prevent nausea and vomiting associated with opioid use.
Primary options
ondansetron: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 4-8 mg intravenously every 12 hours
More ondansetronHigher doses may be required in some patients; consult local protocols for guidance.
These drug options and doses relate to a patient with no comorbidities.
Primary options
ondansetron: children: consult specialist for guidance on dose; adults: 4-8 mg intravenously every 12 hours
More ondansetronHigher doses may be required in some patients; consult local protocols for guidance.
Drug choice, dose and interactions may be affected by the patient's comorbidities. Check your local drug formulary.
Show drug information for a patient with no comorbidities
Primary options
ondansetron
supportive care + admission
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
In addition to stopping the bleeding, monitor vital signs, supplement oxygen, obtain intravenous access, maintain the airway, and support breathing and circulation if required.
For more information on resuscitation, see Shock.
Allocate patients with epistaxis to an area of the emergency department where they can be observed closely, as dislodgement of blood clot may sometimes lead to catastrophic bleeding.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Establish intravenous access
Establish intravenous access with a large-bore cannula at the same time as taking bloods, if indicated, in:
Older patients
Patients on anticoagulants
Haemodynamic compromise
Profuse bleeding
Bleeding >20 minutes.
Control raised blood pressure
The relationship between epistaxis and hypertension is complex and remains unclear.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com There is a paucity of evidence and guidance on how and when to treat hypertension in patients with epistaxis.
In practice, if the patient is hypertensive, consider treatment according to hypertension guidelines and discuss a treatment plan with a senior colleague. See Assessment of hypertension.
Practical tip
In the absence of hypertensive urgency/emergency, US guidelines do not recommend routinely lowering blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleed. Interventions to acutely reduce blood pressure can have adverse effects and may cause or worsen renal, cerebral, or coronary ischaemia.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Monitor blood pressure in patients with acute nosebleeds, and base decisions about blood pressure control on:[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
The severity of the patient's nosebleed
The inability to control the bleeding
Individual patient comorbidities
The potential risks of blood pressure reduction.
If hypertension persists after severe epistaxis, request cardiovascular evaluation to screen for underlying hypertensive disease.[31]Michel J, Prulière Escabasse V, Bequignon E, et al. Guidelines of the French Society of Otorhinolaryngology (SFORL). Epistaxis and high blood pressure. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2017 Feb;134(1):33-5. https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2016.09.011 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27726975?tool=bestpractice.com
Hospital admission
Patients requiring a posterior pack should be admitted.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Because of risk of hypoxia, some hospitals require intensive care unit (ICU) observation of patients with posterior packing; others consider this appropriate specifically for older people and patients with comorbidities.
Follow local post-packing observation protocols.
Patients requiring nasendoscopy or surgery usually require admission, depending on the procedure.
treatment of underlying cause
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Seek senior or haematological advice to manage any risk factors that could contribute to ongoing or recurrent bleeding, such as:[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Hypertension
Anticoagulation
Coagulopathies.
Refer patients with an underlying condition predisposing to epistaxis (including primary bleeding disorders, haematological malignancies, intranasal tumours, or vascular malformations) for appropriate follow-up.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider referring patients with recurrent epistaxis to the ENT clinic for further assessment and management.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Consultation may be necessary with haematology and appropriate specialities if the patient requires long-term anticoagulant therapy and epistaxis is difficult to control.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
epistaxis resolved
1st line – topical intranasal antibiotic or petroleum jelly
topical intranasal antibiotic or petroleum jelly
Prescribe a suitable topical nasal antibiotic cream (e.g., chlorhexidine/neomycin, mupirocin) or petroleum jelly for 7 days.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Children
While most experienced clinicians report that moisturisers and lubricants such as nasal saline, gels, and ointments and use of air humidifiers can help prevent nosebleeds, high-quality evidence to support these treatment strategies is scarce.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
In practice, treat children with recurrent nosebleeds and nasal crusting with topical nasal antibiotic cream for 4 weeks to prevent further bleeding.[43]Royal College of Emergency Medicine (RCEM). Epistaxis. February 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.rcemlearning.co.uk/reference/epistaxis
Primary options
chlorhexidine/neomycin: (chlorhexidine 1 mg/g and neomycin 5 mg/g cream) children and adults: apply intranasally twice daily
OR
mupirocin topical: (2%) children and adults: apply intranasally two to three times daily
nasal hygiene education
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Provide advice to:
Prevent recurrence of the nosebleed, such as:[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Avoiding aspirin and ibuprofen or other NSAIDs
Avoiding straining, bending over, and strenuous exercising (although walking and other gentle activity is permitted)
Refraining from nose blowing
Sneezing with the mouth open
Sleeping with the head slightly raised
Help the patient administer nasal first aid measures in the future.
See Patient discussions.
Children
If simple measures stop epistaxis, discharge the child with education on management at home and preventative measures such as avoiding hot drinks, food, baths, or showers for at least 24 hours, no nose-blowing for one week and no nose-picking. See Patient leaflets.
If the child has had cautery or received packing, or has dry, cracked mucosa, advise the parent to apply petroleum-based gel for one week.
Avoid long-term use of petroleum-based gel because of the risk of chemical pneumonitis if it is inhaled.
follow-up
Additional treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Following pack removal or cautery, discharge clinically stable patients after 4 hours.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
No follow-up is necessary for patients whose epistaxis has:
Stopped spontaneously
Been controlled by first aid measures
Responded to cautery.
Arrange an ENT follow-up appointment for patients discharged with an anterior nasal pack. The ENT department should remove the pack within 24 hours (with leeway for daylight hours) and can assess whether cautery is necessary.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Refer patients with an underlying condition predisposing to epistaxis (including primary bleeding disorders, haematological malignancies, intranasal tumours, or vascular malformations) for appropriate follow-up.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider referring patients with recurrent epistaxis to the ENT clinic for further assessment and management.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Consultation may be necessary with haematology and appropriate specialities if the patient requires long-term anticoagulant therapy and epistaxis is difficult to control.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com
Practical tip
Do not prescribe routine antibiotic cover for patients with an anterior nasal pack that will only be in place for up to 48 hours.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com [16]Beck R, Sorge M, Schneider A, et al. Current approaches to epistaxis treatment in primary and secondary care. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jan 8;115(1-02):12-22. https://www.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0012 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29345234?tool=bestpractice.com
recurrent epistaxis
referral to ENT specialist
Seek senior or haematological advice to manage any risk factors that could contribute to ongoing or recurrent bleeding, such as:[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Hypertension
Anticoagulation
Coagulopathies.
Refer patients with an underlying condition predisposing to epistaxis (including primary bleeding disorders, haematological malignancies, intranasal tumours, or vascular malformations) for appropriate follow-up.[10]Tunkel DE, Anne S, Payne SC, et al. Clinical practice guideline: nosebleed (epistaxis). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(suppl 1):S1-38. https://aao-hnsfjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1177/0194599819890327 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31910111?tool=bestpractice.com
Consider referring patients with recurrent epistaxis to the ENT clinic for further assessment and management.[26]ENT UK. Guideline for management of idiopathic epistaxis in adults. March 2019 [internet publication]. https://www.entuk.org/resources/115/guideline_for_management_of_idiopathic_epistaxis_in_adults
Consultation may be necessary with haematology and appropriate specialities if the patient requires long-term anticoagulant therapy and epistaxis is difficult to control.[6]National ENT Trainee Research Network. The British Rhinological Society multidisciplinary consensus recommendations on the hospital management of epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Dec;131(12):1142-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280691?tool=bestpractice.com

Choose a patient group to see our recommendations
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups. See disclaimer
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer