Epidemiology
As most rib fractures are associated with high-energy impact, their incidence is directly related to the overall incidence of blunt thoracic trauma. About 10% to 40% of those sustaining blunt trauma sustain a rib fracture, with an increase in incidence due to increasing age.[13][14] In young children, studies have shown rib fractures are a result of child abuse 65% to 100% of the time.[2][3][4][5][6][7]
As age increases, the absolute risk of sustaining a fragility fracture is inversely proportional to the patient's bone mineral density, with about 27% of these fractures occurring in the ribs.[15] Additionally, the number of older adults with rib fractures associated with falls is expected to increase as the overall age of the population continues to rise.[16] Patients older than 65 years have an increased risk of morbidity and mortality in the setting of multiple rib fractures compared with younger people.[17][18]
Pneumothorax occurs in about 14% to 37% of rib fractures, haemopneumothorax in 20% to 27%, pulmonary contusions in 17%, and a flail chest in up to 6%.[13][19][20]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing large left-sided pneumothoraxFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].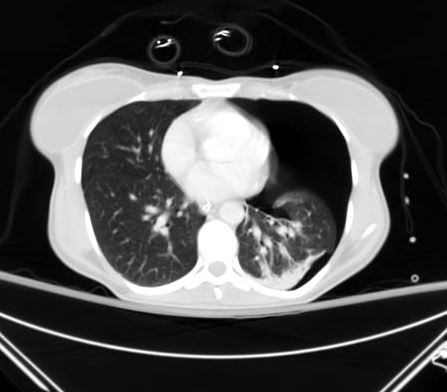 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].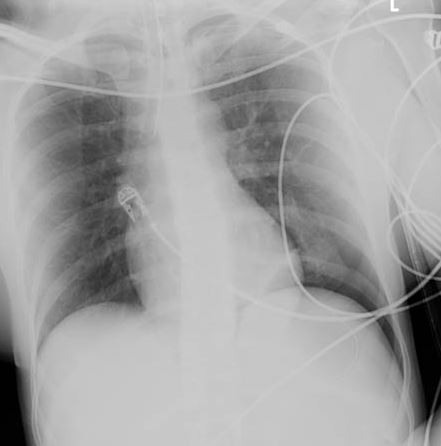
Risk factors
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) in adults has been implicated as a cause of rib and sternal fractures.[23][24] In patients receiving external cardiac massage as a form of CPR, rib fractures were caused in 77% of males and 85% of females.[43] However, the incidence of rib fractures in children following CPR is estimated to be <2%.[23]
The presence of rib fractures without associated trauma has the highest probability of being attributed to non-accidental injury when compared with all other fractures.[44] In young children, studies have shown rib fractures are a result of child abuse 65% to 100% of the time.[2][3][4][5][6][7] The probability of abuse in children with intracranial injury and retinal haemorrhage alone is about 33%, but this probability increases to about 98% with the addition of rib fractures.[8][9] See Child abuse.
High-energy impact fractures concerning for elder abuse include upper (first through fifth) rib fractures.[25] In a study of 92 elder abuse victims, approximately 93% of rib fractures were observed to occur posteriorly.[25][26] Posterior rib fractures commonly occur in elder abuse as a result of punches and kicks to the patient’s back and have a low probability of resulting from accidental trauma.[25][26] See Neglect and abuse of older adults.
As age increases, the absolute risk of sustaining a fragility fracture is inversely proportional to the bone mineral density of the patient, with about 27% of these fractures occurring in the ribs.[15] A prior history of hip fracture or other appendicular skeletal injury after the age of 50 years greatly increases a patient's risk for subsequent rib fracture.[45]
Patients aged >65 years have an increased risk of morbidity and mortality in the setting of sustaining multiple rib fractures when compared with a younger population.[17][18] In one study examining the association of rib fractures with the risk of fatality following a car crash, over 55% of patients aged >60 years who died of a chest injury sustained only rib fractures.[46]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer