Investigations
1st investigations to order
biopsy
Test
SCC in situ (Bowen's disease) displays full-thickness atypia that is confined to the epidermis with an intact basement membrane.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Biopsy showing histology of an in-situ SCC with full-thickness keratinocyte atypiaFrom the private collection of Dr Nwaneshiudu and Dr Soltani [Citation ends].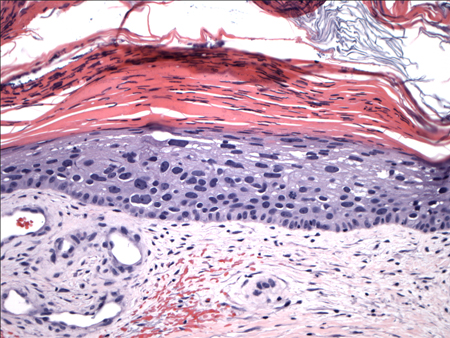
Invasive tumours extend beyond the basement membrane, penetrate into the dermis, and may invade deeper structures.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Biopsy histology showing invasive SCC with keratinocyte atypia involving all layers of the epidermis and islands budding into the dermisFrom the private collection of Dr Nwaneshiudu and Dr Soltani [Citation ends].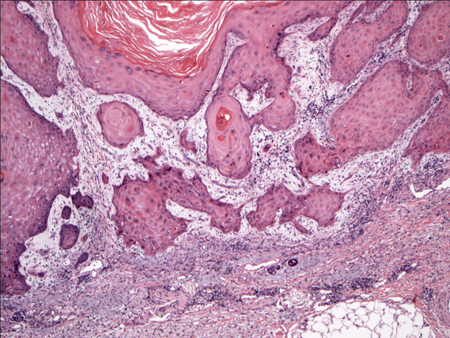
Keratoacanthomas appear as endophytic nodules with a central invagination, replete with keratin. Atypia is minimal and mitoses are rare. Lymphocytic infiltrate is present at the margins of the lesion.
Marjolin ulcers present in an area of previously traumatised, burnt, chronically inflamed or scarred skin, or a non-healing wound.
Verrucous carcinoma presents with features of well-differentiated SCC, exophytic, fungating, verrucous nodules, or plaques on skin or mucosa. The upper portion resembles a wart, consisting of hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis; the lower portion grows in a pushing pattern rather than an infiltrative pattern and consists of well differentiated squamous epithelium.[75]
Actinic keratoses show histological changes of intraepidermal keratinocytic dysplasia, especially in the basal layer.
Result
full thickness keratinocyte atypia
Investigations to consider
CT scan
Test
For patients with extensive disease, i.e. suspected bone disease computed tomography (CT) with contrast is recommended unless contraindicated.[74]
Some evidence suggests that CT is the more accurate modality to detect bony invasion and nodal metastasis.[76]
Result
may show soft tissue mass or erosion of the cortex and medulla of the bone suggestive of bone disease[77]
MRI scan
Test
For patients with extensive disease, i.e. involvement of named nerves, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with or without contrast is preferred. In addition, MRI with and without contrast of the brain may be considered to rule out subclinical cortical involvement in these patients. [74]
Some evidence suggests that MRI is more accurate than CT for the detection of perineural spread.[76]
Result
may show T1 or T2-weighted hyperdense lesions, nerve thickening, loss of fat. May show retrograde tumour enhancement. In muscle, T2-weighted hyperdense signals may be seen[78]
FBC with differential
Test
For high-risk squamous cell carcinoma (i.e., larger and more invasive lesions), to facilitate detection of metastases.
Secondary to bone marrow involvement.
Result
normal, except if bone marrow metastases present
LFTs
Test
For high-risk squamous cell carcinoma (i.e., larger and more invasive lesions), to facilitate detection of metastases.
Result
normal, except if liver metastases present
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer